Chapter 1: Electronic devices · 2020. 5. 8. · Chapter 1: Electronic devices Semiconductor...
Transcript of Chapter 1: Electronic devices · 2020. 5. 8. · Chapter 1: Electronic devices Semiconductor...

Chapter 1: Electronic devices
Semiconductor diode/P-n junction diode: A p-n junction diode is a two terminal device,which is formed by doping one side with p-type dopant and other side with a n- type dopant. A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor material, p-type and n-type, inside a single crystal of semiconductor. The p–n junctions are elementary "building blocks" of most semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells, LEDs, and integrated circuits.
Working principle: There are three possible biasing conditions for p-n junction diode: Zero Bias-No external voltage is applied to the p-n junction diode . Forward Bias- The voltage potential is connected positively to the p-type terminal and negatively to the n- type terminal of the diode.

Reverse Bias- The voltage potential is connected negatively to the p-type terminal and positively to the n- type terminal of the diode. Zero Bias: In this case, no external voltage is applied to the P-N junction diode; and therefore, the electrons diffuse to the P-side and simultaneously holes diffuse towards the N-side through the junction, and then combine with each other. Due to this an electric field is generated by these charge carriers. The electric field opposes further diffusion of charged carriers so that there is no movement in the middle region. This region is known as depletion width or space charge Forward Bias: In the forward bias condition, the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the N-type material and the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the P-Type material. This connection is also called as giving positive voltage. Electrons from the N-region cross the junction and enters the P-region. Due to the attractive force that is generated in the P-region the electrons are attracted and move towards the positive terminal. Simultaneously the holes are attracted to the negative terminal of the battery. By the movement of electrons and holes current flows. In this condition, the width of the depletion region decreases due to the reduction in the number of positive and negative ions.

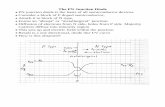
V-I Characteristics:
By supplying positive voltage, the electrons get enough energy to overcome the potential barrier (depletion layer) and cross the junction and the same thing happens with the holes as well. The amount of energy required by the electrons and holes for crossing
the junction is equal to the barrier potential 0.3 V for Ge and 0.7 V for Si, 1.2V for GaAs. This is also known as Voltage drop. The voltage drop across the diode occurs due to internal resistance. This can be observed in the below graph. Reverse Bias: In the reverse bias condition, the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the P-type material and the positive terminal of the battery is connected to theN-type material. Hence, the electric field due to both the voltage and depletion layer is in the same direction. This makes the electric field stronger than before. Due to this strong electric field, electrons and holes want more energy to cross the junction so they cannot diffuse to the opposite region. Hence, there

is no current flow due to the lack of movement of electrons and holes. The electrons from the N-type semiconductor are attracted towards the positive terminal and the holes from the P-type semiconductor are attracted to the negative terminal. This leads to the reduction of the number of electrons in N-type and holes in P-type. In addition, positive ions are created in the N-type region and negative ions are created in the P-type region. Therefore, the depletion layer width is increased due to the increasing number of positive and negative ions.
V-I Characteristics: Due to thermal energy in crystal minority carriers are produced. Minority carriers mean a hole in N-type material and electrons in P-type material. These minority carriers are the electrons and holes pushed towards P-N junction by the negative terminal and positive terminal, respectively. Due to the movement of minority carriers, a very little current flows, which is in nano Ampere range (for silicon). This current is called as reverse saturation current. Saturation means, after reaching its maximum value, a steady state is reached wherein the current value remains same with increasing voltage.

Use of Pn junction diode: 1.rectifiers 2.clippers 3.clampers 4.detector and demodulator. Zener diode: Zener diodes or as they may sometimes be called, reference diodes operate like an ordinary diode in the forward bias direction. They have the normal turn on voltage of 0.6 volts for a silicon diode. However in the reverse direction their operation is rather different. Zener diodes are used to maintain a fixed voltage. They are designed to 'breakdown' in a reliable and non- destructive way so that they can be used in reverse to maintain a fixed voltage across their terminals. Working principle: When a PN junction diode is reverse biased the depletion layer becomes wider.If this reversebiased voltage across the diode is increased continuously the depletion layer becomes more and more

wider.At the same time there will be a constant reverse saturation current due to minority carriers. After certain reverse voltage across the junction the minority carriers get sufficient kinetic energy due to strong electric field.Free electrons with sufficient kinetic energy collide with stationary ions of the depletion layer and knock out more free electrons.Further more new free electrons are created cumulatively.Due to this commutative phenomenon,very soon huge free electrons get created in depletion region and entire diode will become conductive.This type of breakdown of depletionlayer is known as avalanche breakdown,but this breakdown is not quite sharp.There is another type of breakdown in depletion layer which is sharper compared to avalanche breakdown and this is called zener breakdown.When Pn junction diode is highly doped, the concentration of impurity atoms will increase which results into higher concentration of ions in depletion layer that leads thinning of depletion layer.Due to thinning ,voltage gradient across the layer is quite high.If the reverse voltage is continued to increase after a certain applied voltage,the electrons from the covalent bond within the layer come out and make the depletion region conductive.This breakdown is zener breakdown.The voltage at which this breakdown occurs is called zener voltage. VI characteristics: The vi characteristic of the Zener to voltage reference diode is the key to its operation. In the forward direction, the diode performs like any other, but it is in the reverse direction where its specific performance parameters can be utilised.

