Cell Structure Part 2: Eukaryotic Cells (Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells)
description
Transcript of Cell Structure Part 2: Eukaryotic Cells (Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells)

Cell Structure Part 2: Eukaryotic Cells (Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells)
Honors Biology

Eukaryotic Cells
• Divided into compartments• Unicellular or Multicellular • Organelles → structures that have a specific
function in the cell (including the nucleus)• Cytoplasm → region between nucleus and
plasma membrane that surrounds organelles– Filled with cytosol (watery-jelly part) and organelles– Contains centrioles, which help with cell division
reproduction
2

Types of Eukaryotic Cells
1)Animals2)Plants3) Fungi4) Protists

Types of Eukaryotes• Unicellular (Protozoa)
– Protists• Paramecium, amoebae
– Fungi• Yeast
• Multicellular (Metazoa)– Fungi– Plants– Animals
• Reproduction for ALL eukaryotes may be asexual or sexual

ORGANELLES• Very small• Perform various functions for cell• Found in the cytoplasm• May or may not be membrane-
bound

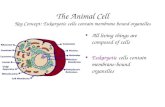
BASIC ANIMAL CELL ORGANELLES
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Nuclear envelope
Ribosome (attached)Ribosome (free)
Cell Membrane
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondrion
Smooth endoplasmicreticulum
Centrioles

BASIC PLANT CELL ORGANELLES

Organelle ListAnimal Cell Both Plant Cell
•Smaller vacuoles •Centrioles •Flagella and cilia•Lysosomes
•Nucleus• Nucleolus• Ribosome• Smooth ER• Rough ER• Golgi apparatus• Mitochondria• Cell Membrane• Cytoplasm • Cytoskeleton•Vesicle•Centrosome
•Cell wall•Large central vacuole•Chloroplasts

CELL OR PLASMA MEMBRANESTRUCTURE• Made of double layer (bilayer) of:
phospholipids and proteins• Surrounds outside of ALL cellsFUNCTION (JOB)• Controls what enters or leaves the cell• Security guard or a fenceFOUND:• ALL CELLS
Outsideof cell
Insideof cell(cytoplasm)
Cellmembrane
Proteins
Proteinchannel
Lipid bilayer
Carbohydratechains

CYTOPLASM OF A CELL
STRUCTURE• Jelly-like substance• Mostly water
• aqueous solutionFUNCTION (JOB)• Provides a solution for
chemical reactions to take place in
• Holds organelles in place • *OceanFOUND:• ALL CELLS
cytoplasm

NUCLEUSSTRUCTURE• Contains the DNA (genetic
information) in chromosomes• Bounded by a
nuclear envelope (membrane) with pores
• Usually the largest organelleFUNCTION (JOB)• Controls the normal
activities of the cell
• Main OfficeFOUND:•All eukaryotic cells

12
NUCLEAR ENVELOPE• Double membrane
surrounding nucleus• Also called nuclear membrane• Contains nuclear pores for
materials to enter & leave nucleus
• Connected to the rough ER
Nuclear pores

13
INSIDE THE NUCLEUS The genetic material (DNA) is found
DNA is spread out And appears as CHROMATINin non-dividing cells(NOT TIGHTLY COILED)
DNA is condensed & wrapped around proteins forming as CHROMOSOMES in dividing cells(TIGHTLY COILED)

NUCLEOLUSSTRUCTURE• Inside nucleus• Cell may have 1 to 3 nucleoli• Disappears when cell dividesFUNCTION (JOB)• Makes ribosomes (ribosomal
subunits)Found:• All Eukaryotic Cells
14

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
• Folded membranes• Moves supplies from one part of the cell to another
– This helps maintain homeostasis
• Detoxifies the cell• Two types of ER…
15

ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (RER)
STRUCTURE• Has ribosomes on its
surfaceFUNCTION (JOB)
– Makes more membrane– Modifies and helps make
proteins that are being transported out
FOUND:• Plant and animal cells

SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (SER)
STRUCTURE• Has NO ribosomes on its
surface• Usually attached to RERFUNCTION (JOB)• Makes lipids (membranes)• Regulates calcium
(muscles)• Destroys toxins (Liver)FOUND:Plant and animal cells 17

Golgi Apparatus• Receives vesicles (of protein) from the ER• Processes, sorts, and ships proteins • NOT interconnected• One side = receives vesicles• One side = ships to plasma membrane or become
lysosomes• Looks like a flattened stack of pancakes
18
UPS/Fedex warehouse packing center

GOLGI APPARATUS (BODIES)STRUCTURE
Stacks of flat sacsLooks like pancakes with
syrup drips“Pankcakes” NOT
connectedFUNCTION (JOB)• Modify• Sort• Package • molecules from ER for
storage OR transport in transport vesicles
FOUND:• Plant and animal cells
Transport vesicle
“syrup bubble”

Lysosomes
• Digestive/recycling center of the cell• Sac of digestive enzymes• Produced by the Rough ER
and Golgi• Breaks down “bad” organelles
20
Like a garbage disposal!

