The Head and Neck. Upper Respiratory Tract Nasal Cavity Nostril Oral Cavity Larynx Pharynx.
The Head and Neck. Upper Respiratory Tract Nose Nostril Nasal Cavity Oral Cavity Pharynx pg 992.
-
Upload
darrell-harrison -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
5
Transcript of The Head and Neck. Upper Respiratory Tract Nose Nostril Nasal Cavity Oral Cavity Pharynx pg 992.

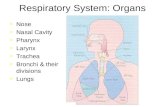
The Head and Neck

Upper Respiratory Tract
NoseNostrilNasal CavityOral CavityPharynx
pg 992

Nose
Nose is the only portion of the RT that is externally visible CT, bone, hyaline cartilage
Air enters here during breathingPasses through the external nares (nostrils)
pg 1023

VestibuleSuperior to nostrilsSkin lined with:
Sebaceous glandsGreasy secretionCollect dirtLubricate Kill bacteria
Sweat glandsAcidicSlows growth of bacteria
Hair folliclesTrap small particles of dirt
VibrissaeNose hairsFilter large particles (insects)
pg 1013

Nasal Cavity
Functions:Provides airway for respirationMoistens and warms airFilters inhaled airResonating chamber for speechHouses olfactory receptors
2 divisions:External noseInternal nasal cavity
pg 1023

Nasal Cavity
Divided into R and L by nasal septumContinuous with the nasopharynx
through the internal nares (choanae)
pg 992

Nasal Cavity
Boundries:Roof – ethmoid bone (cribiform plate)Floor – maxilla (palatine process)
palatine (horizontal plate)Lateral walls – nasal bones, superior and middle nasal
conchae of ethmoid bone, inferior nasal conchae, maxilla, palatine bone
Hard palatePalatine bones and maxillary bone
Soft palateSkeletal muscle posterior portionEnd in uvula

Lining of the Nasal Cavity
Respiratory Mucosa Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Goblet cells Lamina propria
Mucous and serous cells Venous plexus Function is to filter and warm inhaled air Highly innervated
Sneeze!
Olfactory Mucosa Roof of nasal cavity Houses smell receptors No goblet cells Cilia modified for olfaction
www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/.../Respiratory03.htm

Nasal Conchae
Project medially from each lateral wall3 structures:
Superior of ethmoid boneMiddle of ethmoid boneInferior
Functions:Create turbulence to increase:
Filters air Heats airMoistens airReclaim heat and moisture during exhalation
pg 1023

Paranasal Sinuses
Air filled cavities that surround the nasal cavity
Lined by mucosaPerform same function
as nasal cavity and lightens skull
Located in Frontal, Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Maxilla bonespg 1018

Pharynx
Connects the nasal cavity and mouth to larynx and esophagus
Extends from base of skull to level of C6
vertebraCommon passage for food and air Lined with skeletal muscleDivided into:
NasopharynxOropharynx Laryngopharynx
pg 992

Tonsils
Lymphoid organMALT
Swellings of the mucosa lining the pharynxForm ring around the entrance to the pharynx4 groups:
PalatineLingualPharyngealTubal
Remove pathogens pg 992

Nasopharynx
Location: Posterior to nasal cavity Inferior to sphenoid bone Superior to level of soft palate
ONLY an air passageway Closed off during swallowing by the soft palates’ uvula
Giggling! Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium Contain:
Pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids) Tubal tonsils
pg 992

Oropharynx
Location: Posterior to the oral cavity Extends inferiorly from level of the soft palate to level of
the esophagus Swallowed food and inhaled air pass through hereStratified squamous epitheliumContain:
Palatine tonsils Lingual tonsils
pg 992

Laryngopharynx
Location:Lies posterior to larynxContinuous with the esophagus and larynx
Common passageway for food and airFood – esophagusAir - larynx
Stratified squamous epithelium
pg 992

Larynx “Voice box”Extends from C4 to C6
Attachments:Hyoid bone superiorlyContinuous with trachea inferiorly
Functions:VocalizationProvides open airwaySwitches to route air and food into proper channels
Innervation: VagusSuperior part = stratified squamous epitheliumBelow vocal cords= ciliated pseudostratified columnar
pg 1001

