Windows server 2008 r2
-
Upload
pts-ian -
Category
Technology
-
view
1.630 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Windows server 2008 r2

Ian Dela Cruz
PARTNER TECHNOLOGY SPECIALISTMICROSOFT DEVELOPMENT PARTNER

IIS 7.5 ASP .NET on Server
Core Enhanced FTP and
WebDAV Administration
Modules & Cmdlets
Hyper-V™ with Live Migration
Hot Add/Remove VM Storage
Remote Desktop Services
Power Management Windows PowerShell AD Administrative
Center Best Practices
Analyzer
Management Web
Technology Investment Areas
Virtualization
Solid Foundation for Enterprise Workloads
256 Core Support Componentization Boot from SAN or VHD Support for Solid-state Devices File Classification Infrastructure
Scalability and Reliability
DirectAccess™ BranchCache™ Enhanced Group Policies RemoteApp & Desktop Connections
Better Together with Windows 7

Some of the Top Reasons for Virtualization
Can be used to move those applications between servers and protect users from outages due to a physical server failure
In fact, ESG research indicates that virtual machine disaster recovery, backup, and mobility follow closely behind consolidating more physical servers in the list of the top ten server virtualization initiatives.
Source: ESG Research Report, 2010 IT Spending Intentions Survey, January 2010.Source: ESG Research Report, 2009 Data Center Spending Intentions Survey, March 2009.

Microsoft VirtualizationFrom the Datacenter to the Desktop
Management
Desktop Virtualization
Application Virtualization
Session Virtualization
Server Virtualization
User StateVirtualization
Folder RedirectionRoaming Profiles

Why Are Customers Virtualizing?
Server Consolidation Energy & Space
Reduction Application
Compatibility
Rapid Provisioning High Availability Business Continuity
Dynamic Datacenters & Desktops
Accelerated Responsiveness
IncreaseIT Efficiency
Enable Business Agility
DriveCosts Down
SAN
“Why is virtualization such a big deal? A lot of people understand, and they think it's about saving money, it's about saving power, it's about green IT, it's about space, and that's certainly true. But in our perspective, it's much, much bigger than that, and people are just now beginning to understand that. We think that there's a major transformation taking place in IT. This major transformation that's been taking place for years is starting to accelerate, and we believe that virtualization is a major enabler and catalyst of that transition that's taking place.”
- Tom Bittman, Gartner VP and Chief of Research of Infrastructure and Operations, at Microsoft’s Virtualization Launch Event

2.8 GHz DualCore Processor
ProcessorCore 1 Active
ProcessorCore 2 Inactive
ProcessorCore 4 Inactive
ProcessorCore 3 Inactive
Power Management
Core ParkingAdjusting P-statesCentralizedstorage Processor
Core 1
P-State=0
P-State Percent Frequency0 100 2.800 GHz1 90 2.520 GHz2 85 2.380 GHz3 75 2.100 GHz4 60 1.680 GHz5 50 1.400 GHz
P-State Percent Frequency0 100 2.800 GHz1 90 2.520 GHz2 85 2.380 GHz3 75 2.100 GHz4 60 1.680 GHz5 50 1.400 GHz
ProcessorCore 2
P-State=4
Storage AreaNetwork

Server Core Parking
Scheduling virtual machines on a single server for density as opposed
to dispersionThis allows “park/sleep” cores by putting them in deep C states
Overview
Significantly enhances Green IT by being able to reduce power required for CPUs
Benefits

Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 Processor
Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 Processor
Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 Processor
Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 Processor
Windows Server 2008 (w/o core parking)
16 LP Server

Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 ProcessorProcessor is
“parked”
Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 Processor
Server Core Parking
16 LP Server
Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 Processor
Core 1 Core 1
Core 1 Core 1
1 ProcessorProcessor is
“parked”

How Fast can use Activate Hyper-V?
The first virtual machine was up and running 25 minutes and 22 mouse clicks after starting a bare metal installation of Windows Server 2008 R2.
Source: ESG Lab Validation Report, July 2010

Overall Edition Differentiation
Scal
abili
ty
Hig
h Av
aila
bilit
y
Secu
rity
Feat
ures
Virt
ualiz
atio
n
1 Physical processor15 User Limit8 GB RAM
Specialized Editions
4 Physical processors32 GB RAM
Web Role (IIS) OnlyFor Internet Facing Web Servers
64 Physical processors2 TB RAMUnlimited Virtualization Rights1
Hot Add/Replace Memory*Hot Add/Replace Processors*Failover ClusteringCross-Fire ReplicationSupport for Intel’s MCA2
Web (IIS) and Application Roles Only for Database, Customer and LOB Apps.
8 Physical processors2 TB RAM4 Virtual Machine + HostHot Add Memory*Failover ClusteringCross-Fire ReplicationActive Directory Federation ServicesActive Directory Certificate ServicesUnlimited RRAS, IAS ConnectionsUnlimited RDS Gateway ConnectionsUnlimited DFS Roots
64 Physical processors2 TB RAMUnlimited Virtualization RightsHot Add/Replace Memory*Hot Add/Replace Processors*Failover ClusteringCross-Fire ReplicationActive Directory Federation ServicesActive Directory Certificate ServicesUnlimited RRAS, IAS ConnectionsUnlimited RDS Gateway ConnectionsUnlimited DFS Roots
Editions
4 Physical processors32 GB RAM1 Virtual Machine + Host

