Ic Engines by Bhargav Aparoksham
-
Upload
ashravani1996 -
Category
Documents
-
view
11 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Ic Engines by Bhargav Aparoksham
IC ENGINES
By JayachadraiahIC ENGINESWhat is an Engine ?An Heat engine is a machine designed to convert heat energy from a fuel into useful mechanical motion.Ex : In a car, fuel energy is converted into mechanical motion of the car using an internal combustion engine.
Types of Heat engines : 1. External combustion engines (ECE) : In these engines combustion of fuels takes place externally. In an External combustion engine, working fluid gets energy using boilers by burning fossil fuels or any other fuel, thus the working fluid does not come in contact with combustion products. ex: Steam engine, here the working fluid is steam
2. Internal Combustion engines (ICE) :Theinternal combustion engineis anenginein which thecombustionof afuel takes place internally in a combustion chamber.
In an Internal combustion engine, combustion takes place within working fluid of the engine, thus fluid gets contaminated with combustion products.Petrol engine is an example of internal combustion engine, where the working fluid is a mixture of air and fuel
Energy Conversion Process in an engine :
Engine Classification :
Parts & Components of an IC Engine:
1. Piston :cylindrical shaped mass that reciprocates back and forth in the cylinder, transmitting the pressure forces in the combustion chamber to the rotating crankshaft.
2. Connecting rod :It is a rod or linkage that connect the reciprocating piston with the rotating crankshaft.
3. Crankshaft :It is a rotating shaft through which engine work output is supplied to external systems. Fixed with the cylinder block, and receives motion forces from the piston.
4. Cylinder :Circular cylinders in the engine block inside which the piston reciprocate, and beneath which crank is fixed, thus confining the motion linkage.
5. Camshaft :Rotating shaft used to push open valves at proper time in the engine cycle. The cam profile is made to give such desired movement to the valve.
Other Important Components :Block : Body of the engine containing cylinders, made of cast iron or aluminium.Head : The piece which closes the end of the cylinders, usually containing part of the clearance volume of the combustion chamber.Combustion chamber: The end of the cylinder between the head and the piston face where combustion occurs.The size of combustion chamber continuously changes from minimum volume when the piston is at TDC to a maximum volume when the piston at BDC.
Push rods : The mechanical linkage between the camshaft and valves on overhead valve engines with the camshaft in the crankcase.Crankcase : Part of the engine block surrounding the crankshaft.In many engines the oil pan makes up part of the crankcase housing.Exhaust manifold : Piping system which carries exhaust gases away from the engine cylinders, usually made of cast iron Fig: Engine Components
Intake manifold :Piping system which delivers incoming air to the cylinders, usually made of cast metal, plastic, or composite material.In most SI engines, fuel is added to the air in the intake manifold system either by fuel injectors or with a carburetor.The individual pipe to a single cylinder is called runner.
Carburetor : A device which meters the proper amount of fuel into the air flow by means of pressure differential.For many decades it was the basic fuel metering system on all automobile (and other) engines.Spark plug : Electrical device used to initiate combustion in an SI engine by creating high voltage discharge across an electrode gap.
Engine Terminology :Top Dead Center (TDC): Position of the piston when it stops at the furthest point away from the crankshaft.Bottom Dead Center (BDC): Position of the piston when it stops at the point closest to the crankshaft.
Stroke : Distance travelled by the piston from one extreme position to the other : TDC to BDC or BDC to TDC.Bore :It is defined as cylinder diameter or piston face diameter; piston face diameter is same as cylinder diameter( minus small clearance).Swept volume/Displacement volume : Volume displaced by the piston as it travels through one stroke.Clearance volume : It is the minimum volume of the cylinder available for the charge (air or air fuel mixture) when the piston reaches at its outermost point (top dead center or outer dead center) during compression stroke of the cycle.
VIDEO :
Classification of IC Engines:IC Engines can be classified in to no of ways . Some of the important types are based on,
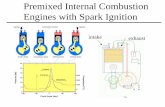
Based on no of Engine cycles :1. Four stroke engine: A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes which comprise a single thermodynamic cycle. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction.The four strokes are:1- Intake,2- Compression,3- Power,4- Exhaust
4-Stroke CI engine cycle:
VIDEO :
2. Two stroke engine : A two-stroke ,two-cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine which completes a power cycle in only one crankshaft revolution and with two strokes, or up and down movements, of the piston in comparison to a "four-stroke engine", which uses four strokes to do so. This is accomplished by the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happening simultaneously and performing the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions at the same time.
Based on type of ignition:1. Spark Ignition or Petrol Engine :The term spark-ignition engine refers to internal combustion engines where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. These types of engines are generally petrol engines
2. Compression Ignition or Diesel engines: Here the heat generated from compression is enough to initiate the combustion process, without needing any external spark.Compression ignition engines are mostly diesel engines.
Based on the arrangement of cylinders :Based on the arrangement of cylinders :Based on cylinder arrangement :
In a mutli cylinder engine the cylinders can be arranged in a no of different ways . Based on their arrangement they are classified into :1. Inline : Here the cylinders in line to the crankshaft 2. Flat : Here the cylinders are arranged opposite to each other.3. V : Here the cylinders are arranged perpendicular to each other in a V shape as shown.
inline
V
flatBased on Valve position :
Based on Engine Speed :
Based on Method of air supply :
Based on Method of Fuel supply :
Based on type of Fuel used :
Based on yype of Cooling system :
Based on type of Application :
Valve and Port Time Diagrams:In a piston engine, the valve timing is the precise timing of the opening and closing of the valves. In an internal combustion engine these are usually poppet valves .In general an engine will have a period of "valve overlap" at the end of the exhaust stroke, when both the intake and exhaust valves are open.TDC = Top dead centreBDC = Bottom dead centreIO = Inlet valve opensIC = Inlet valve closesEO = Exhaust valve opensEC = Exhaust valve closes
VIDEO :
Conclusion:What you have learnt ?I.C. ENGINES: Definition of Engine And Heat Engine, I.C Engine Classification Parts ofI.C.Engines, Working of I.C. Engines, Two Stroke & Four Stroke I.C.Engines SI & CI Engines, Valveand Port Timing Diagrams.