Fabrication Technology(1) nMOS Fabrication CMOS Fabrication –p-well process –n-well process...
-
Upload
brendan-boyd -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
1
Transcript of Fabrication Technology(1) nMOS Fabrication CMOS Fabrication –p-well process –n-well process...

Fabrication Technology(1)
• nMOS Fabrication• CMOS Fabrication
– p-well process– n-well process– twin-tub process

Fabrication Technology(2)• All the devices on the wafer are made at the same time
• After the circuitry has been placed on the chip – the chip is overglassed (with a passivation layer) to protect it– only those areas which connect to the outside world will be left
uncovered (the pads)
• The wafer finally passes to a test station– test probes send test signal patterns to the chip and monitor the output
of the chip
• The yield of a process is the percentage of die which pass this testing
• The wafer is then scribed and separated up into the individual chips. These are then packaged

Fabrication Technology(3)

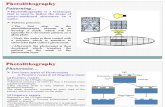
Fabrication Technology(4)Photolithography process

Fabrication Technology(5)Resists
• negative: areas to be preserved are hardened after exposure to light
• positive: areas to be preserved are not exposed to light
Exposure
UV light used to sensitize the resist using a mask.
DevelopResist areas that are exposed (positive)or not exposed (negative) are removedwith an acid and water wash. resist protected area
resist exposed area

Fabrication Technology(6)
EtchAreas that are exposed and not protectedby the resist are etched with an acid and water wash. What is left are, depending on the layer being worked on, are patterns that expose underlying layers.

Cmos Inverter Fabrication

Cmos Inverter Fabrication

Layout of an Inverter
Back is metallized to provide a good ground connection

Step 1:Make the N-Well
Top view
Cross-sectional view
Mask 1

Step 2: Deposit Field Oxide

Step 3: Open Field with Active Mask
Mask 2

Step 4: Deposit Gate Oxide
The thickness and the quality of the gate oxide are two of the most critical fabrication parameters, since they strongly affect the operational characteristics of the MOS transistor, as well as its long-term reliability.

Step 5: Deposit Polysilicon

Step 6: Get Oxide Cut (etch)
Mask 3

Step 7: N-Diffusion Implant

Step 8: P-Diffusion Implant

3/13/2005
Step 9:Deposit More Oxide

Step 10: Contact Cut Etch
Mask 4

Step 11: Metal 1 Deposit
Mask 5

Step 12:Deposit More oxide

Steps 13 & 14: Planarize(Polish) & Via Cut(Etch)
Mask 6

Step15: Metal 2 Deposition

Step 16: Passivation Layer(Scratch Protect)
Metal 1
Metal 2
Gate oxide
Field Oxide
Polysilicon
N-Diffusion
P-Diffusion
np np
N wellP substrate