Intranet & Extranet
description
Transcript of Intranet & Extranet

Intranet & Extranet
To understand Intra-business e-BusinessTo describe Intranet and ExtranetTo understand corporate portals

TCP/IP
• Message is sent from application layer to TCP layer• Message broken down into packets• TCP assigns a port number and sequence number• Packets and TCP header, passed on to IP• IP gives packets destination address• Hardware turns alphabetic text packets into electronic signals
and transmit over phoneline• ISP router examines destination address and sends off• At the receiving end we start at the bottom of stack• Headers are stripped off as packet goes up the stack• When data reaches to application layer, message is assembled
into its original form
Application
IP
TCP
Hardware Internet
Application
IP
TCP
Hardware
Sending computer Receiving computer

So We have...
• Internet– Most common platform for B2C
We also have...• Intranet
– Most common platform for internal corporate system
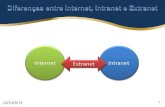
• Extranet– The most common platform for B2B

Intranets
– Internal Web– Primary platform to serve internal information needs– A wide variety of services– A platform for provision of news and training– A collaboration platform for the employees– Enables easy access to corporate resources– Could be connected to Internet

Advantages and disadvantages of Intranets
• Advantages– Low cost of converting client/server network – Secure internal networks
• Through use of Firewalls
• Disadvantage– Information overload

Types of Intranet
• A business to employee (B2E)– Employees procure for themselves (needed
supplies)– Corporate shop– Information dissemination to employees
• between units within the business
• between employees within the business

Application ServersERP
Legacy System
Client’sBrowser
Intranet
Product DatabaseCustomer Database
Internet
Firewall
Web ServersE-Mail
Architecture of Intranet

Corporate Portal
• Emerging due to information over-load• Personalised• Single point of access• Rich content• Narrow community• Can be delivered in phases

Corporate Portal FrameworkAneja et al, Intel Technology Journal Q1
CorporatePortal
Applications
ExternalWeb Sites
OrganisationalKnowledge
Base
DocumentsCollaboration
Products
InternalWeb Sites
Publishing
DataWarehouses
KnowledgeManagement
Search
News andNews Feeds
ExternalContent
ExternalServices
Personalisation
Collaboration
Integration BusinessIntelligence
ExternalInformationResources
InternalInformationResources
AccessibilityS
ecu
rity
Scalability
Ext
ens
ibili
ty

Extranets
– Extended Intranet– Primary platform for B2B exchanges– A meeting place for for trading partners– Adds value to customer experience– Uses Internet infrastructure– Non-proprietary technical tool that supports EC

Benefits of Extranets
– Enhanced communication– Productivity enhancements– Business enhancements– Cost reduction– Information delivery

Advantages and disadvantages over proprietary networks
• Advantages– Ubiquity of access– Open standards– Less costly
• Disadvantages– System Vulnerability– Slow Links– Human Factors

EnterpriseNetwork
CorporateClient
CorporateClient
Server
WirelessRoamingClient
Web
Internet
ISP
WebClient
WebClient
The Architecture of Extranet
BrowserDialling softwareConnection Device
Remote AccessServerWeb
Server
Firewall
BrowserRemote Access ServerRemote dial-in SoftwareDialling softwareFirewallWeb ServerIntranetVPN

Need for Security
• Need– Encryption
• Ensures privacy and Integrity
– Authentication• Provides identification of remote user

Virtual Private NetworksTunnelling Technology
– VPN • A network that uses public network to transmit data in secure and private
manner
– IPSEC• Supported by Internet Engineering task force (IETF)• Supported by the new IP6• Designed to supports new encryption algorithms
TCP
IPIPSEC