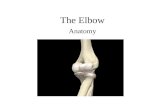
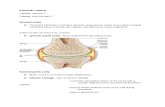
Joints. Types of joints Fibrous Cartilagenous Synovial Fibrous Cartilagenous Synovial.
-
Upload
baldwin-hamilton -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Joints. Types of joints Fibrous Cartilagenous Synovial Fibrous Cartilagenous Synovial.

JointsJoints
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

Types of jointsTypes of joints
Fibrous
Cartilagenous
Synovial
Fibrous
Cartilagenous
Synovial

FibrousFibrousImmoveable
Ex, plates of skull
Immoveable
Ex, plates of skull
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

CartilageneousCartilageneous
Partially moveableConnected by cartilageEx, joints between vertebrae
Partially moveableConnected by cartilageEx, joints between vertebrae
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

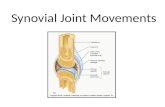
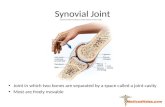
SynovialSynovial
Hinge Joint between 3rd metacarpal and long pastern
Ball and SocketJoint between femur and ilium
Hinge Joint between 3rd metacarpal and long pastern
Ball and SocketJoint between femur and ilium
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

Can you name the bones?Can you name the bones?
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

SkullSkull
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Premaxilla (incisive bone)Holds alveoli for upper incisor teeth
MaxillaHolds alveoli for molar and premolar
teethMandible (lower jaw)
Holds alveoli for all teeth of lower jaw What we would call the mouth…
Premaxilla (incisive bone)Holds alveoli for upper incisor teeth
MaxillaHolds alveoli for molar and premolar
teethMandible (lower jaw)
Holds alveoli for all teeth of lower jaw What we would call the mouth…
What we would call the mouth…

And all the rest…And all the rest…
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

SpineSpine1. Cervical Vertbrae2. Thoracic Vertebrae3. Lumbar Vertebrae4. Sacrum5. Caudal/Coccygeal Vertebrae
1. Cervical Vertbrae2. Thoracic Vertebrae3. Lumbar Vertebrae4. Sacrum5. Caudal/Coccygeal Vertebrae
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

Cervical VertebraeCervical Vertebrae
Make up the neck of the horse1st cervical vertebra = Atlas2nd cervical vertebra = Axis
Make up the neck of the horse1st cervical vertebra = Atlas2nd cervical vertebra = Axis

Thoracic VertebraeThoracic Vertebrae
18 Characteristically have high spines3rd and 4th form the withers
18 Characteristically have high spines3rd and 4th form the withers

Lumbar VertebraeLumbar Vertebrae
6Characteristically long and flat
6Characteristically long and flat

Sacrum
Coccyx
Sacrum
Coccyx
Made up of 6 sacral vertebrae fused together
Made up of 15-21 coccygeal vertebrae
Made up of 6 sacral vertebrae fused together
Made up of 15-21 coccygeal vertebrae

QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.Ribs & SternumRibs & Sternum
18 pairs of ribsFirst 8 pairs are connected to the
sternumSternum ~ breast bone
Made up of 6-8 sternebrae and cartilage
18 pairs of ribsFirst 8 pairs are connected to the
sternumSternum ~ breast bone
Made up of 6-8 sternebrae and cartilage

ForelegForeleg

Shoulder bone’s connected to the…
Shoulder bone’s connected to the…
Scapula
Humerus
Radius
Ulna (not a functional bone in a horse)
Scapula
Humerus
Radius
Ulna (not a functional bone in a horse)

From the wrist distally…From the wrist distally…Carpus
Forms what is commonly called the knee joint in a horse
Metacarpus3rd metacarpal, or cannon bone is the
only functional metacarpalSplint bones- small bones running
parallel to the cannon bone on either side***Splints is a condition when the splint bone
sustains a fracture
Carpus Forms what is commonly called the knee
joint in a horseMetacarpus
3rd metacarpal, or cannon bone is the only functional metacarpal
Splint bones- small bones running parallel to the cannon bone on either side***Splints is a condition when the splint bone
sustains a fracture

