Cell Structure Part 2: Eukaryotic Cells (Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells)
Plant Cells
description
Transcript of Plant Cells

Plant Cells

FLASHBACKAre plants eukaryotic or prokaryotic?What does eukaryotic mean?

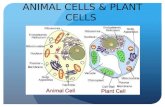
Parts of a Plant Cellcell wallcell membraneGolgi apparatuschloroplast
vacuole membrane
raphide crystal
druse crystal
mitochondrion
cytoplasm
smooth ER
ribosome
Golgi vesicles
nucleusrough ER
nucleolus
amyloplastLarge central vacuole

Cell WallSurrounds the plasma membrane3 layers
Middle LamellaPrimary WallSecondary Wall

Middle Lamella1st layer formedOuter wall of the cellShared by adjacent cells and cements them together

Primary Cell WallINDSIDE middle lamellaRigid skeleton of cellulose microfibrils in a gel-like matrix of pectic and cellulose compounds. Contains everything that is located between plasma membrane and the cuticle

Primary Cell Wall Functions
Structural & mechanical supportMaintain cell shapeResist turgor pressureControl rate and direction of growthCarbohydrate storageCell-cell interactions

Secondary WallFormed after cell enlargement is completed.Extremely rigidContains lignin- brown phenolic polymerPresent in trees and shrubs

PlasmodesmataSmall passages that penetrate all layers of the cell wallPathways for transporting cytoplasmic molecules

Plasma (cell) MembranePhospholipid bilayer
Sandwich model- phospholipid layers sandwiched between protein layers
Embedded glycoproteinsWater permeableNot permeable to molecules and ions by simple diffusionGatekeeper for the cell.

Golgi ApparatusStack of flattened membrane-bound sacsStorage, modification, and secretion of proteins and lipids Lipids and proteins can be used within the cell or destined to leave the cell

Calcium Oxalate Crystals
Located in the central vacuolePotentially toxicRaphide crystals-pointy and needle likeDruse crystals-faceted

MitochondrionMembrane-bound organelle“power house” of the cellRespiration takes place here.

Golgi vesicle Membrane boundBuds from Golgi apparatusContain proteinsFuse with membrane and discharge contents in a process called exocytosis

RibosomeSite of protein synthesisComposed of small sub unit, large sub unit, and central groove.

ERSmooth ER
Membrane bound system of folded sacsProvides a membrane surface where a variety of complex carbohydrates and lipids, including phospholipids are synthesizedDetoxifies toxic substances
Rough ERAttached ribosomes

Nucleolus Where rna is synthesized

NucleusMembrane boundWhere chromatin is stored

Large Central VacuoleLarge membrane bound sacStores water, salts, pigments, and potentially toxic molecules.Helps maintain rigidity

OthersAmyloplast- a membrane-bound organelle made of layers of starchLysosome- membrane-bound organelle containing hydrolytic (digestive) enzymesPeroxisome- a membrane-bound organelle that contains specific enzymes imported from cytosol (e.g. catalase)

Chloroplast IntroMembrane bound organelleSite of photosynthesis

GROUPS OF FOURCELL CITY
Take 15

Endosymbiont TheoryChloroplasts and mitochondria house their own DNA.It is possible to track lineage through chloroplasts and mitochondria.Chloroplasts and mitochondria have their own phospholipid membrane.

Endosymbiont TheoryScientists believe that plant and animal cells acquired chloroplasts and mitochondria through the process of symbiogenesis
Symbiogenesis is acquiring cells or dna from other organisms.In other words: