Western Blotting
-
Upload
thoppe-rajendran-sriram -
Category
Documents
-
view
37 -
download
4
Transcript of Western Blotting

WESTERN BLOTTINGSriram T R

WHO DISCOVERED THIS TECHNIQUE?
This Technique was discovered by Dr. Douglas Lake of the University of Arizona School of Medicine's Department of Microbiology and Immunology.

WHAT IS WESTERN BLOTTING?
A technique in which proteins are separated by gel electrophoresis and transferred to a membrane sheet. A specific protein is then identified through its reaction with a labeled antibody.

Why is it called W.B.?It was called after the technique “Southern blotting”(as a joke) which uses the same approach to detect DNA in cellular or tissue extracts. Southern blotting was first described by “Southern” in 1975.Western Blotting was first used by Towbin in 1979.Actually the technique is known as immunoblotting.

WHERE IS THIS TECHNIQUE USED?
The HIV Test known as "Western Blot" uses the same technique, where the goal is to detect the presence of antibody in a sample. Known HIV infected cells are opened and their proteins separated and blotted on a membrane. Then the serum to be tested is applied. Free antibody is washed away, and a secondary antibody is added that binds to human antibody and is linked to an enzyme. The stained bands then indicates the proteins to which the patient's serum contains antibody.

STEPS IN A WESTERN BLOT
The first step is gel electrophoresis.
(The proteins of the sample are separated according to size on a gel.)
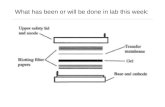
The second is Membrane Transfer. (The proteins in the gel are then transferred onto a membrane made of nitrocellulose by applying current.)
The third step is Blocking and Antibody Treatment. (Blocking is used to prevent non-specific protein interactions between the membrane and the antibody protein.)

FİRST STEP Seperation step. The proteins in the extract are seperated by
their size (molecular weight) on a gel using electrophoresis.
SDS-PAGE Gel: Sodium dodesyl sulphate-Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.







SECOND STEP Transfer step. The transfer of the proteins onto the
nitrosellulose membrane. The proteins seperated on the SDS-PAGE gel
are trasferred to the membrane by using electrophoresis. The localization of the proteins do not change.


Transfer of proteins to the membrane






THİRD STEP Blocking. Primary antibody incubation step. The primary antibodies which specifically
recognize the proteins of intrest are used. Immunohistochemistry = Tissue section or cell Western blotting = nitrosellulose membrane


INTERESTING FACT
When Blocking in Western Blotting the solution most used is Carnations Non Fat Dry Milk.
No one knows why Carnation’s works best !

FOURTH STEP
Secondary antibody incubation step. Use of secondary antibody which recognizes the
primary antibody used in the third step.


FİFTH STEP Visualization step Making the antigen-antibody complex visible
(staining). Autoradiography (radioactive P). Avidin-biotin coplex have chromogen. Fluoresence method.


Where WB is used?Cancer biology and pathologyMicrobiologyImmunologyProtein biochemistryTissue studiesTesting antibodies














![Western Blotting BCH 462[practical] Lab#6. Objective: -Western blotting of proteins from SDS-PAGE.](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/56649dc85503460f94abe06c/western-blotting-bch-462practical-lab6-objective-western-blotting-of.jpg)



