Prokaryote Cells And Eukaryote Cells
description
Transcript of Prokaryote Cells And Eukaryote Cells

Prokaryote Cells And
Eukaryote Cells

Essential Questions
• What are the major differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
• What are the differences between Prokaryotes/Eukaryotes and viruses?
• What is the hierarchy of an organism’s level of organization?
• What are the relative sizes of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and viruses?

First, what is a cell?!• Cells are smallest unit of life.• Discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 using
microscope.• Every thing we know about cells we call “cell theory”.
– Developed in 1838 by observations of Schleiden and Schwann

Cell Theory says that….
1. All living things are made of one or more cells.
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. In other words, cells are like the building blocks of all living things.
3. New cells are only made from existing cells.

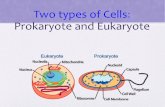
There are two types of cells:
Prokaryotic Cellsand
Eukaryotic Cells

These are two distinct types of cells with STRUCTURAL differences.
Prokaryotes
Bacteria
Eukaryotes
Animal Plant


Prokaryotes: (pro-care-ee-ohts)
• Smallest, most simplest cell.• Single celled organism.• Does not have a nucleus.• Singular circular chromosome with DNA,
located near center of cell within cytoplasm.• Has ribosomes but no other organelles.• Has cell wall – structure around cell membrane,
provides structure and support.

• Some have capsule that surrounds cell wall.• Flagella – tail like structure; enables
movement.• Pilus (Pili) – hair like structures around
bacteria that help with attachment to host or in reproduction.
• All bacteria are prokaryotes– Bacteria have 3 different shapes.
– Bacillus –rod shaped– Coccus – round shaped– Spirilum – spiral shaped

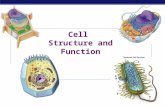
Eukaryote Cell
Aore complex cell with a nucleus and many
organelles.

Traits of Eukaryotes: (you-care-ee-othts)
• More complex• Has a nucleus where genetic material of
cell is stored. • Have many organelles that work
together doing specific jobs to help cell function.

More traits of Eukaryotes: (you-care-ee-othts)
• Can be unicellular or multi-cellular organisms. • Some have cilia -hair-like structures that protrude
from their cells.– helps some cells move through their environment.– On other cells helps move substances across
their surfaces.• ex. cells of human respiratory.
• All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic cells.


Complex Eukaryotes• Complex organisms have a body system that is arranged into a
certain order called a hierarchy.

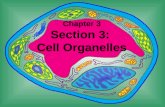
Organelles
• Small structures inside cell that perform specific function.
• Examples include mitochondria, nucleus, and Golgi body

Cell
• Basic unit of structure & function in life.
• Building blocks of all living things.

Tissue
A group of the same kind of cells working
together for a specific purpose.

Organs
A part of an organism made up of tissues that do a specific job.

Organ Systems
A group of organs that work together for a specific job.

Organism
Any living thing.

Viruses• Nonliving.• Smaller than prokaryotes or eukaryotes.• Can not be seen by compound microscopes.• Not made of cells, has no organelles, and no nucleus.• Can not reproduce on own.