Edition Comparison By Server RoleServer Role Enterprise Datacenter Standard Itanium Web Foundation
Web Services (IIS)
Application Server
Print and Document Services
Hyper-V
Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services
Active Directory Rights Management Services
DHCP Server
DNS Server
Fax Server
UDDI Services
Windows Deployment Services
Active Directory Certificate Services 1 1
File Services 2 2
Network Policy and Access Services 3 5
Remote Desktop Services 4 6
Active Directory Federation Services
Windows Server Update Services (WSUS)
- Full - Partial/Limited - Not Available
1 – Limited to creating Certificate Authorities – no other ADCS features (NDES, Online Responder Service). See ADCS role documentation on TechNet for more information2 – Limited to 1 standalone DFS root3 – Limited to 250 RRAS connections, 50 IAS connections and 2 IAS Server Groups4 – Limited to 250 Remote Desktop Services connections 5 – Limited to 50 RRAS connections, 10 IAS connections6 – Limited to 50 Remote Desktop Services connections

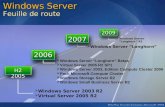
Top Reasons to Upgrade
Powerful Hardware and Scaling FeaturesReduced Power ConsumptionHyper-VReduced Desktop Costs with VDIEasier and More Efficient Server ManagementManaging Data Not Just Managing StorageUbiquitous Remote AccessImproved Branch Office Performance and Management

Active DirectoryImprove IT Operational EfficiencyStrengthen SecurityImprove Information Worker Productivity

Agenda
ChallengesWhat is Active Directory?IT and the Business Benefits of AD
Increases IT Operational EfficiencyStrengthens Network SecurityIncreases Information Worker Productivity
Getting Started with AD

Challenges
Identity ManagementA lot of user ids and directoriesWeak passwordsSecuring access to networks and applicationsRising help desk costs
Server and Desktop ManagementGetting to standard configurationsManaging server and desktop settingsRouge applications on the desktopKeeping systems up-to-date

What is Active Directory?
Focal point for network & user management Central authority for network & application security Integration point for bringing systems together
•Account Information•Privileges•Profiles•Policies•Single Sign-On
Windows Users
•Network Resources•File Shares•Printers•Policies
Windows Servers
•Configuration•Security•Quarantine•Policies
Windows Clients
•Directories•Databases•Mainframes•UNIX
Other Systems
•Product Information•Privileges•Profiles•Policies•Automated
deployment
Microsoft Products•Configuration•Quality of Service•Security Policies•Single Sign-On
Network Devices
•Configuration•Security Policy•VPN & Remote
Access•Quarantine•Single Sign-On
Firewall Services
•Single Sign-On•Automated
deployment•Configuration•App-specific directory
data
3rd Party Applications
•Operational Efficiency•Improved Security•Improved Productivity•Interoperability
Active Directory
Foundation for Identity & Access Management

The Role of AD…
Automate the Lockdown Windows SystemsEnforce the use of strong passwords & credentialsSimplify managing access to network resources
Increase efficiency of managing Windows by up to 30%
Reduce the number of directories and passwordsCentral management of Windows servers & desktops
Find people, applications, and resources fasterEmpower employees with rich collaboration capabilitiesSingle Sign-on to integrated applications and resources
StrengthenSecurity
Improve Employee
Productivity
Increase ITOperationalEfficiency

Increase Efficiency by up to 30%*
IT Operational Efficiency
1. Simplify identity administrationProvide single sign-on to all network resources
One directory to manage users & network resources
Common identity store for other products
2. Enable distribution of IT workloadEasily delegate administrative tasks
Customizable administrative interfaces ease use
Distribute tasks by role, group or individual
3. Automate IT workloadCentrally manage software deployment
Increase accessibility of data
Selectively control computer settings
* - Study of 56 AD-specific case studies showed an average efficiency increase of 31% or $91,476

