Muscle: Contractions and Neural Control More than ___ muscles in the animal body Characteristics of...
-
Upload
crystal-davidson -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of Muscle: Contractions and Neural Control More than ___ muscles in the animal body Characteristics of...

Muscle:Contractions and Neural Control

More than ___ muscles in the animal body
Characteristics of muscle dictate its function
Mammalian and avian – long, unbranched, and threadlike that taper at both ends
Muscle Fiber = ___________________

Function
• Movement of skeleton• Blood pressure/supply• Transport of ingesta• Generation of Body heat• Circulation of blood

Muscle general anatomy
• Tendon (tough connective tissue)
• Muscle
• Tendon

Embryonic development - Myoblasts
• Muscle: Myotome (myoblast) cells migrate to various places in the embryo – Chemotaxis – ____________________– Morphogens – chemicals produced in
one area which effect distant cells

Growth
• Hypertrophy: cells increase in _____• Hyperplasia: addition of more cells
• Growth: increase in muscle and bone
• Fattening: accumulation of fat

Skeletal Muscle Types: Slow- and Fast-Twitch Fibers
• Divided on basis of contraction speed:
– Slow-twitch (type I fibers). • ______________________: • Muscles which get used a lot, for long periods of time• Fowl that fly often, have dark breast (pectoral) meat
– Fast-twitch (type II fibers).• _________________: fast twitch, easy to fatigue, lots of
___________________ present• ________________________: light colored pectorals
– Intermediate: have a combination of the two• Most muscles
• Differences due to different myosin ATPase isoenzymes that are slow or fast.


Upper Motor Neuron Control of Skeletal Muscles
• Cerebellum:– Receives sensory input from muscle
spindles
• No descending tracts from the cerebellum.– Influences motor activity indirectly.
• All output from cerebellum is inhibitory.– Aids motor coordination.

Upper Motor Neuron Control of Skeletal Muscles (continued)
• Basal nuclei:• Profound inhibitory effects on the
activity of lower motor neurons.– Damage to basal nuclei result in
increased muscle tone.

Anatomy of Skeletal MuscleFigure 12.1
• Epimysium – CT that surrounds ______________
• Perimysium – CT that surrounds muscle bundle
• Endomysium – CT that surrounds ____________________
• Sarcolemma – “____________” – Elastic CT that surrounds the myofibrils– Invaginations form a network of tubules
called the transverse tubules “T-tubules”

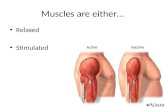
Muscle types
• Striated muscle– ___________ – Autonomic control
• Smooth muscle – _________________________– No striations
• Cardiac muscle– ____________________– ______________________ control

Skeletal Muscle
• Sarcoplasm – cytoplasm • Nuclei – multinucleated• Myofibrils – unique to muscle tissue
– Long, thin, cylindrical rods 1 to 2 µm in diameter
– Bathed in sarcoplasm – Consists of: ________________________
•Thick & Thin

Structure of Skeletal Muscle


Sarcomere

Skeletal Muscle
• Myofilaments– Thick are aligned parallel to each other– Thin , parallel to thick– These “bands” of parallel fibers give SM striated
appearance
• A and I bands– Called this due to light refractions– _________band is denser than ___________
• Shows up darker in pictures
– Both are bisected by thin, dense lines

Skeletal Muscle
• A and I bands– I band is bisected by line called: _______– Unit of myofibril between 2 different Z
disks is called: ____________________• Includes the A band and parts of the I band• Is the repeating structural unit of the myofibril •Basic unit in _____________ & ________________• Length of sarcomere is not constant and will
differ depending on relaxation or contraction

Myofilaments
• Thick and thin differ in dimensions and chemical composition– Thick
• 14 to 16 nanometers (nm = 1 billionth of a meter)
• Constitute the ______________ of sarcomere• ____________________ is the predominant protein
– held in position by other proteins some of which are located in the M line

Myofilaments
• Thin– 6-8 nm in diameter– Extend 1.0 µm on either side of the Z disk– Filaments constitute the ________ of the
sarcomere– Extend into the _________________– I band only contains the ________ filaments

Myofilaments
• ________________ – only thick filaments are present
• ________________ – thick and thin are located– Shows 6 thin filaments surrounding each
thick

Z- Disk• Z disk
– Comprised of z-filaments which connect actin molecules
– Z line is composed of 4 z-filaments which attach actin molecules from each sarcomere

Proteins of myfofibril
• 20 different proteins associated with myofibrils– 6 proteins account for 90% of total myofibrillar
protein– Decreasing order of abundance:
• Myosin• Actin• Titin• Tropomyosin• Troponin• Nebulin

Proteins of myofibril
• Major Contractile Proteins– Actin – 20% of myofibrillar protein
Globular – G - actin Form a “super helix”Globular – G - actin Form a “super helix”

Actin myofilaments are made of globular actin (G-actin) monomers and other proteins.

Proteins of myofibril
• Major Contractile Proteins– Myosin – 45% of myofibril protein
Elongated RodThickened end: Head – 2 of them
Thin end: TailIn-between: neck


Proteins of myofibril
• Major Contractile ProteinsMyosin– 2 fractions: ________ and
__________meromyosin– Center of A band – myosin contains only rods,
no heads• Known as pseudo H zone
– Heads are functionally active during contraction• Form a cross-bridge with ______________


Proteins of myofibril• Tropomyosin
5% of myofibrillar protein– Lies in close contact with ____________– Lies in grove with __________

Proteins of myofibril
• Troponin: 5% of myofibril protein– In groove of _________________– Lies astride the tropomyosin strands

Proteins of myofibril
• Titin: 10% of myofibrillar protein– Scaffold for alignment of filaments
during myofibril and sarcomere formation

Proteins of myofibril
• Nebulin: 4% of myofibril protein– Anchors thin filaments to Z disks– Serves as a template for assembly /
scaffold for stability of thin filaments

Muscle Contraction
• Each myofibril contains myofilaments.• 2 major ones involved with contraction
– Thick filaments aka ________________:• A bands contain thick filaments (primarily composed
of myosin).• Myosin initiates the contraction• There an enzyme that converts ATP to ADP and
Phosphate
– Thin filaments aka ___________________:• I bands contain thin filaments (primarily composed of
actin).• Most abundant protein • Major constituent of muscle
– Center of each I band is Z disc.



Mechanisms of Contraction (continued)
• Sarcomere:– _____ disc to ________ disc.– M lines:
• Produced by protein filaments in a sarcomere.– Anchor myosin during contraction.
• Titin:– Elastic protein that runs through the myosin
from ____ line to ____________.• Contributes to elastic recoil of muscle.

Mechanisms of Contraction (continued)
• Tropomyosin:– Part of the “___________” filament
• Continuous stand that sits on actin• Exposes the actin binding site
• Troponin:– Inhibits actin-activated myosin ATPase
Activity

Sliding Filament Theory of Contraction
• Sliding of filaments is produced by the actions of cross bridges.– Cross bridges are part of the myosin
proteins that extend out toward actin.• Form arms that terminate in heads.
– Each myosin head contains an ATP-binding site.• The myosin head functions as a myosin
ATPase.


Sliding Filament Theory of Contraction (continued)
• Muscle contracts:– Occurs because of sliding of thin
filaments over and between thick filaments towards center.• Shortening the distance from Z disc to Z
disc.
• A bands:– Contain ______________.
• Move closer together.
– Do not shorten.

Sliding Filament Theory of Contraction (continued)
• I bands: – Distance between A bands of successive
______________________.– Decrease in length.
• H bands shorten.– Contain only _____________.– Shorten during contraction.

Contraction• Myosin binding site splits ATP to ADP and Pi.• ADP and Pi remain bound to myosin until
myosin heads attach to actin.• Pi is released, causing the power stroke to
occur.• Power stroke pulls actin toward the center of
the A band.• ADP is released, when myosin binds to a
fresh ATP at the end of the power stroke.


Contraction (continued)
• Release of ADP upon binding to another _______, causes the cross bridge bond to break.
• Cross bridges detach, ready to bind again.
• Synchronous action:– Only 50% of the cross bridges are
attached at any given time.


Regulation of Contraction
• Regulation of cross bridge attachment to actin due to:– Tropomyosin:.
• Lies within grove between double row of G-actin.
– Troponin:• Attached to tropomyosin.
• Serves as a switch for muscle contraction and relaxation.– In relaxed muscle:
• Tropomyosin blocks binding sites on actin.


