Genaral - Joints · SYNOVIAL JOINTS CHARACTERSTICS:-1. Articular cartilage 2. Articular capsule 3....
Transcript of Genaral - Joints · SYNOVIAL JOINTS CHARACTERSTICS:-1. Articular cartilage 2. Articular capsule 3....


Definition
� Junction between 2 or more bones
� It is a device to permit movement
2

Classification
SYNARTHROSIS
AMPHIARTHROSIS
DIARTHROSIS
3

Classification
REGIONAL
SIMPLE
COMPOUND
COMPLEX
4

A. Structural classification-1. Fibrous joints
Sutures PLANE SUTURE SERRATE SUTURE

1. Fibrous joints
6
Sutures DENTICULATE SUTURE SQUAMOUS SUTURE

1. Fibrous joints
7
SuturesSchindylesis

A. Structural classification1. Fibrous joints
8
Gomphosis
Syndesmosis

Cartilaginous Joint� Primary cartilaginous or
Synchondrosis.
� Epiphyseal plate
� 1st chondrosternal joint
� Costochondral joint
9

Cartilaginous Joint
10
• Secondary cartilaginous or symphysis.

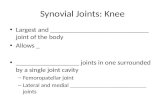
SYNOVIAL JOINTS
CHARACTERSTICS:-
1. Articular cartilage2. Articular capsule 3. Synovial membrane
with Synovial fluid4. Ligaments5. Articular disc or
meniscus.6. Bursa.

Acc. To axis of movement/shape of articular surfaceUniaxial Biaxial Polyaxial Plane
1 degree freedom of movement
2 degree freedom of movement
3 degree freedom of movement
Articularsurface flat
1.Hinge 1.Ellipsoid 1.Ball & socket
2.Pivot 2.Saddle
3.Condylar

UNIAXIAL JOINTSHINGE (Ginglymus)-� 1. Elbow joint.
� 2. Ankle joint.
� 3. Interphalangial joints .

UNIAXIAL JOINTS
Pivot type: ( Trochoid)
1. Atlanto axial joint
2. Superior & inferior radioulnar joints.

UNIAXIAL JOINTS� Condylar joint
1. Knee joint
2. Mandibular joint

Acc. To axis of movement/shape of articular surfaceUniaxial Biaxial Polyaxial Plane
1 degree freedom of movement
2 degree freedom of movement
3 degree freedom of movement
Articularsurface flat
1.Hinge 1.Ellipsoid 1.Ball & socket
2.Pivot 2.Saddle
3.Condylar

BIAXIAL JOINTS� Ellipsoid joint
� 1. Radio carpal joint( Wrist joint)
� 2. Metacarpophalangealjoints
� 3. Atlanto-occipital joint.

BIAXIAL JOINTSSaddle (Sellar) joint
1. 1st Carpometacarpal joint of thumb
2. Sterno - Clavicular joint.
3. Calcaneocuboid joint.
4. Incudomalleolar joint.
5. Femoropatellar joint

Acc. To axis of movement/shape of articular surfaceUniaxial Biaxial Polyaxial Plane
1 degree freedom of movement
2 degree freedom of movement
3 degree freedom of movement
Articularsurface flat
1.Hinge 1.Ellipsoid 1.Ball & socket
2.Pivot 2.Saddle
3.Condylar

POLYAXIAL JOINTS• Ball & socket / spheroidal joints.� 1. Shoulder joints.� 2. Hip joint� 3.Talo-calcaneo-navicular joint.

Acc. To axis of movement/shape of articular surfaceUniaxial Biaxial Polyaxial Plane
1 degree freedom of movement
2 degree freedom of movement
3 degree freedom of movement
Articularsurface flat
1.Hinge 1.Ellipsoid 1.Ball & socket
2.Pivot 2.Saddle
3.Condylar

PLANE (Gliding ) JOINTS
� 1. Intercarpal joints.
� 2. Inter-tarsal joints.
� 3. Intervertebral joints.

MOVEMENTSTYPES
1.Gliding
2.Angular� Flexion� Extension

MOVEMENTS (Cont..)� 3. Abduction- Axis
� 4. Adduction - Axis
5. Rotation

MOVEMENTS (Cont..)
� 6. Circumduction
25

Blood Supply of Joints� Articular & epiphysial branches.
� circulus articularis vasculosus.
� The articular cartilage is avascular.
26

Nerve Supply of Joints• Capsule & Ligaments : Rich
nerve supply
• Synovial membrane : Poor nerve supply
• Articular cartilage : Non –nervous
• Hiltons law
27


Dislocation of Joint
� Articular surface of joint are abnormally displaced.
� Subluxation:
29

Sprain (Ligament Tear)
30

Arthritis� Types :
� Rheumatic� Rheumatoid � Osteoarthritis� Tuberculosis
31

Joint Prostheses
32
�� ArthroplastyArthroplasty

Synovial cyst

Arthroscopy

� DEFINITION� CLASSIFICATION� SYNOVIAL JOINTS� BLOOD SUPPLY� NERVE SUPPLY� APPLIED ASPECTS

Classification
SYNARTHROSIS
AMPHIARTHROSIS
DIARTHROSIS
36

Classification
REGIONAL
SIMPLE
COMPOUND
COMPLEX
37


�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������