Staphylococci The Staphylococci Morphology & Identification Gram positive Facultative anaerobes ...
-
Upload
dustin-armstrong -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
2
Transcript of Staphylococci The Staphylococci Morphology & Identification Gram positive Facultative anaerobes ...


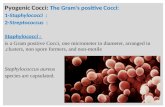
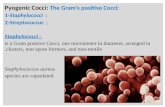
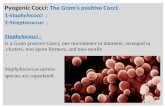
The StaphylococciStaphylococci

Morphology & Identification
Gram positiveGram positive Facultative anaerobesFacultative anaerobes Grape like-clustersGrape like-clusters Catalase positiveCatalase positive Major components of Major components of
normal flora normal flora skinskin nosenose
Catalase test(过氧化氢酶)
(-) (+)

Staphylococcus aureus

Antigenic Structure

Pathogenesis
• Catalase
• Coagulase
• Hyaluronidase and Lipase ipase
• Hemolysin or sphingomyelinase Csphingomyelinase C
• Leukocidin
• Exfoliative Toxin
• Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin (superantigen)
• Enterotoxins
Protein AProtein Aimmunoglobulinimmunoglobulin
Fc receptorFc receptor
BACTERIUMBACTERIUM
PHAGOCYTEPHAGOCYTE

Pathogenesis of staphylococcal infections
Stye:Stye:麦粒肿麦粒肿
Carbuncle:Carbuncle:痈痈
ImpetigoImpetigo ::脓疱疮脓疱疮

Suppurative• Skin Skin Furuncle; Protein A, Leukocidin, Hemolysin Furuncle; Protein A, Leukocidin, Hemolysin Stye; lipase Stye; lipase Impetigo; contagious Impetigo; contagious Epidermal necrolysis Epidermal necrolysis Exfoliative Dermatitis (6,7,8); Exfoliative toxin Exfoliative Dermatitis (6,7,8); Exfoliative toxin Mastitis Mastitis Abscess (deep tissue); granulation; coagulase, hyaluronidase (burn, Abscess (deep tissue); granulation; coagulase, hyaluronidase (burn,
wound) wound)
• Systemic Systemic
Bactermia (from abscess, wound, burn) Bactermia (from abscess, wound, burn) , , Osteomyelitis (tibia) Osteomyelitis (tibia) ,,Pneumonia Pneumonia

• Food poisoningFood poisoning
• Toxic shock syndromeToxic shock syndrome
• babiesbabies– scalded skin syndromescalded skin syndrome
* ExfoliatinExfoliatin
• feverfever• scarlatiniformscarlatiniform rash rash• desquamationdesquamation• vomitingvomiting• diarrheadiarrhea• myalgiasmyalgias
• not a human infectionnot a human infection
• food contaminated from humans food contaminated from humans
– growth growth
– enterotoxinenterotoxin
• onset and recovery both occur within few hoursonset and recovery both occur within few hours
• VomitingVomiting/ / nauseanausea/ / diarrheadiarrhea/ / abdominal abdominal //painpain

Infections associated with indwelling devicesInfections associated with indwelling devices

Laboratory
• A. Direct examination; Gram Stain
• B. Primary media; BAP
• C. Differential Tests.
1. Mannitol Salts
2. Coagulase
3. DNase
• D. Phage typing
• E. Antibiotic Sensitivity (plasmid, B lactamase) : penicillin /methicillin/vancomycin
API STAPH Kit

GRAM POSITIVE COCCI
S. aureus hemolyticmannitol yellow
+ -Staphylococcus (Clusters) Streptococcus (pairs & chains)
Catalase
• BETA: Bacitracin S.pyogenes (group A)
CAMP/Hippurate S. agalactiae (group B)
HemolysisCoagulase
S. epidermidisnonhemolytic (usually)mannitol white
(2) ALPHA: Optochin/Bile Solubility S. pneumoniae
• GAMMA: Bile Esculin 6.5% NaCl Group D* Enterococcus
Bile Esculin 6.5% NaCl Group D* Non-Enterococcus
(*can also be beta or alpha hemolytic)
Note: Strep. viridansare alpha hemolytic andnegat ive for all the testsbelow
+
++
++
+
+
-
-
Summary Figure (Identification Scheme)

Staphylococcus epidermidisStaphylococcus epidermidis• major component skin floramajor component skin flora• opportunistic infections opportunistic infections
– less common than less common than S.aureusS.aureus• nosocomial infectionsnosocomial infections
– heart valvesheart valves• IdentificationIdentification
– Non-hemolytic Non-hemolytic ((sheep blood agarsheep blood agar))– Does not ferment mannitolDoes not ferment mannitol– Non-pigmented Non-pigmented – Coagulase-negativeCoagulase-negative
Staphylococcus saprophyticusStaphylococcus saprophyticus
• urinary tract infectionsurinary tract infections • coagulase-negative coagulase-negative
– not differentiated from not differentiated from S. epidermidisS. epidermidis

The Streptococcus


Streptococcus


Morphology & Identification
• facultative anaerobefacultative anaerobe• Gram-positiveGram-positive• ChainsChains or pairsor pairs• CatalaseCatalase negativenegative (staphylococci are catalase positive)(staphylococci are catalase positive)