Fingers???Fingers???
Technically - phalanges1st Phalange - Proximal Phalanx - Long
Pastern2nd Phalange - Middle Phalanx - Short
Pastern3rd Phalange - Distal Phalanx - Coffin
Bone
Technically - phalanges1st Phalange - Proximal Phalanx - Long
Pastern2nd Phalange - Middle Phalanx - Short
Pastern3rd Phalange - Distal Phalanx - Coffin
Bone

More…More…
Proximal and Distal SesamoidsNavicular Bone
Proximal and Distal SesamoidsNavicular Bone QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressorare needed to see this picture.

QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Can you name them?

Hind LegHind Leg

Pelvic GirdlePelvic Girdle
Os Coxae ~ half of the pelvic girdle3 bones fused together
IliumIschiumPubis
Os Coxae ~ half of the pelvic girdle3 bones fused together
IliumIschiumPubis QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressorare needed to see this picture.

Hip bone’s connected to the…
Hip bone’s connected to the…
FemurPatella ~ knee capCrus = Fibula and Tibia
Fibula isn’t functional; fuses with length of tibia
FemurPatella ~ knee capCrus = Fibula and Tibia
Fibula isn’t functional; fuses with length of tibia

How high’s the ankle?How high’s the ankle?
Tarsus ~ Hock Joint (corresponds to human ankle)
Metatarsus3rd metatarsal (Cannon Bone) = only
functional metatarsalSplint bonesPhalanges
Long (1) & Short (2) PasternsCoffin Bone (3)
Sesamoids and Navicular Bone
Tarsus ~ Hock Joint (corresponds to human ankle)
Metatarsus3rd metatarsal (Cannon Bone) = only
functional metatarsalSplint bonesPhalanges
Long (1) & Short (2) PasternsCoffin Bone (3)
Sesamoids and Navicular Bone

QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Now you know the bones…
Now you know the bones…
…Can you name all 205 to 210 of them?…Can you name all 205 to 210 of them?

While you were learning the names of the bones,
did you notice any connection between the human skeleton and the
equine
?
While you were learning the names of the bones,
did you notice any connection between the human skeleton and the
equine
?QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressorare needed to see this picture.
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

Here are just a few..Here are just a few..
We have almost the exact number of bones as horses
Horses’ forelegs are almost identical to our arms in position, the only real difference being the elongation of the bones that make up our wrist, hand and fingers in the horses’ knee, lower leg (cannon), ankle and hoof
We have almost the exact number of bones as horses
Horses’ forelegs are almost identical to our arms in position, the only real difference being the elongation of the bones that make up our wrist, hand and fingers in the horses’ knee, lower leg (cannon), ankle and hoof

Connections cont’d…Connections cont’d…
The same is true for their hindlegs ad our legs: up to the knee, they’re almost the same, only less mobile around the joints in a horse. Our ankle bones, foot bones and toes are elongated to make the cannon and splints, pastern and hooves of a horse
The same is true for their hindlegs ad our legs: up to the knee, they’re almost the same, only less mobile around the joints in a horse. Our ankle bones, foot bones and toes are elongated to make the cannon and splints, pastern and hooves of a horse

DifferencesDifferencesThe main differences between a horse’s skeleton
and a human’s skeleton come from a horse being a quadraped while humans are bipeds
This changes the angle of the limbs in relation to the spine, the length of the neck, and the shape of the head
Horses’ being prey animals and humans predators also affects the skull; a horse’s orbits are laterally positioned because they are monocular, and their jaw is longer to provide for the powerful molars they use to chew their fibrous diet
The main differences between a horse’s skeleton and a human’s skeleton come from a horse being a quadraped while humans are bipeds
This changes the angle of the limbs in relation to the spine, the length of the neck, and the shape of the head
Horses’ being prey animals and humans predators also affects the skull; a horse’s orbits are laterally positioned because they are monocular, and their jaw is longer to provide for the powerful molars they use to chew their fibrous diet

QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
The End
The End