Western blotting and elisa
Transcript of Western blotting and elisa

Western Blotting & ELISA
By
Majid KB
Adnan Khan
Anissullah
Malik hamza
Irfan Khan
Fazal
Imran

Western blotting
• The Western blot is an analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a given sample of tissue homogenate or extract.
&
• Immunoblotting: because an antibody is used to specifically detect its antigen
• Western blot for Proteins was Developed by George Stark using antibodies to locate Proteins

Western blotting
• Western blotting is based on building antibody-protein complex through specific binding of antibodies to proteins immobilized on a membrane.
• Then detecting the bound antibody through several detection methods

The Western blotting workflow
• Sample preparation
• Gel electrophoresis
• Transfer
• Blocking & Antibody probing
• Detection
• Analysis

Sample preparation • Protein from all sources can be used for western blotting such as from
single cell, whole tissues, extracellular matrices, biological fluids.
• Protein can be extracted from the sample in three distinct steps:
• Cell lysis: Physical method (ultra sonication, homogenization etc.)
Chemical method (use of detergents)
Biological method (enzymatic digestion)
• Protein isolation from the rest of cellular components:
Centrifugation, DNase and other lysis buffer is used for the removal of cell organelles, nucleic acids, polysaccharides etc.
• Protein purification:

Gel Electrophoresis
• PAGE (Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is mainly used for the separation of protein particles.
• SDS is added to the gel and running buffer to denature the protein molecules which will ensure that your proteins are separated solely on the basis of size and not on three-dimensional structure.
• Molecular weight markers are used to define the size of proteins run in a gel. Markers are composed of different proteins of known size.
• As proteins are not directly visible in the gel, the gel must be stained. Proteins are usually stained with dyes such as Blue, Silver stain, or Deep Purple.

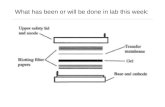
Protein Transfer
• Protein are transferred from the gel to a solid support membrane such as nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF).
• The proteins transferred from the gels are immobilized which makes it possible to detect the proteins on the membrane using specific antibodies.
• Electro-blotting is mainly used which uses electric field to pull proteins from the gel onto the PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane.
• The proteins move from within the gel onto the membrane while maintaining the organization they had within the gel


Blocking &Antibody Probing
• Western blotting involves the immobilization of biomolecules on a membrane and blocking the spaces not already occupied by proteins.
• As non-specific binding of antibodies to the membrane reduces the specificity and sensitivity of the assay.
• Two main classes of blocking agents (proteins and non-ionic detergents) are commonly used for western blotting.

Antibody Probing
• Western blotting protocols usually uses a non-labeled primary antibody directed against the target protein and labeled secondary antibody directed against the constant region of the primary antibody.
• The secondary antibody serves not only as a carrier of the label but is also a mechanism to amplify the emitted signals because secondary antibodies are most often polyclonal and can bind primary antibody at different epitopes simultaneously.

Antibody Probing
• Alkaline phosphatase (AP) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) are the two most commonly used enzymes for protein detection using chromogenic substrates.
• Other antibody probes used for protein detection are:
• Fluorophores
• Biotinylated secondary antibodies
• Radioisotopes.

Detection
• Different detection system are used in western blotting based on fluorescence, chromogenic or radio-isotopic detection.
• Enzymatic detection methods require the addition of a substrate that emits light when it reacts with an enzyme conjugated to a secondary antibody.
• Fluorescence-based detection requires the excitation of fluorophore using a light source of a specific wavelength causing light emission.

Chemiluminescence Fluorescence-based detection

Analysis
• Detection of signals, using either X-ray film, scanners or a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera-based imager, results in image containing visible protein bands.
• the presence and the amount of a protein of interest is estimated by visual analysis, and the size can be determined by comparison to a known molecular weight marker
Molecular weight
markers 1 2 3 4
Mr 102 000 Mr 76 000
Mr 52 000

Applications of Western Blotting
• Diagnosis of HIV by ELISA involves the western blotting technique.
• Western blotting technique is also used to detect some forms of Lyme Diseases.
• Western blotting technique is used in definitive test for BSE.
• Confirmatory test for Hepatitis-B involves western blotting technique.
• Western blotting test is used in the analysis of Biomarkers such as hormones, growth factors and cytokines.
• This technique is also employed in The Gene expression studies.

Limitations of Western Blotting
• Very delicate and time consuming process. A minute imbalance at any level of the procedure can skew the results of entire process.
• Cause erroneous in bands or no bands due to insufficient transfer.
• Well trained techniques are required for this technique.
• Primary antibody availability is crucial.
• It is just a Semi-Quantitative test. Only estimation and not a precise
• measurement of molecular weight of the protein is possible.