Cell surface structure of S pyogenes and extracellular substances
•Lancefield groupsLancefield groups
*one or more species per groupone or more species per group
*surface antigens: M, T, Rsurface antigens: M, T, R
groupable streptococcistreptococci •A, B and DA, B and D–most importantmost important
•C, G, F C, G, F –RareRare
Non-groupableNon-groupable
•S. pneumoniaeS. pneumoniae
–pneumonia pneumonia
•viridans streptococciviridans streptococci
–e.g.e.g. S. mutans S. mutans
*dental dental cariescaries

Lipoteichoic Acid and F-proteinLipoteichoic Acid and F-protein
fibronectinfibronectin
lipoteichoic acidlipoteichoic acidF-proteinF-protein
epithelial cellsepithelial cells

M proteinM protein
• major target major target – natural immunitynatural immunity
• strain variationstrain variation– antigenicityantigenicity
• re-infectionre-infection– occurs with different strainoccurs with different strain

M protein M protein
M proteinM protein
fibrinogenfibrinogen
rrr
peptidoglycanpeptidoglycan
rrr
IgGIgG
Complement Complement IMMUNEIMMUNE
NON-IMMUNENON-IMMUNE

Toxins & Enzymes

Hemolysis
alpha
beta
gamma

Classofication of Streptococci of Particular Medical Interest

Pathogenesis of S pyogenes infections.

S. . pyogenes (pyogenes (Group A) Group A) -suppurative-suppurative
• affect all ages peak incidence at affect all ages peak incidence at 5-15 years of age 5-15 years of age
• non-invasive non-invasive – pharyngitis pharyngitis
– skin infection, impetigoskin infection, impetigo
• invasive bacteremia invasive bacteremia – toxic shock-like syndrome toxic shock-like syndrome – "flesh eating" bacteria"flesh eating" bacteria– pyrogenic toxinpyrogenic toxin

• Scarlet fever Scarlet fever rash rash erythrogenic toxinerythrogenic toxin • rheumatic fever rheumatic fever inflammatory diseaseinflammatory disease life threateninglife threatening chronic sequalaechronic sequalae fever fever HeartHeart JointsJoints rheumatic NOT rheumatoid arthritisrheumatic NOT rheumatoid arthritis• Acute glomerulonephritis Acute glomerulonephritis
immune complex disease of kidneyimmune complex disease of kidney
Rheumatic fever -etiologyRheumatic fever -etiology M protein M protein
– cross-reacts heart myosin cross-reacts heart myosin
– autoimmunityautoimmunity cell wall antigens cell wall antigens
– poorly digested poorly digested in vivoin vivo
– persist indefinitelypersist indefinitely
Post-infectious diagnosis (serology)Post-infectious diagnosis (serology)
• antibodies to streptolysin Oantibodies to streptolysin O
• important if delayed clinical sequelae important if delayed clinical sequelae occuroccur
• superantigensuperantigen• T cell mitogen T cell mitogen • activates immune activates immune
systemsystem

Group B streptococcus - Group B streptococcus - identificationidentification
• neonatal meningitisneonatal meningitis• septicemiasepticemia• transmission transmission
– vaginal floravaginal flora
hemolysishemolysis• hippurate hydrolysishippurate hydrolysis• CAMP reactionCAMP reaction
– increases increases hemolysis of hemolysis of S. aureusS. aureus

Group D streptococcusGroup D streptococcus• Growth on bile esculin agarGrowth on bile esculin agar
– black precipitate black precipitate
• 6.5% saline6.5% saline• growgrow
– enterococcienterococci• no growth no growth
– non-enterococcinon-enterococci

EnterococciEnterococci
• distantly related to other streptococcidistantly related to other streptococci• genus genus EnterococcusEnterococcus • gut floragut flora
– urinary tract infection urinary tract infection • fecal contaminationfecal contamination
– opportunistic infectionsopportunistic infections• particularly endocarditisparticularly endocarditis
• most common most common E. (S.) faecalisE. (S.) faecalis• resistant to many antibiotics resistant to many antibiotics
– including vancomycinincluding vancomycin• terminal D-ala replaced by D-lactate terminal D-ala replaced by D-lactate

Viridans streptococciViridans streptococci• diverse species diverse species • oral oral • dental cariesdental caries hemolytic and negative for other tests hemolytic and negative for other tests • non-groupable.non-groupable.• includes includes S. mutansS. mutans
– endocarditis endocarditis
– tooth extractiontooth extraction

Streptococcus pneumoniae
S. pneumoniae - diplococci
• capsule: capsule: • pneumolysinpneumolysin: : • Surface protein adhesinand Surface protein adhesinand
secretory IgA protease. secretory IgA protease. • Teichoic acid and the Teichoic acid and the
Peptidoglycan fragment, Peptidoglycan fragment, phosphorylchorine .phosphorylchorine .
• leading cause pneumonialeading cause pneumonia– particularly young and oldparticularly young and old– after damage to upper after damage to upper
respiratory tractrespiratory tract*e.g. following viral infection*e.g. following viral infection
• bacteremiabacteremia• meningitismeningitis• middle ear infections (otitis media)middle ear infections (otitis media)

