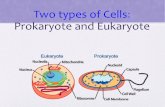
Prokaryote Classification
-
Upload
mrstabor -
Category
Technology
-
view
7.398 -
download
2
Transcript of Prokaryote Classification

Prokaryote Classification

Domains Bacteria and Archaea• Classified by Shape
– Cocci
– Bacilli
– Spirilla

Domains Bacteria and Archaea• Classified by Shape
– Vibrio
– Spirochete

Domains Bacteria and Archaea• Classified by Configuration
– Pairs
– Chains
– Clusters


Domains Bacteria and Archaea
• Gram Stain– Developed by
Hans Christian Gram in 1884
– Still used in laboratories as a “first step” in diagnostics

Domains Bacteria and Archaea
• Gram negative– Pink– Tend to be more
pathogenic (disease causing)
– Have a thinner cell wall
• Gram positive– Purple– Have a thicker cell wall

Reproduction of Prokaryotes
• Binary fission1. The DNA replicates and
attaches to cell membrane.2. The cell grows.3. The DNA copies separate,
cell grows larger.4. The cell splits into two
daughter cells.


Reproduction of Prokaryotes
• Endospores– A thick, protective
membrane formed when conditions are bad.
– Can survive boiling, freezing, drought, etc
– Will grow when conditions are favorable.

Prokaryotes in the Ecosystem
• Nitrogen Fixation• Recycling Nutrients• Cleaning up Pollution• Production of Medicines• Production of Food Products• Digestion of Food for Animals• Pathogenic Bacteria

Nitrogen Fixation
• All eukaryotes need nitrogen for basic cellular function.
• Nitrogen is a major component of proteins and DNA.
• Bacteria take nitrogen out of the air and convert it to a form plants can use.


Recycling Nutrients
• Decay is caused by bacteria and fungi.
• Organic matter is recycled into original elements by bacteria.
• Composted material important garden component

Cleaning up Pollution
• BIOREMEDIATION uses living things to change polluting chemicals into less harmful chemicals.– Mine tailings
– Oil spills
– Agricultural Waste
– Municipal Waste

Production of Medicines
• Genetically modified bacteria produce:– Antibiotics– Insulin– Anti-cancer drugs

Dangerous Bacteria
• PATHOGENIC bacteria cause diseases.
• These bacteria attack:– Animals
– Plants
– Protists
– Fungi
– Other bacteria!