Pyogenic Cocci : The Gram’s positive Cocci : 1- Staphylococci : 2- Streptococcus :
description
Transcript of Pyogenic Cocci : The Gram’s positive Cocci : 1- Staphylococci : 2- Streptococcus :

n
Pyogenic Cocci: The Gram’s positive Cocci:1-Staphylococci :2-Streptococcus :
Staphylococci : is a Gram positive Cocci, one micrometer in diameter, arranged in clusters, non spore formers, and non-motile.
Staphylococcus aureus species are capsulated.

n
Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic bacteria .All species grow best on nutrient agar and blood agar.Mannitol salt agar is a selective media for Staphylococcus species.It can grow at a temperature range of 15-45 C, and NaCl concentration as high as 15%.

n
Clinical significance of Staphylococcus aureus :1-Localized skin infections.
2-Acute endocarditis.
3-Pneumonia.
4-Septicemia. Staphylococcus impetigo
5-Food poisoning:(Food born intoxication).

n
Streptococcus: Gram positive cocci ,occur in pairs and in short chains.None-motile, none- spore formers, some strains are capsulated. Strict anaerobes and facultative anaerobes.
Gram positive Streptococci: in chains.

Classification of Streptococcus species:Streptococcus species are classified according to hemolytic
activity .

n
Beta-Hemolytic: Alpha Hemolytic
Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus pneumoniae

n
Clinical significance of Streptococcus pyogenes :1-Acute pharyngitis and tonsilitis.
2-Impetigo and deep skin infection .
3 -Acute Rheumatic fever. Due to the bacteria M protein .
Streptococcus tonsilitis
4-Acute nephritis. Due to antibodies interaction with glomerulus .

n
The Gram negative Diplococci:Neissereiae meningitidisNeissereiae gonorrhoeae
Gram negative cocci , Kidney-shaped, occur in pairs, in clinical specimens: present inside the polymorphonuclear cells.

n
They grow best on Thayer-Martin Medium; Chocolate agar
supplemented by vancomycin and nystatin .
Both factor X and V (hemoglobin, NAD) are required for
Neissereiae species cultivation.
A 5-10 % CO2 is required for primary cultivation.
Neissereiae growth
On Chocolate agar.

n
Clinical significance:Neissereiae meningitidis
1-Meningitis and Meningococcemia.2-Septicemia.
Neissereiae gonorrhoeae1-Urinary tract infection: (Most common):
A-Gonococcal Urethritis .
B-Pelvic inflammatory disease .

nN
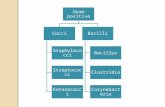
Gram positive Bacilli
Non-BranchingBranching
ActinomycesSpore formers Non-spore formers
Aerobic Anaerobic
Bacillus anthracis
Bacillus cereus
Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium tetani
Acid-fast Non-acid fast
Mycobacterium CorynebacteriumListeria
Lactobacillus

The Gram’s positive spore former aerobic bacilli:
The genus Bacillus:Gram-positive spore-forming, non-motile, bacilli arranged in chains.
Bacillus anthracis species are capsulated in tissue and spore-formerin the culture.
Gram’s stain smear Malachite green spore stain .

n
Bacillus anthracis grows on nutrient agar or blood agar in presence of oxygen (obligate aerobic bacteria) .
On the blood agar, Bacillus anthracis colonies are non-hemolytic, with irregular border.
Growth of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus anthracis.

n
Clinical significance:Bacillus anthracis :
1-Cutaneous anthrax : Spore germination in skin ,
a papule development , converted into malignant
pustule.2-Pulmonary anthrax :( Woolsorter’s disease:)
- hemorrhagic lymphadenitis .
Bacillus cereus :Enterotoxins cause food poisoning.

The Gram positive spore-forming anaerobic bacilli:
The genus Clostridium:Gram-positive spore-forming, anaerobic large bacilli .
Clostridium tetani species forms terminal spores, while sub-
terminal or central oval spores are produced by Clostridium
perfringens.
Microscopic Drum-stick Appearance of
Clostridium tetani

n
All Clostridium species are obligatory anaerobic.On blood agar, Clostridium perfringens species produce zone of complete hemolysis surrounded by wider zone of incomplete hemolysis.Clostridium tetani colonies show beta hemolytic activity.

Clinical significance: Clostridium perfringens :
1-Myonecrosis (gas gangrene) : Caused by alpha toxin which damages host and blood cells.
2-Food poisoning: caused by Enterotoxin.