Role of Ca2+ in Muscle Contraction
• Muscle Relaxation:– [Ca2+] in sarcoplasm low when
tropomyosin blocks attachment.• Prevents muscle contraction.• Ca2+ is pumped back into the SR in the
____________________________.
– Muscle relaxes.

Sarcoplasmic Reticulum & T Tubules
• Membranous system of tubules and cisternae (reservoirs for calcium)
• Found around each _________________
• T-tubules:– Associated with __________________– T tubule runs transversely across the
sarcomere at the AI junction.

Sarcoplasmic Reticulum & T Tubules
• SR: Longitudinal tubules of reticulum:– Converge in H zone which forms a
fenestrated collar– At AI junction:- the longitudinal tubules
join with terminal cisternae– Longitudinal tubules extend in both
directions from fenestrated collar to terminal cisternae



Contraction-Relaxation
• Plasma membrane is depolarized by an AP
• The AP is conducted deep into the muscle fibers along the T-tubules In response to T-tubule depolarization, dihydropyridine receptors in the muscle undergo a confrontational change that directly link to Ryanodine receptors in the SR membrane – caused opening of Ca ++ channels in the SR membrane

Contraction-Relaxation (cont.)
• Myosin cross bridged attach to the actin filaments; ratchet through 4 steps ATP binds the ATPase site on the myosin head, causing myosin to detach from the thin (actin) filament
• The cycle repeats

Muscle Fuel Consumption During Exercise

Metabolism of Skeletal Muscles
• Lactate threshold: – % of max. 02 uptake at which there is a
significant rise in blood [lactate].• During light exercise:
– Most energy is derived from aerobic respiration of _______________________.
• During moderate exercise:– Energy is derived equally from _________________
and _________________________.• During heavy exercise:
– Glucose supplies 2/3 of the energy for muscles.• Liver increases _____________________________.

Metabolism of Skeletal Muscles (continued)• Oxygen debt:
– Oxygen that was withdrawn from ___________ and __________________ during exercise.
– Extra 02 required for metabolism tissue warmed during exercise.
– 02 needed for metabolism of lactic acid produced during anaerobic respiration.
• When person stops exercising, rate of oxygen uptake does not immediately return to pre-exercise levels.– Returns slowly.

Metabolism of Skeletal Muscles (continued)• Phosphocreatine (creatine phosphate):
– Rapid source of renewal of ___________.– ADP combines with creatine phosphate.
• [Phosphocreatine] is ________ times [ATP].– Ready source of high-energy phosphate.


• Characteristics– No striations– Centrally located nucleus– Autonomic control– Major proteins – ________ & ___________
• Proteins not arranged in any particular order = no striations
Smooth Muscle

Smooth Muscle
• Does not contain sarcomeres.
• Contains > content of actin than myosin (ratio of 16:1).
• Myosin filaments attached at ends of the cell to dense bodies.
• Contains gap junctions.

Smooth Muscle
• Smooth Involuntary– ________________ resistance– Individual cells, centrally located (one)
nucleus, no striations– Independent of higher nervous centers– Autonomic NS (Para and Sym control)– Includes: Digestive, Respiratory,
Vascular

Smooth Muscle Contraction
• Depends on rise in free intracellular Ca2+.• Ca2+ binds with ________________.
– Ca2+ calmodulin complex joins with and activates myosin light chain kinase.
• Myosin heads are phosphorylated.– Myosin heads binds with actin.
• Relaxation occurs when Ca2+ concentration decreases.

Cardiac Muscle
• Contain actin and myosin arranged in sarcomeres.
• Contract via sliding-filament mechanism.
• Adjacent myocardial cells joined by gap junctions.– APs spread through
cardiac muscle through gap junctions.
• Behaves as one unit.– All cells contribute to
contraction.

Cardiac Muscle
• Striated involuntary: Cardiac– Fatigue resistance– Don’t have to think about it (Autonomic NS)
• Branched: allows for nerve impulses to branch as well
• Cells arranged sort of side by side. In each cell is once nucleus. On each side is an intercalated disk
• Usually just have one nucleus, sometimes 2– Striated: proteins in them overlap