ELISA

Introduction• The enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) is an assay technique
designed for detecting and quantifying peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones.
• The ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine and plant pathology, as well as a quality-control check in various industries.
• The process of the ELISA result in a colored end product which correlates to the amount of analyte present in the original sample.

Introduction
• ELISAs are typically performed in 96 well (or 384 well) polystyrene plates.

Principle
• Principle of Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISAs) is based on the specific interaction between antibody and antigen.
• The ELISA can be used to detect antigens that are recognized by an antibody or it can be used to detect antibodies that are recognized by an antigen.

ELISA Procedure

Antibodies for ELISA• All ELISA formats rely on the specific
interaction between an antigen and a matching antibody.
• The antibodies used in an ELISA can be either:
• monoclonal (capable of specific binding to a single unique epitope)
• OR• polyclonal (capable of binding to
multiple epitopes).

Probes for ELISA
• Radioactive isotopes, enzymes and fluorescent dyes are different types of chemical tags that have been conjugated to secondary or primary antibodies(probes) to make probes detectable.
• Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is most commonly used for blotting, immunoassays and it converts its substrate ABTS (2,2'-Azinobis [3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid]-diammonium salt) in green end product.

Blocking & Washing Buffers
• A blocking buffer is a solution of irrelevant protein, with a small percentage of detergent. Blocking buffer block the places where target proteins have not been attached.
• Washing buffer are used to remove nonspecifically bound and unbound reagents.
• Washing is performed by buffers such as Tris-buffered saline (TBS) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) with detergent such as 0.05% Tween-20.

Types of ELISA
• INDIRECT ELISA
• DIRECT ELISA
• SANDWICH ELISA
• COMPETETIVE ELISA
NON -COMPETETIVE ELISA

Indirect ELISA
• Antigen is added to plate.
• Added Blocking buffer.
• Suitable primary antibody is added.
• Secondary antibody- HRPO is then added
which recognizes and binds to primary
antibody.
• TMB substrate is added, is converted to
detectable form.

Advantages of Indirect Detection
• Wide variety of labeled secondary antibodies are available commercially.
• Sensitivity is increased because each primary antibody contains several
epitopes that can be bound by the labeled secondary antibody, allowing
for signal amplification.
Disadvantages of Indirect Detection
• Cross-reactivity may occur with the secondary antibody, resulting in nonspecific signal.
• An extra incubation step is required in the procedure.

Direct ELISA
• Apply a sample of known antigen to a surface.
• Enzyme linked primary antibody is applied to the plate.
• Wash the plate. After this wash, only the antibody-antigen complexes remain attached.
• Apply a substrate which is converted by the enzyme to elicit a chromogenic signal.

Advantages of Direct Detection
• Quick methodology since only one antibody is used. • Cross-reactivity of secondary antibody is eliminated.
Disadvantages of Direct Detection
• Labeling of every primary antibody is time-consuming and expensive.
• Little signal amplification.

Sandwich ELISA• Plate is coated with suitable antibody.• Blocking buffer is added.• Sample is added to plate so antigen is bounded by capture antibody.• A suitable biotin labeled detection antibody is added to plate.• Enzyme HRPO is added and binds the biotin labeled detection antibody.• TMB substrate is added and converted by HRPO to colored product.

Competitive ELISA
• Solid phase coated with antibody
• Add unknown amount of unlabeled antigen and known amount of labeled antigen
• Free and labeled antigen are captured
• Color formation by oxidation of substrate into a colored compound

Advantages
• Suitable for complex samples, since the antigen does not require purification prior to measurement.
Disadvantages
• Each antigen may require a different method to couple it to the enzyme.

• Presence of antigen or the presence of antibody in a sample can be detected by ELISA.
• ELISA can be used to determination of serum antibody concentrations in a virus test (such as HIV test).
• ELISA can also be used in home pregnancy test.
• It is used in food industry to detect potential food allergens such as milk, peanuts, walnuts, almonds, and eggs.
• ELISA can also be used in toxicology as a rapid presumptive screen for certain classes of drugs.
Applications of ELISA

• A positive result correctly confirming the presence of an antibody does not necessarily mean the patient is sick. The body can continue to produce antibodies even though the person may have had the disease earlier and recovered.
• People may be poor producers of an antibody or may have some interfering substance in their blood. The amount of antibody, consequently, may be too low to measure accurately or may go undetected. This result is termed a false negative.
Limitations of ELISA

• Western blotting and Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are both based on the specific interaction between antigen and antibody.
• They are widely used as diagnostic tools in medicine and as quality control measures in various industries.
• They also used as analytical tools in biomedical research for the detection and quantification of specific antigens or antibodies in a given sample.
Conclusion