GRAM POSITIVE COCCI
S. aureus hemolyticmannitol yellow
+ -Staphylococcus (Clusters) Streptococcus (pairs & chains)
Catalase
• BETA: Bacitracin S.pyogenes (group A)
CAMP/Hippurate S. agalactiae (group B)
HemolysisCoagulase
S. epidermidisnonhemolytic (usually)mannitol white
(2) ALPHA: Optochin/Bile Solubility S. pneumoniae
• GAMMA: Bile Esculin 6.5% NaCl Group D* Enterococcus
Bile Esculin 6.5% NaCl Group D* Non-Enterococcus
(*can also be beta or alpha hemolytic)
Note: Strep. viridansare alpha hemolytic andnegat ive for all the testsbelow
+
++
++
+
+
-
-
Summary Figure (Identification Scheme)

Streptex antiserum
Latex agglutination - streptococci
Quellung reactionQuellung reaction • using antisera using antisera
• capsule "fixed" capsule "fixed"
• visible microscopicallyvisible microscopically
Not optochin sensitiveoptochin sensitive
Bile solubility test

Prevention and TreatmentPrevention and Treatment
• Immunity ; 14 capsule types mixedImmunity ; 14 capsule types mixed vaccinevaccine
• MMost strains susceptible to ost strains susceptible to penicillin penicillin , but , but resistance is resistance is commoncommon

• Gram negative Gram negative • diplococci (pairs of diplococci (pairs of
cocci)cocci)• oxidase positiveoxidase positive
• Culture: 5-10% COCulture: 5-10% CO22
• Thayer Martin. Thayer Martin. – selective selective – chocolate agarchocolate agar
* heated bloodheated blood
NeisseriaNeisseria

Capsule
LPS
N. meningitidis
Virulence FactorsSimilar, but –Differencesin utilization
HemolysinIgA protease
PILIOpacity (OPA) proteinsOuter Membrane Proteins
N. gonorrhoeae
LPS
PILIOpacity (OPA) proteinsOuter Membrane Proteins
IgA protease
NO capsuleNO hemolysinX

Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Using the Gram stain in patient specimens, the organisms are most often observed in polymorphonuclear leukocytes
Gram stain of pure culture Urethral exudate
• After 2-14 daysAfter 2-14 days •FFound only in manound only in man• GGonorrheaonorrhea: : second most common venereal second most common venereal diseasedisease

Pili = key in anchorage of organisms to mucosal epithelium.Nonpiliated gonococci are avirulent
Porin proteins (Por) = prevent phagolysosome fusion & allow intracellular survival [ also called protein I]
Opacity proteins (Opa) = binding of organisms to epithelium[also called protein II]
Reduction-modifiable proteins (Rmp) = protection against bactericidal antibodies [ also called protein III]
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
OUTER MEMBRANE PROTEINS

Bartholin’s DuctUrethritis

Disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI). Fever, polyarthritis (or monoarticular septic arthritis), and/or dermatitis(pustules on a hemorrhagic base).
Purulent conjunctivitis/Ophthalmia neonatorum Infection in newborns during vaginal delivery

SmearSmear• polymorphonuclear cellpolymorphonuclear cell• Gram negative cocciGram negative cocci many in cellsmany in cells• CultureCulture
• lactamase-resistant cephalosporinlactamase-resistant cephalosporin– e.g. ceftriaxonee.g. ceftriaxone
• resistant strains resistant strains – common common – produce produce lactamases lactamases– destroy penicillindestroy penicillin
Antibiotic therapyAntibiotic therapy

N. meningitidisN. meningitidis (the "meningococcus")

NeisseriaNeisseria meningitidismeningitidis
• resides resides in man onlyin man only • usually sporadic cases usually sporadic cases
– mostly young mostly young childrenchildren
• outbreaks outbreaks – adults adults – crowded conditions crowded conditions
* e.g. army e.g. army barracksbarracks
• 1-4 1-4 daysdays• SSecond most common econd most common
meningitis meningitis – pneumococcus, pneumococcus,
most common most common • FFatal if untreated atal if untreated • RResponds well to esponds well to
antibiotic therapyantibiotic therapy– penicillin penicillin
Upper respiratory Upper respiratory tracttract infection infection
– adhesion pili adhesion pili
BloodstreamBloodstream BrainBrain
Meningococcal Meningococcal meninigitismeninigitis

DiagnosisDiagnosis
• spinal fluid spinal fluid – Gram negative Gram negative
diplococci diplococci within within
polymorphonuclear cellspolymorphonuclear cells– meningococcal meningococcal
antigens antigens
• CultureCulture– Thayer Martin agarThayer Martin agar
• capsulecapsule– inhibit phagocytosisinhibit phagocytosis
• anti-capsular antibodiesanti-capsular antibodies
– stop infectionstop infection
• antigenic variationantigenic variation– serogroupsserogroups
• vaccine vaccine – multiple serogroups multiple serogroups
PreventionPrevention