CMOS Fabrication EMT 251. Objectives To discussed the fundamentals of CMOS fabrication steps. To...
-
Upload
keegan-hitchen -
Category
Documents
-
view
269 -
download
1
Transcript of CMOS Fabrication EMT 251. Objectives To discussed the fundamentals of CMOS fabrication steps. To...
Objectives
• To discussed the fundamentals of CMOS fabrication steps.
• To examined the major steps of the process flow.
• To overview the cross section view of a circuit
• Photolithography (photo)– Process of transferring pattern on mask to photoresist
layer on wafer surface (pre-pattern the chip)• Etching
– Process of permanently removed the unwanted part of design on wafer surface to get the desired pattern
• Diffusion– Process of introducing dophant layer by movement of
dophant atoms from high concentration to low concentration area at high temperature
• Ion implantation– Process of introducing dophant layer by bombardment
of high energy dophant ion in high electric field chamber
• Oxidation– Process of growing thick or thin SiO2 layer depend on
oxide application• CMP
– Process to physically grind flat to have a planar surface for better exposure at photo process.
SourceDrain
Gate
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
Source (Arsenic, Phosphorous, Boron)
Drain (Arsenic, Phosphorous, Boron)
Gate (Aluminum, Polysilicon)
MOSFET
NMOS
P-type substrate
N-type dopant for Source & Drain
Inversion layer is formed to conduct electricity
NMOS
P-type substrate
N-type dopant for Source & Drain
Inversion layer is formed to conduct electricity
PMOS
N-type substrate
P-type dopant for Source & Drain
Inversion layer is formed to conduct electricity
PMOS
N-type substrate
P-type dopant for Source & Drain
Inversion layer is formed to conduct electricity
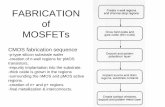
WELL FORMATIONWELL FORMATION
ISOLATION FORMATIONISOLATION FORMATION
TRANSISTOR MAKINGTRANSISTOR MAKING
INTERCONNECTIONINTERCONNECTION
PASSIVATIONPASSIVATION
PROCESS FLOW
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESSwell formation
• Grow epitaxy layer (made from SiO2) as mask layer for well formation
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESSwell formation
• By *photolithography and etching process, well opening are made
*photolithography and etch processes are shown in next slides
Well will be formed here
Photolithography (CED)
P-substrateSi02
photoresist
• Photoresist coating (C)
• Masking and exposure under UV light(E)
• Resist dissolved after developed (D)– Pre-shape the well
pattern at resist layer
P-substrate
mask
UV light
Opaque area
Transparent area
etching
• Removing the unwanted pattern by wet etching
• Resist clean• Desired pattern
formed
P-substrate
P-substrate
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESSwell formation
• Ion bombardment by ion implantation• SiO2 as mask, uncovered area will
exposed to dophant ion
Phosphorus ion
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESSisolation formation
• Increase SiO2 thickness by oxidation at high temperature
• Oxide will electrically isolates nmos and pmos devices
Thick oxide
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESStransistor making
• By photolithography and etching process, pmos and nmos areas are defined
pmos will be formed
here
nmos will be formed
here
LOCOS (isolation structure)
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESStransistor making
• Grow very thin gate oxide at elevated temperature in very short time
Gate oxide
• Photolithography (photo) and etching to form gate pattern
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESStransistor making
gate
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESStransistor making
• Photo process to define the nmos’s active (source and drain) area and VDD contact
• Ion implantation with Arsenic ion for n+ dophant.
• Photoresist and polisilicon gate act as mask
photoresist
Arsenic ion
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESStransistor making
• Nmos’s Source and drain with VDD contact formation
• Resist removal
source drainVDD
contact
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESStransistor making
• Photo process to define the GND contact and pmos’s active area (source and drain)
• Ion implantation with boron ionto have p+ dophant
• Photoresist and gate act as mask
Boron ion
photoresist
CMOS FABRICATION PROCESStransistor making
• Pmos’s source and drain formation with GND contact
• Resist removal
GND contact Pmos’
source
Pmos’s drain
GLOSSARY• Photolithography (photo)
– Process of transferring pattern on mask to photoresist layer on wafer surface (pre-pattern the chip)
• Etching– Process of permanently removed the unwanted part of design on
wafer surface to get the desired pattern• Diffusion
– Process of introducing dophant layer by movement of dophant atoms from high concentration to low concentration area at high temperature
• Ion implantation– Process of introducing dophant layer by bombardment of high
energy dophant ion in high electric field chamber• Oxidation
– Process of growing thick or thin SiO2 layer depend on oxide application
• CMP– Process to physically grind flat to have a planar surface for better
exposure at photo process.

















































![CMOS Fabrication [Compatibility Mode]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/577cdf861a28ab9e78b17027/cmos-fabrication-compatibility-mode.jpg)