Joints (Articulations) Functions of joints Classifying Joints: Functional or Structural Naming...
-
Upload
madison-short -
Category
Documents
-
view
240 -
download
1
Transcript of Joints (Articulations) Functions of joints Classifying Joints: Functional or Structural Naming...

Joints (Articulations) • Functions of joints
• Classifying Joints: Functional or Structural
• Naming Movements of Bones Around Joints
• Types of Joints Based on Movement
• Selected Key Joints: Shoulder, Elbow, Hip, Knee
• Joint Injuries
• Chronic Joint Conditions: Arthritis

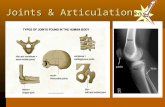
Types of Synovial Joints Based on Shape

Types of Synovial Joints Based on Shape
Plain hinge joints pivot on condyloid saddle ball-sockets.

Joints (Articulations) • Functions of joints
• Classifying Joints: Functional or Structural
• Naming Movements of Bones Around Joints
• Types of Joints Based on Movement
• Selected Key Joints: Shoulder, Elbow, Hip, Knee
• Joint Injuries
• Chronic Joint Conditions: Arthritis



Shoulder (Glenohumeral) Joint
• Bones and features involved
• Head of humerus and glenoid fossa of the scapula
• Type of joint
• Ball-and-socket joint
• Stability/strength of joint
• Coracohumeral ligament supports the weight of the upper limb
• Three glenohumeral ligaments—weak anterior reinforcements
• Reinforced by tendon of the long head of biceps and 4 rotator cuff tendons
• Four rotator cuff tendons encircle the shoulder joint:
• Stability is sacrificed for greater freedom of movement
• Allowable movements
• Diarthrotic
• Flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, medial and lateral rotation


Elbow Joint• Bones and features involved
• Radius and ulna articulate with the humerus
• Hinge at trochlear notch of ulna and trochlea of humerus
• Type of joint
• Hinge joint
• Stability/strength of joint
• Anular ligament —surrounds head of radius
• Two capsular ligaments restrict side-to-side movement:
• Ulnar collateral ligament
• Radial collateral ligament
• Allowable movements
• Diarthrotic
• Flexion and extension only


Hip (Coxal) Joint• Bones and features involved
• Head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis
• Type of joint
• Ball-and-socket joint
• Stability/strength of joint
• 4 Reinforcing ligaments:
• Iliofemoral ligament
• Pubofemoral ligament
• Ischiofemoral ligament
• Ligamentum teres
• Allowable movements
• Flexion, extension, rotation, adduction, abduction, circumduction
• Good range of motion, but limited by the deep socket
• Acetabular labrum (ring of cartilage around cavity—enhances depth of socket, difficult to dislocate


Knee Joint• Bones and features involved
• Largest, most complex joint of body• Three joints surrounded by a single joint
cavity: femoropatellar, lateral and medial tibiofemoral joints
• Type of joint
• Femoropatellar joint - plane joint with gliding
• Lateral and medial tibiofemoral hinge joints between the femoral condyles and the C-shaped lateral and medial menisci (semilunar cartilages) of the tibia
• Stability/strength of joint
• Capsule is reinforced by muscle tendons:
• Quadriceps and semimembranosus tendons
• Joint capsule is thin and absent anteriorly
• Anteriorly, the quadriceps tendon gives rise to patellar ligament
• Capsular and extracapsular ligaments prevent hyperextension
• Intracapsular ligaments
• Allowable movements
• Diarthrotic
• Allows flexion, extension, and some rotation when knee is partly flexed

Joints (Articulations) • Functions of joints
• Classifying Joints: Functional or Structural
• Naming Movements of Bones Around Joints
• Types of Joints Based on Movement
• Selected Key Joints: Shoulder, Elbow, Hip, Knee
• Joint Injuries
• Chronic Joint Conditions: Arthritis

Common Joint Injuries• Sprains
• The ligaments are stretched or torn
• Partial tears slowly repair themselves
• Complete ruptures require prompt surgical repair
• Cartilage tears
• Due to compression and shear stress
• Fragments may cause joint to lock or bind
• Cartilage rarely repairs itself
• Repaired with arthroscopic surgery
• Dislocations (luxations)
• Occur when bones are forced out of alignment
• Accompanied by sprains, inflammation, and joint immobilization
• Caused by serious falls or playing sports
• Subluxation—partial dislocation of a joint

Inflammatory and Degenerative Conditions
• Bursitis
• An inflammation of a bursa, usually caused by a blow or friction
• Treated with rest and ice and, if severe, anti-inflammatory drugs
• Tendonitis
• Inflammation of tendon sheaths typically caused by overuse
• Symptoms and treatment similar to bursitis

Joints (Articulations) • Functions of joints
• Classifying Joints: Functional or Structural
• Naming Movements of Bones Around Joints
• Types of Joints Based on Movement
• Selected Key Joints: Shoulder, Elbow, Hip, Knee
• Joint Injuries
• Chronic Joint Conditions: Arthritis

Lyme Disease: Acute Arthritis
• Caused by bacteria transmitted by the bites of ticks
• Symptoms: skin rash, flu-like symptoms, and foggy thinking
• May lead to joint pain and arthritis
• Treatment: antibiotics

Clinical Forms of Arthritis (Three Chronic Types)
1. Osteoarthritis
• Most common chronic arthritis
• Irreversible, degenerative (“wear-and-tear”) arthritis
• 85% of all Americans develop OA, more women than men
• Probably related to the normal aging process
• More cartilage is destroyed than replaced in badly aligned or overworked joints
• Exposed bone ends thicken, enlarge, form bone spurs, and restrict movement
• Treatment: moderate activity, mild pain relievers, capsaicin creams, glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate
•100 different types of inflammatory or degenerative diseases that damage joints
•Most widespread crippling disease in the U.S.
•Symptoms: pain, stiffness, and swelling of a joint
•Acute forms: caused by bacteria, treated with antibiotics
•Chronic forms: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis

2. Rheumatoid arthritis
• Chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease of unknown cause
• Begins 40-50 years of age, more common in women
• Signs and symptoms include joint pain and swelling (usually bilateral), anemia, osteoporosis, muscle weakness, and cardiovascular problems
•RA begins with synovitis of the affected joint
• Inflammatory blood cells migrate to the joint, release inflammatory chemicals, cartilage erodes, scar tissue forms, bone ends connect.
•Treatment: aspirin, long-term use of antibiotics, and physical therapy; anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressants; new biological response modifier drugs neutralize inflammatory chemicals
Clinical Forms of Chronic Arthritis

Clinical Forms of Chronic Arthritis
3. Gouty Arthritis
• Inflammation of joints is caused by a deposition of urate crystals from the blood in joints and soft tissues, followed by inflammation
• Typically affects the joint at the base of the great toe
• Can usually be controlled with diet: drugs, plenty of water, less red meat, avoidance of alcohol
• More common in men
• In untreated gouty arthritis, the bone ends fuse

Joints (Articulations) • Functions of joints
• Classifying Joints: Functional or Structural
• Naming Movements of Bones Around Joints
• Types of Joints Based on Movement
• Selected Key Joints: Shoulder, Elbow, Hip, Knee
• Joint Injuries
• Chronic Joint Conditions: Arthritis