Plant cells
-
Upload
punxsyscience -
Category
Documents
-
view
780 -
download
0
Transcript of Plant cells

Plant Cell
By: Brandon Bennett,Carla Paul, and Jared Weber

Cell WallThe function of the cell wall is to provide protection and structural support to the cells. It separates the inside of the cell from the outside. It transport of specific supplies in and out of the cell. Also it recognition of other cells.
Carla Paul

Plasma Membranethis organelles function is to separate the interior of the cell from the outside environment. Cell membranes do a variety of processes that include cell adhesion, ion conductivity, and cell signaling. They control the movement of substances that go in and out of a cell.
Jared Weber

CytoplasmThe function of the cytoplasm forms the ground substance of the cell. Cytoplasm is to hold the cell organelles of the cell. Its main function is suspension of the organelles, their nutrients, and products.
Carla Paul

Nucleus- the nucleus is an organelle and it’s function is to maintain the genes and to control all of the activities and organelles in a cell. The nucleus controls were protein and other nutrients go to in a cell.
Jared Weber

NucleolusThe function of the nucleolus it contains all the DNA of the cell. Its used as instructions to create the building blocks of the cell. The nucleolus produces ribosomes, the organelles that manufacture proteins in the cell. It is a control center in the middle of the nucleus.
Carla Paul

VacuoleThe vacuole is an organelle that usually found in plant cells but can be found in animal of bacterial cells. A few of the vacuoles functions are containing water, containing waste, maintaining internal pressure, and stores different materials.
Jared Weber

Golgi ApparatusThe function of the Golgi apparatus is to modify, sort, and package protein and other materials from the cellular endoplasmic reticulum for storage within the cell. Golgi apparatus also transports it to different parts of the cell. It carries out the breakdown of the proteins and formation of small, active fragments.
Carla Paul

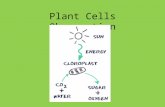
Chloroplastschloroplasts are organelles that are usually found in plant and eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy and store it into storage molecules. The chloroplast uses light energy, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water to conduct photosynthesis.
Jared Weber

RibosomesCan be found on the endoplasmic reticulum or floating in the cytoplasm. They follow instructions from the nucleus to create the proteins needed..
Brandon Bennett

Rough Endoplasmic ReticulumThe endoplasmic reticulum prepares the proteins for transport to the Golgi Apparatus, the packaging plant of the cell, or straight to other parts of the cell. Ribosomes dot the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum and make proteins.
Brandon Bennett

Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumThe endoplasmic reticulum prepares the proteins for transport to the Golgi Apparatus, the packaging plant of the cell, or straight to other parts of the cell. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for producing lipids.
Brandon Bennett

MitochondriaMitochondria produce ATP to fuel the action of the cell. Mitochondria use glucose to make this energy rich molecule.
Brandon Bennett