N
Clostridium botulinum : -Botulism :
Food poisoning, lead to progressive striated muscle paralysis.
Clostridium tetani :-Tetanus :General muscle paralysis .
Clostridium difficile :-Diarrhea, and pseudomembranous colitis due to long-term
antibiotic therapy .

The Non-spore former acid-fast Bacilli:
The genus Mycobacterium:The Mycobacteria are acid-fast, non-motile, non-spore forming rods. The microbe can not be stained well by Gram’s stain due to the presence of waxy capsule.

n
Mycobacterium is best demonstrated by Ziehl -Neelsen staining technique; the microbes appear as thin pink rods arranged singly or in groups. Once stained, they resist decolorization with 2% H2SO4 and 95% alcohol (Acid-fast, Alcohol fast).

n
Mycobacterium is strict aerobic, grows very slowly (2-4 weeks) on
Lowenstein-Jensen medium; produce dry creamy colored colonies.
Culture characteristics of Tubercle bacilli on Lowenstein Jensen medium .

The Non-spore Non-acid fast bacilli: The genus Corynebacterium:
Gram positive pleomorphic long rods with swollen one end (club-shaped).They lie in small groups joined at angles to each other giving characteristic Chinese-letter arrangement
Corynebacterium bacilli arranged as Chinese-letter.Note the metachromatic Granules.

n
Aerobe or facultative anaerobe; grows rapidly on Loeffler’s
serum at 37 C giving opaque white colonies within 4-12 hours.
On blood tellurite; the organism reduces
tellurite and produce grey-black colonies

a Clinical significance of Corynebacterium:1-Upper respiratory tract: Diphtheria.
Pseudo-membrane appearance. Marked lymph node enlargement.
2-Skin infection. Diphtheria skin lesion.

n
n
Gram’s negative Bacilli
Enterobacteriaceae
Lactose Fermenter
Non-Lactose
fermenter
E. coliKlebsiella
SalmonellaShigella
Vibrio’s Curved-S,U Shaped
bacilli
Spirochetes
Coccobacilli
Vibrio cholera
CampylobacterHelicobacter
Treponema
Brucella

General properties of Enterobacteriaceae :1 -Short rods, and non-spore formers.
2 -All are motile (by peritichous flagellae) except
Klebsiella and Shigella
3 -Aerobes or facultative anaerobes.
4 -Oxidase negative and catalase positive .
5 -All ferment glucose with acid or acid and gas production and reduce nitrate to nitrite.

n
Based on lactose fermentation, Enterobacteriaceae species are divided into:
1-Lactose fermenters as: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella 2-Non-lactose fermenters as: Salmonella, Shigella .

Clinical significance of some Enterobacteriaceae species :1 -E.coli :
Urinary tract infection. Gastroenteritis.
2-Klebsiella : Lower respiratory tract infection.
Urinary tract infection.
3-Salmonella: Typhoid fever, and food poisoning.
4-Shigella: Dysentery.

The Vibrios :-Vibrios are gram-negative aerobic comma shaped curved
bacilli, motile with a single polar flagellum.Vibrio cholerae serogroups O1 and O139 are responsible of epidemic cholera .
They grow on different media at high pH (8.5-9.5) as alkaline peptone water and TCBS.

Curved S, U-shaped bacilli:The Genus Helicobacter and Campylobacter :
-Gram’s negative pleomorphic S or U-shaped Bacilli.-Fastidious microbe grow best on Enriched media
supplemented by Bovine serum albumin and antibiotics -Microaerophilic bacterium (5% O2, 10% CO2)
Clinical significance:1-Helicobacter:
peptic ulcer disease.2-Campylobacter: Gastroenteritis .

Coccobacilli :The Genus Brucella:
Gram-negative non-motile, non-capsulated short coccobacilli .
Aerobic bacteria; grow best on liver extract agar at 5-10% CO2 .

n
Clinical significance: Brucella melitensis : Malta fever.
It is mainly a pathogen of goats and sheep .
It the strain found in the Mediterranean area and Arabian
Gulf.
Brucella abortus: Malta fever.
infects cattle mainly but can infect other animals.

Spirochetes:Treponema pallidum :
-It has a characteristic helical shape, tightly coiled bacilli like a telephone cord.
-All are Gram’s negative spiral bacilli with endoflagella-Because it can not be stained by Gram’s stain ;
wet-mount Preparation should be examined by Darkfield - microscopy .
Clinical significance:-Primary, secondary, and
late stage Syphilis .