IT Operational Efficiency
AD as a multi-purpose directoryNOS infrastructure directory
Applications directory
Network devices
Consolidate Domains & ServersNo limitation on number of users
Improved AD scalability = less hardware
Reduce the number of domains
VPN Firewall
LOBApplication
B2B/B2C InternetApplication
ActiveDirectory
NT Domains
LDAPDirectories
Mainframe/UNIX
Reduce Directories or Domains Through Consolidation

IT Operational Efficiency
Use Group Policy to:Manage configuration of servers, desktops & groups of usersAutomate enforcement of IT policiesAutomate system updates &application installationsConsistently implement security settings across the enterpriseImplement standard computingenvironments for users
Active Directory IT Staff
Group Policy
Many Users
Many Desktops& Servers
One-to-Many Management of Users & Computers

Improves IT productivityReduces need for logon scriptsLimits configuration errorsEnhances end-user satisfactionMinimizes image maintenanceReduces overall image count
Group Policy Preferences

The Role of AD…
Automate the Lockdown Windows SystemsEnforce the use of strong passwords & credentialsSimplify managing access to network resources
Increase efficiency of managing Windows by up to 30%
Reduce the number of directories and passwordsCentral management of Windows servers & desktops
Find people, applications, and resources fasterEmpower employees with rich collaboration capabilitiesSingle Sign-on to integrated applications and resources
StrengthenSecurity
Improve Employee
Productivity
Increase ITOperationalEfficiency

Strengthens Security
Security templates can ensure enterprise-wide securityPrevent end-users from modifying desktop configurations or settingsSoftware Restriction Policies precisely control what software can be runEnable audit of events & changes
Automate the Lockdown of Windows Systems

Strengthens Security
Granular control of password policyHistory, age, min/max length, complexity
Define account lockout policiesDuration, threshold, reset time
Enable use of two-factor authenticationSmartcards, biometrics, other tokens
Extend security policy to non-Windows systems via Kerberos & LDAP
Strong Passwords and Logon Credentials

Strengthens Security
Remote Access policies control access to network resources via dial-in or VPN
Other polices apply regardless of how a client connects to the network
Once connected, network access control can:
Quarantine & check the “health” of client
Clients who pass get network access
Clients who do not pass can be blocked
Health maintenanceQuarantined clients can be given access to resources to get to a healthy state
Simplify Managing Access to Network Resources

The Role of AD…
Automate the Lockdown Windows SystemsEnforce the use of strong passwords & credentialsSimplify managing access to network resources
Increase efficiency of managing Windows by up to 30%
Reduce the number of directories and passwordsCentral management of Windows servers & desktops
Find people, applications, and resources fasterEmpower employees with rich collaboration capabilitiesSingle Sign-on to integrated applications and resources
StrengthenSecurity
Improve Employee
Productivity
Increase ITOperationalEfficiency

Employee Productivity
End-users can easily findprinters based on their current location or capability required
Easily search AD for users, groups or distribution lists
Integrated with Exchange, Outlook, SharePoint & presence technologies
Find IT Resources Faster

Employee Productivity
AD enables “smart connections”Connect users & teams to share knowledge
Provide just-in-time communicationEnable end-user self-serviceLocate & connect with expertsShare contacts, groups & GAL across products
Single sign-on enhances productivity
& Active Directory
Enable Rich Collaboration

Employee Productivity
One credential – Multiple uses
Reduce time spent logging in
Reduce number of passwords
Reduce helpdesk costs
Provision or suspend users faster
Extend to the webWeb single sign-on products
Integrate customers & business partners
Exchange
SharePointPortal
File Share
Windows IntegratedApplications
Firewall& VPN
B2B/B2C/LOB Applications
Mainframe/UNIX
Single Sign-on to Integrated Applications

Additional Features of AD DS
Active Directory Recycle BinActive Directory module for Windows PowerShell and Windows PowerShell™ cmdlets Active Directory Administrative CenterActive Directory Best Practices AnalyzerActive Directory Web ServicesAuthentication mechanism assuranceOffline domain joinManaged Service AccountsActive Directory Management Pack

Additional Features of AD DS
AuditingFine-Grained Password PoliciesRead-Only Domain ControllersRestartable Active Directory Domain ServicesDatabase Mounting ToolUser Interface ImprovementsOwner Rights

Deliver Value to the Business
Automate the lockdown of Windows systemsEnforce the use of strong passwords & credentialsEliminate orphan accounts
Increase efficiency of managing Windows by up to 30%Central management of Windows servers & desktopsReduce the number of directories & passwordsAutomate provisioning & password resets
Find people, applications, and resources fasterEmpower employees with rich collaboration capabilitiesSingle Sign-on to integrated applications & resources
Increase ITOperationalEfficiency
StrengthenSecurity
Improve Employee
Productivity


© 2003-2004 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.This presentation is for informational purposes only. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, in this summary.