Larynx All hyaline cartilage except epiglottis Composed of 9 cartilages connected by membranes and ligaments:
1 Thyroid 1 Cricoid 1 Epiglottis 2 Arytenoid 2 Corniculate 2 Cuneiform
pg 1000
pg 1001

Laryngeal Cartilages
Thyroid CartilageLargeShield shapedFormed by 2 platesContains laryngeal prominence
Adam’s Apple!!
pg 998

Laryngeal Cartilages
Cricoid Inferior to thyroid cartilageForms a complete ringDirectly superior to trachea
pg 998

Laryngeal Cartilages
EpiglottisComposed of elastic cartilageCovered by mucosaProjects upward from anterior wall of laryngeal inlet to
level of base of tongueClose off larynx during swallowing
pg 999

Vocal Cords
Located in the larynxMucosal folds formed by vocal ligaments
Composed of elastic fibers Run from arytenoid cartilages (posterior) to the thyroid cartilages
(anterior)
Exhaled air passes over them and causes vibration Force of air = volume Length & tension of folds = pitch
False vocal cords Vestibular folds (superior to true)
pg 1008

Thyroid Gland
Location: In anterior neck On trachea, inferior to larynx
2 lateral lobes Connected by the isthmus Butterfly shape
Largest endocrine gland in body Produces Thyroid hormone (TH)
Increases metabolic rate Calcitonin
Depresses excess levels of Ca+ in blood
pg 966

Thyroid Gland
Internally, composed of folliclesFollicular cells
TH
Parafollicular cellsCalcitonin
Blood supplySuperior thyroid arteries
Branches of external carotids
Inferior thyroid arteriesBranches of subclavians

Parathyroid Gland
Two pairsLocated on the deep surface of the lateral lobes
of the thyroid glandProduce parathyroid hormone
Increases blood calcium levels
pg 966

Hyoid BoneLocation:
Inferior to mandible In anterior neck
Associated with the skull Only bone in skeleton that does not articulate directly to
another bone!!!
Attaches via ligaments to temporal bone, larynxComposed of:
Body 2 pairs of horns
Functions: Moveable base for tongue Points of attachment for larynx and neck muscles
Sternohyoid, thyrohyoid, pg 803

Oral Cavity and Associated Organs
MouthTongueTeeth
External Salivary glands
pg 992

Mouth - Oral Cavity
Food enters alimentary canal through hereMucosa-lined
Thick stratified squamous epithelium, with keratinization in some areas
Boundaries: Lips anteriorly Cheeks laterally Palate superiorly Tongue inferiorly Oropharynx posteriorly
Mouth divided into 2 parts: Vestibule Oral cavity proper
pg 1041

Mouth
Lips (labia) and CheeksKeep food inside mouth during chewingComposed of skeletal muscle surrounded by skinLips formed by orbicularis oris muscleCheeks; Muscles of Mastication
Temporalis & Masseter (elevate mandible, close mouth) Buccinator (chewing) Digastric (lower mandible against resistance, opens mouth) Pterygoids (lateral movements)
Palate: forms the roof of the mouthSoft palate (posterior) rises to close off nasopharynx
during swallowing; made of skeletal muscleHard palate (anterior) provides surface for tongue to force
food against during chewing

Tongue
Functions Grips and moves food between teeth during chewing Mixes food with saliva = BOLUS Moves bolus down pharynx Speech production Houses taste buds (= gustation)
Creates floor of mouth Attachments: hyoid, mandible, styloid process, soft palate Made of Skeletal muscle with a CT septum
Intrinsic muscles (change shape; rolling) Extrinsic muscles (movement; protrude, retract) Motor = Hypoglossal (CN XII) Sensory = Mandibular (CN V3), Facial (CN VII), Glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
pg 1037

Moving Bolus
Swallowing voluntarily initiated (pharynx)Peristalsis = propulsion
InvoluntaryAlternate waves of contraction and relaxation of muscles
in organ walls (e.g. esophagus)Squeezes food from one organ to nextSome mixing
www.answers.com

Salivary Glands
Compound tubuloalveolar glands Intrinsic salivary glands
In mucosa of tongue, palate, lips and cheeks Keeps mouth moist at all times
Extrinsic salivary glands Lie external to mouth Connected by ducts Secrete only during eating or prior to (“mouth watering”) 3 paired glands:
ParotidSubmandibularsublingual
pg 863
pg 1043

