Classification of Matter · Classification of Matter •Heterogeneous Mixture: combination of...
Transcript of Classification of Matter · Classification of Matter •Heterogeneous Mixture: combination of...

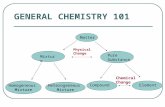
Classification of Matter
Composition of Matter
Properties of Matter

Matter and Chemistry
Chemistry
The study of the composition, properties,
and reactions of matter, particularly at the
level of atoms and molecules.

Matter-Anything with mass that takes up
space
Atom-Basic unit of matter

Compounds vs. Elements
Molecules- Two or more atoms joined
together.
Compounds- The combination of two or
more elements.
All compounds are molecules but not all
molecules are compounds.

Chemical Formula
-Shows how many elements or molecules
are in each unit of a substance
Example: H₂O = 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen
Example: 2H₂O= 2 water molecules


Composition of Matter
• Substance: has a fixed
composition, either an
element or a compound
• Element: all atoms in
the substance have the
same identity

Classification of Matter
• Heterogeneous Mixture: combination of
substances in which different materials
can be easily distinguished
• Homogeneous Mixture: combination of
substances in which two or more gaseous,
liquid, or solid substances are blended
evenly throughout

Classify The Following as a
Substance or a Mixture:
• Copper Penny
• Salad Dressing
• T-Shirt (75% cotton, 25% polyester)
• Kool-Aid
• Milk
• Chalk (Calcium Carbonate)

Composition of Matter
• Solution: homogeneous mixture of particles so
small that they cannot be seen with a
microscope and will never settle to the bottom of
their container
• Colloids: heterogeneous mixture of particles
larger than those in solutions, but not heavy
enough to settle out
• Suspension: heterogeneous mixture containing
a liquid in which visible particles settle

Properties of Matter
• Physical Properties:
characteristics of a
material that can
change without
changing the identity
of its substances
• Examples: color,
shape, size, density,
melting point, boiling
point, flexibility

Properties of Matter
• Physical Changes:
changing only
physical properties
• changing size,
changing shape, or
changing state

Properties of Matter
• Chemical
Properties:
characteristics of a
substance that
indicate whether it
can undergo certain
chemical changes
• Examples:
flammability, reaction
to light

Properties of Matter
• Chemical Changes:
change of one substance to
another
• Rotting, burning, forming
bubbles or solids in a liquid,
rusting

Properties of Matter
• Conservation of
Mass: matter is never
created or destroyed
• Example: a log burns,
the matter left behind
or released is ash,
gases, and smoke.
The mass of all these
equals the mass of
the log

Chemical & Physical Changes
Which of the following undergo physical changes? Which undergo chemical changes?
1.Baking soda and vinegar produce CO2, H2O, and sodium acetate
2.A burning candle
3.Melting wax
4.Boiling water
5.An antacid dissolves in water and produces gases
6.Add mentos to soda
7.Add Kool-Aid powder to water








![[PPT]Chapter 17:classification of matter - Scioto Valley Home · Web viewChapter 17:classification of matter MATERIALS ARE MADE OF A PURE SUBSTANCEOR A MIXTURE OF SUBSTANCES. A PURE](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5aee76d27f8b9a572b8cc143/pptchapter-17classification-of-matter-scioto-valley-viewchapter-17classification.jpg)