The Central Nervous System. Components: -Brain and spinal cord -Bone: skull/vertebral column...
-
Upload
edwin-cory-russell -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of The Central Nervous System. Components: -Brain and spinal cord -Bone: skull/vertebral column...

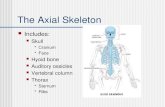
The Central Nervous System

Components:
- Brain and spinal cord- Bone: skull/vertebral
column- Membranes and fluid

Meninges: membranes that surround the CNSThree Layers:1. Dura Mater: outer layer
next to bone and continues in vertebral column
2. Arachnoid mater: middle layer; covers brain/spinal cord
3. Pia mater: inner layer that covers nervous tissue. FX: nourishmenst of nerve

Meningitis: inflammation of meninges that is caused by bacteria/virus- Mainly infects children- May cause:
- Loss of vision/hearing- Paralysis- Mental Retardation

Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF): clear, watery substance that brings nutrients and protection to neurons
- Fills the subarachnoid space
- 500 ml secreted daily/absorbed by blood
- Absorbs forces which may damage brain

Spinal Cord:
- 31 segments (vertebrae)
- Each segment has a pair of spinal nerves
- Branch out into body (PNS)
- Central canal filled with CSF

White vs. Gray Matter
White Matter: neuron tissue with myelinated axons
Gray Matter: neuron tissue with unmyelinated axons

Spinal Cord Functions
1. Conduct nerve impulse along nerve tracts
Two Nerve Tracts:A. Ascending: sensory to
brainB. Descending: motor
impulse to organ/gland
2. Center for spinal reflexes

Reflexes: quick, involuntary, predictable reactions
- does not involve the brain
- Reflex arc: sensory neuron interneuron motor neuron
Ex. Knee-jerk reaction, pain reaction

The Brain
Primary Functions:1. Interprets sensory
information2. Issues motor commands to
skeletal muscles3. Carries higher mental
functions (memory/reasoning)
4. Coordinates muscle movements
5. Centers/pathways for regulatory visceral activities

Brain Organization:
1. Cerebrum (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital lobes)
2. Cerebellum3. Brain Stem – connect
brain to spinal stem- Diencephalon- Midbrain- Pons- Medulla oblongata

Cerebrum:
- Largest part of the brain- Divided into two
primary lobes:-right and left cerebral hemispheres
Corpus Callosum: nerve fibers for connections and communications between hemispheres

Cerebrum
Surface Features:1. Sulcus: shallow
grooves2. Fissure: deep grooves3. Gyrus: elevated ridges

Cerebral Cortex: outside of the cerebrum
- Gray matter, 2-5mm, white matter beneath
FX:1. Motor areas
(voluntary):2. Sensory areas
(interpretation)3. Association areas
(conscious behavior)

1. Primary Motor Areas: in the frontal lobe- Located in the Post-
central and Pre-central gyrus
- Brocc’s: controls muscle action of mouth, tongue, larynx
- Pgs: 410-414

2. Association Areas: higher info processes
- Control memory, reasoning, verbalizing, judgment, emotion, concentration, planning, problem solving

Cerebral Lobes and Their FX:Sensory Function Motor Function Assoc. Function
Frontal:
Parietal:
Temporal:
Occipital:
Voluntary muscle Concentration, planning, judgment,
problem solving
Temp., touch, pressure, pain
Understand speech; words to express
thought
Remembering visuals; musichearing
visionCombining visual
images

Basal Ganglia
1. Serve as a relay station for motor impulses
2. Coordinates motor activities
3. Passes impulses from brain stem to spinal cord
4. Secretes dopamine- Gray matter deep in
cerebrum

Ventricles (409)
- Interconnecting cavities deep in cerebral hemispheres and brain stem
- Continuous with central canal of spinal cord
- Filled with CSF- Creates bouancy for the
brain

Brain Stem:
- Region of brain that connects the cerebrum to spinal cord
Four Parts:1. Pons2. Diencephalon3. Mid brain4. Medulla oblongata

Diencephalon: 3 parts
1. Thalamus – relay station for incoming sensory inputs
2. Hypothalamus – maintains homeostasis
3. Limbic System: produces emotions and modifies behavior; fear, anger, pleasure, sorrow

Pons: “bridge”
- Regulates breathing rhythm
- Relays impulses from cerebrum to spinal cord
- 3 cranial nerves from pons

Medulla Oblongata
FX:1. Control hear rate2. Vasometer center
(dilates/constricts blood vessels)
3. Regulates breathing with pons

Reticular Formation:
FX: consciousness by interconnecting several portions of the brain

Sleep: suspension of voluntary body functions and consciousness (partial)
Two Types: determined by electro encephalogram (EEG)

1. Non Rapid Eye Movement (NREM)
- Waves are slower; longer wavelength
- 4 stages (I – IV)- “light” sleep to “deep”
sleep

2. Rapid Eye Movement (REM)- “Paradoxical Sleep”- Most important type of sleep- Allows the portions of the
brain to rest- Higher oxygen consumption
in brain than when awake- Dreaming occurs- Increased body temp., heart
rate, respiratory and blood pressure
- Muscle inhibition- 90 minutes after sleep begins

Sleep Importance:- 1/3 of our lives is spent asleep- Lack of REM leads to depression
and other disorders- Brain works through days
events/emotions- Dream: “frustrated desires and
attempts to fulfill one’s wishes” – Freud
- Alcohol suppresses REM- Sleep requirements change as we
age (16 hrs to 7 hrs as adults)- Adults are light sleepers- Daily mediation/prayer increases
REM

The Peripheral Nervous System
Two Branches1. Somatic NS (voluntary
nerves)2. Autonomic NS
(involuntary )Two Nerve Types3. Cranial Nerves (brain)4. Spinal Nerves (spinal
cord)

Cranial Nerves:
- 12 pairs- All originate from brain
stem (except 1st pair)- Designated by number
and function (p. 469)

1. Olfactory Nerve (smell)

2. Optic Nerve (sight)

3. Oculomotor Nerve (eye muscle)

4. Trochlear Nerve (eye muscle)

5. Trigeminal Nerve (mouth)

6. Abducens Nerve (eye muscle)

7. Facial Nerve (facial muscle) – 5 branches (pg 471)

8. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (auditory)

9. Glossopharangeal Nerve (tongue/pharynx)

10. Vagus Nerve (neck and chest)

11. Accessory Nerve (soft palate, pharynx)

12. Hypoglossal Nerve (tongue, speaking, chewing/swallowing)

Spinal Nerves:
- 31 pairs from spinal cord- Each contains 1000s of
nerve fibers- Named after the
vertebral column

Spinal Nerves
- C: 8- T: 12- L: 5- S: 5- Co: 1- Total: 31

-Very short Nerves
- Divided into dorsal root, ventral root, dorsal ramus, and ventral ramus

Cauda Equina: “horse tail”
- the end of the spinal cord
- Between L1 and L2- Many nerve roots and
rootlets

Dermatomes
- Area of skin that has sensory nerve fibers from a particular nerve