Salivary Glands
Produce saliva Mixture of water, ions, mucus and enzymes Moistens mouth Dissolves food for taste Binds food into a bolus Enzymes digest starch Bicarbonate buffer neutralizes acids Kill microorganisms Contains proteins to promote growth of beneficial bacteria
pg 1046

Teeth – From Eruption to EdentateFunction:
Ingestion and mechanical breakdown of food
Have 2 sets of teeth (dentitions)Primary dentition / deciduous (milk) teethPermanent dentition
Incisors: rip, cutCanines: tear and piercePremolars: grindingMolars: grinding
pg 1056

Teeth
GomphosisSynarthrosisPeg in socket with ligament
The sockets (alveoli) are in gum-covered margins in mandible and maxilla
Periodontal ligaments (collagen fibers) anchor tooth in bony socketContinous with gingiva (gum)

Teeth Substances
Enamel Made of calcium salts Avascular, acellular Not renewed or replaced HARDEST substance in body!!!!
Dentin Underlines enamel Forms bulk of tooth Made of minerals and collagen Maintained during life Harder than bone
Cementum Calcified external surface Attaches tooth to periodontal ligament

Teeth
Regions: Crown
Covered with enamelProjecting into oral cavity
Neck (gumline) Root
Area beyond neck in alveolus
Pulp cavity Center of tooth Loose CT with vessels and nerves Supplies nutrients to hard tissues

Teeth
Root Canal Portion of the pulp cavity in the root
Apical foramen Opening into the root canal at the tip of each root
Blood supply Superior/Inferior Alveolar artery, branches of External Carotid artery
Innervation Maxilla = Superior Alveolar Nerves Mandible = Inferior Alveolar Nerves

Teeth at Birth
Number of erupted teeth = 0Jaws covered by gingiva (gums)
Lots of drooling!!!

First Teeth – 6 Months
Lower central incisors first to appear 8 Incisors = 6-10 months 4 Canines = 16-20 months 4 1st Molars = 12-16 months 4 2nd Molars = 20-24 months
20 deciduous teeth emerge by age 2 Dental formula
Describes the number and position of classes of teeth (half of the mouth)
2I, 1C, 2M 2I, 1C, 2M X 2 = 20
****No premolars!
Deciduous teeth dental formula:
pg 1056

Adolescence – AdultPermanent teeth enlarge and develop
Roots of deciduous teeth reabsorbed Teeth loosen and fall out Begin to erupt from 7-13 years of age Third molars (wisdom teeth) emerge from 17-25 years
May be absent!!
Adult dental formula:
2I, 1C, 2P, 3M
2I, 1C, 2P, 3MX 2 = 32
pg 1056

Tooth Troubles
Cavities (caries)Demineralization of enamel by bacteria In severe cases, erodes the dentin of toothMost severe cases erosion penetrates pulp cavity

Tooth Troubles
Gingivitis Inflammation of the gingiva caused by plaque
accumulationLeads to…….
Periodontitis Infection of periodontal ligament leading to its
destruction along with the bone around the teethLeads to toothlessness!

Triangles of the Neck
Neck subdivided into two trianglesSeparated by the sternocleidomastoid
muscleAnterior trianglePosterior triangle

Triangles of the Neck: Posterior
Boundries:Anterior - sternocleidomastoidPosterior - trapezius Inferior – clavicle
Contents:Nerves: accessory nerve, phrenic nerve, brachial
plexusArtery: SubclavianVein: External jugular
pg 948

Triangles of the Neck: Anterior
Boundries: Anterior - midline Posterior - sternocleidomastoid Superior – inferior margin of the mandible
Contents: Glands: Submandibular Muscles: Suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscles Artery: Common carotid Vein: Internal jugular, External jugular Nerve: Accessory
pg 954










![Consonants: articulation and transcription - Arbeitsbereicheastechow/Lehre/WS04.5/IntroLing/ho_2005...pharynx [G. Rachenraum, Pharynx]: the tubular cavity which constitutes the throat](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ad1fcd67f8b9a0f198be4c3/consonants-articulation-and-transcription-astechowlehrews045introlingho2005pharynx.jpg)