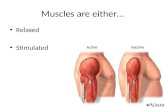
Muscle Contractions
description
Transcript of Muscle Contractions

Muscle Contractions

Do Now
• Homework Review

Review

Review
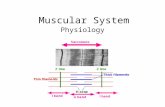
• All muscle must be stimulated• In between axon and muscle is a neuromuscular junction
• Motor axon breaks into several branches called axon terminals
• Each branch forms a neuromuscular junction with a single muscle cell• 1 neuron stimulates many muscle fibers
• Motor unit – neuron and all the muscles it stimulates

Review
• Neuron and muscle fibers DO NOT touch• Separated by small, fluid filled gap called the synaptic
cleft• Acetylcholine (neurontransmitter) carries the impulse
across the gap and delivers the message• If enough acetylcholine is released, the permeability of
the receiver changes, allowing for sodium to enter the surface• Results in possible muscle contraction

Types of Muscle Contraction
• 3 Different types of muscle contraction that are used in a variety of situations• Isometric• Eccentric• Concentric

Isometrics
• Isometrics are when there is a muscle contraction, but not change in muscle length
• Great strengthening tool, used when pain is felt in a ROM• Example: Planks, Pushing a wall, wall squat• Can exert considerable force on an immovable object,
even though not movement occurs

Concentric
• Most widely known form of muscle contraction• During contraction, muscle length shortens to overcome
resistance• Example: Bicep curl

Eccentric
• Commonly underutilized muscle strengthening technique• Resistance is greater than the muscular force being
produced• Leads to a lengthening of the muscle while contracting,
instead of a shortening• Not to say that the weight has to be too heavy to lift

Resistance Training Techniques
• There are a countless number of ways to improve in strength training• Functional Exercises• Isometrics• Progressive Resistance Exercise• Isokinetics• Plyometrics

Functional Exercises
• What does functional mean to you?• Functional has to do with “sport specific” exercises• Ladder drills• LAX stick• Football• Basketball
• “Kinetic Chain”

Homework
• Students are going to work in groups• Due Monday, each group must determine a concentric,
eccentric and isometric exercise for their muscle group given. Students will pick muscle group out of a hat