LYSOSOMESSTRUCTURE• They have a low pH • Contain digestive enzymes
FUNCTION (JOB)• Break down food, bacteria & old
cell parts• Lyse & release enzymes to break
down/recycle cell parts• Programmed for cell death
(APOPTOSIS)• Think= “Lysol” cleanerFound:Animal cells only
(a) Phagocytosis: lysosome digesting food
1 µm
Lysosome containsactive hydrolyticenzymes
Food vacuole fuses with lysosome
Hydrolyticenzymes digestfood particles
Digestion
Food vacuole
Plasma membraneLysosome
Digestiveenzymes
Lysosome
Nucleus

CYTOSKELETONSTRUCTURE• Made of proteins• Microfilaments-threadlike• Intermediate Filaments • Microtubules-tubelike
FUNCTION (JOB)• Network of fibers that help cell
maintain cell shape• Also help move organelles around• Structural support for animal cellsFOUND:• ALL CELLS

CILIA & FLAGELLAFUNCTION (JOB) of Flagella• Moves WHOLE cells
FUNCTION (JOB) of Cilia• Moves fluids or small particles across cell
surface
FOUND:• Animal cells and some plants• Flagella (prokaryotes)

CILIA & FLAGELLASTRUCTURE• Made of protein
tubes called microtubules
Cilia –Shorter –more numerousFlagella – Longer – fewer (usually 1-3)

Vacuoles• Storage “containers”
– Store various substances– The “closet” of the cell
STRUCTURE AND FOUND:• In animals = small and numerous• In plants = one large central vacuoleFUNCTION:
– Stores mostly water but also waste and nutrients– Helps with the structure of a plant cell
25

Energy Organelles
• Two “energy” organelles– Chloroplasts– Mitochondria
• Both contain their own DNA
26

Energy Organelles• Chloroplast
– Site of Photosynthesis– Converts energy from the sun into chemical energy– Only in Plants and some Protists
• Mitochondria– Site of Cellular Respiration makes ATP
• ATP required for cell activity!!!!– ENERGY!! Powerhouse of the cell– Found in almost all eukaryotic cells– Two membranes inner membrane is folded up to
increase the surface area27

STRUCTURE• Bean shape• DOUBLE membrane• Has its own DNA• Folded inner membrane
called CRISTAE (increases surface areafor more chemical reactions)
• Interior called MATRIX
MITOCHONDRION(PLURAL = MITOCHONDRIA)

29
FUNCTION (JOB)• “Powerhouse” of cell• Makes cellular energy (ATP)• More active cells like muscle
cells have MORE mitochondria• Site of CELLULAR
RESPIRATION (burning glucose)
MITOCHONDRION (CON’T)

INTERESTING FACT ---• Mitochondria
Come from cytoplasm in the EGG cell during fertilization
Therefore …• You inherit your
mitochondria from your mother!

CHLOROPLASTSSTRUCTURE• Bean shape• DOUBLE membrane• Sacs (“coins”) called Thylakoids• Thylakoids stack called Granum
(pl. =grana)• Stroma – gel in middle• Has its own DNA
FUNCTION (JOB)• Found only in autotrophs• Carries out photosynthesis
FOUND:• PLANT CELLS

CELL WALLSTRUCTUREFound in:• plants
• Made of cellulose• Fungi
• Made of chitin• Bacteria
• Made of peptidoglycan
FUNCTION (JOB)• Protect• Maintain shape
Cell wall

Cell Structures – Plant Cells ONLY• Cell Wall
– Rigid, tough– Made of cellulose
• Large Central Vacuole– Fills with water and increases turgor pressure (pressure in a cell)
• Chloroplasts
33

RIBOSOMESSTRUCTURE• Made of PROTEINS and rRNAFUNCTION (JOB)• Make proteins– amino acids to make proteins• Process called TRANSLATIONFOUND:ALL CELLS

RIBOSOMES (CON’T)Can be attached to
Rough ER (proteins made exit cell)
OR
Be free (unattached) in the cytoplasm
(proteins made stay INSIDE cell)

CENTRIOLESSTRUCTURE• Found only in animal
cells• Paired structures near
nucleus (“t” shape”)• Made of microtubulesFUNCTION (JOB)• Appear during cell
division• Help to pull chromosome
pairs apart to opposite ends of the cell

CENTRIOLES & THE MITOTIC SPINDLE
**Made of MICROTUBULES (Tubulin)

NOW…LET’S PRACTICE

Animals vs. Plants
39
• Cell wall• Large central
vacuole• Chloroplasts
• Smaller vacuoles • Centrioles • Flagella and cilia• Lysosomes
• Nucleus• Nucleolus• Ribosome• Smooth ER• Rough ER• Golgi• Mitochondria• Cell Membrane• Cytoplasm • Cytoskeleton•Vesicle•Centrosome