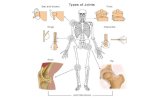
Joints Chapter 8. Classifying Joints Functions Flexibility for movement Hold bones together...
-
Upload
augustine-byrd -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Joints Chapter 8. Classifying Joints Functions Flexibility for movement Hold bones together...

Joints
Chapter 8

Classifying Joints
Functions• Flexibility for movement• Hold bones together
Classification• Structural• Functional
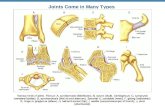
Fibrous Joints Cartilaginous Joints Synovial Joints
Binding material Joined by fibrous tissue
Joined by articular (hyaline) cartilage
Separated by synovial fluid cavity
Cavity Present No No Yes
Functional Type Synarthroses(immovable)
Amphiarthroses(slightly movable)
Diarthroses(freely movable)
Examples SuturesSyndesmosesGomphoses
SynchondrosesSymphyses
Joints of limbs

Fibrous Joints• Sutures
– Only b/w skull bones– Bind, but allow growth– As an adult CT ossifies = synostoses
• Syndemoses– Longer than sutures– Length of ligament determines mov’t– E.g interosseous membrane and tibia-
fibula distal ends• Gomphoses
– Tooth in alveolar socket– E.g periodontal ligament

Cartilaginous Joints
• Synchondroses– Temporary, become synostoses– E.g Epiphyseal plates and coastal cartilage
• Symphyses– Cartilage fused to fibrocartilage pad/plate– Strength with flexibility– E.g. intervetevbral discs and pubic symphysis

Synovial Joint Structure
• Synovial cavity filled w/ synovial fluid– Viscous, but thins with mov’t
• Articular capsule enloses cavity– Fibrous capsule (ext-) DICT– Synovial membrane (int-) LCT
• Articular cartilage (hyaline)• Reinforcing ligaments– Double jointed = looser/stretchier
ligaments and capsule

Synovial Joints
• Prevent friction– Bursae are flattend fibrous synovial sacs– Tendon sheaths are elongated bursa wrapped around a
tendon• Provide stability
– Articular surface shape• Determine mov’t & some stability
– Ligaments• Prevent excessive/undesirable mov’t• Inadequate stabilization stretches
(taffy) = snapping– Muscle tone
• Tendons stay taut so reactive

• Plane - intercarpal and –tarsals– Slip 1 or 2 ways (A)
• Hinge – elbow and interphalengeal– 1 plane of mov’t (B)
• Pivot – C1 & C2 or radius & ulna (C)– 1 plane of mov’t
• Condyloid - metacarpophalangeal (knucles)– 2 planes of mov’t (D)
• Saddle – carpometacarpal joint (thumb)– 2 planes of mov’t (E)
• Ball and socket – shoulder or hip joint– 3 planes mov’t (F)
Synovial Joint Shapes

Synovial Joint Movements• Gliding
– Slips surfaces across one another
• Flexion/extension – Reduces angle of joint/ increases
angle
• Abduction/adduction– Away from center/ toward midline
• Pronation/supination– Face or palm down/ face or palm up
• Rotation/circumduction– Turning on an axis/ making small
circles
• Inversion/eversion– Turn sole medially/ turn sole
laterally
• Dorsiflexion/plantar flexion (foot and wrist)– Flex/ point
• Protraction/retraction– Jaw out/jaw in
• Elevation/depression– Lift superiorly/move inferiorly

Knee Joint
anteriorcruciateligament
• Single cavity w/ 3 joints• Capsule partially encloses• Strong vertical force, weak lateral• Patellar ligament (knee-jerk)
– Prevent hyperextension• Fibular and tibial collateral ligaments
– Prevent lateral and medial rotation w/extension• Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments (tibial attachment)
– ACL: runs up posteriorly & laterally; prevents forward tibia mov’t– PCL: runs up anteriorly & medially; prevents backward tibia & forward
femur mov’t• Lateral and medial meniscus

Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
• Mandibular condyle and fossa mismatched shape– Shallow socket = easy dislocation
• Reset: thumbs in molars, push inferior and posterior
• Pain and disorders from muscles tension– Lateral exclusion, side to side mov’t, unique to
mammals– Grinding, clenching, biting

Clinical Terms• Sprain: stretching/tearing of a ligament• Dislocation (luxation): bones forced out of position• Bursitis: inflammation on bursa; blow or friction• Arthritis: synovial membrane thickens, production
decrease– Osteoarthritis – degenerative; tissue thickens & bone spurs
formed– Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune– Gouty arthritis – uric acid accumulation in soft tissue joints
• Synovitis: inflammation of synovial membrane• Tendinitis: inflammation of tendon sheaths, overuse;