Use of zener diode: 1.voltage regulator 2.voltage shifter 3.waveform clipper Light emitting diode (LED): A light emitting diode (LED) is known to be one of the best optoelectronic devices. The device is capable of emitting a fairly narrow bandwidth of visible or invisible light when its internal diode junction attains a forward electric current or voltage. The visible lights that an LED emits are usually orange, red, yellow, or green. The invisible light includes the infrared light. Working principle: We know that a P-N junction can connect the absorbed light energy into its proportional electric current. The same process is reversed here. That is, the P-N junction emits light when energy is applied on it. This phenomenon is generally called electro luminance, which can be defined as the emission of light from a semi-conductor under the

influence of an electric field. The charge carriers recombine in a forward P-N junction as the electrons cross from the N-region and recombine with the holes existing in the P-region. Free electrons are in the conduction band of energy levels, while holes are in the valence energy band. Thus the energy level of the holes will be lesser than the energy levels of the electrons. Some part of the energy must be dissipated in order to recombine the electrons and the holes. This energy is emitted in the form of heat and light. The electrons dissipate energy in the form of heat for silicon and germanium diodes. But in Galium-Arsenide-phosphorous (GaAsP) and Galium-phosphorous (GaP) semiconductors, the electrons dissipate energy by emitting photons. VI characteristics:
Use of led: 1.TV backlighting 2.Smartphone Backlighting 3.LED displays 4.Automotive lighting.

Integrated circuit:- An integrated circuit (IC), sometimes called a chip or microchip, is a semiconductor wafer on which thousands or millions of tiny resistors, capacitors, and transistors are fabricated. An IC can function as an amplifier, oscillator, timer, counter, computer memory, or microprocessor. A particular IC is categorised as either linear analog or digital, depending on its intended application. IC's are are of Linear , digital and mixed types Digital ICs operate at only a few defined levels or states, rather than over a continuous range of signal amplitudes. These devices are used in computers, computer networks, modems, and frequency counters. The fundamental building blocks of digital ICs are logic gates, which work with binary data, that is, signals that have only two different states, called low (logic 0) and high (logic 1). Digital IC's are mostly used in computers. They are also referred as switching circuits because their input and output voltages are limited to two levels - high and low i.e. binary. They include: 1. Flip-flops 2. Logic gates 3. Timers 4. Counters 5. Multiplexers 6. Calculator chips 7. Memory chips 8. Clock chips 9. Microprocessors 10. Microcontrollers 11. Temperature sensors Mixed type applications - cars (automotive controls), televisions, computers, microwaves, portable devices like laptops, MP3, play stations, cameras, cellular phones to ship equipments, aero planes, space craft’s. These are also used in switching telephone circuits and data processing. They also found applications in military equipments. The most common application of IC is digital watch which tells hour,

second, minute, day and month. Another common but important application is scientific calculator which can perform basic functions like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division as well as complex functions like square root, cube, permutations, combinations , trigonometric functions, etc The advantages of Integrated Circuits are: 1. Very small size: Hundred times smaller than the discrete circuits. 2. Lesser weight: As large number of components can be packed into a single chip, weight is reduced 3. Reduced cost: The mass production technique has helped to reduce the price. 4. High reliability: Due to absence of soldered connection, few interconnections and small temperature rise failure rate is low. 5. Low power requirement: As the size is small power consumption is less. 6. Easy replacement: In case of failure chip can easily be replaced. Applications of integrated circuits: 1. Power amplifiers 2. Small-signal amplifiers 3. Operational amplifiers 4. Microwave amplifiers 5. RF and IF amplifiers 6. Voltage comparators 7. Multipliers 8. Radio receivers

Chapter 2
Electronic circuits
Rectifier: A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. Need for rectifier: For the reasons associated with economics of generation and transmission, the electric power available is usually an a.c supply.The voltage varies sinusoidally and has a frequency of 50 Hz.It is used for lighting, heating and electric motors.But there are many applications (e.g electronic circuits) where d.c supply is needed.When such a d.c supply is required, the mains a.c supply has to be rectified. Basically there are two types of rectifier : 1.Half wave rectifier 2.Full wave rectifier. Half wave rectifier:

The half-wave rectifier circuit using a semiconductor diode (D) with a load resistance RL but no smoothing filter is given in the figure. The diode is connected in series with the secondary of the transformer and the load resistance RL. The primary of the transformer is being connected to the ac supply mains. The ac voltage across the secondary winding changes polarities after every half cycle of the input wave. During the positive half-cycles of the input ac voltage i.e. when the upper end of the secondary winding is positive w.r.t. its lower end, the diode is forward biased and therefore conducts current. If the forward resistance of the diode is assumed to be zero (in practice, however, a small resistance exists) the input voltage during the positive half-cycles is directly applied to the load resistance RL, making its upper-end positive w.r.t. its lower end. The waveforms of the output current and output voltage are of the same shape as that of the input ac voltage. During the negative half cycles of the input ac voltage i.e. when the lower end of the secondary winding is positive w.r.t. its upper end, the diode is reverse biased and so does not conduct. Thus during the negative half cycles of the input ac voltage, the current through and the voltage across the load remains zero. The reverse current, being very small in magnitude, is neglected. Thus for the negative half cycles, no power is delivered to the load.

Thus the output voltage (VL) developed across load resistance RL is a series of positive half cycles of alternating voltage, with intervening very small constant negative voltage levels, It is obvious from the figure that the output is not a steady dc, but only a pulsating dc wave. To make the output wave smooth and useful in a DC power supply, we have to use a filter across the load. Since only half-cycles of the input wave are used, it is called a half wave rectifier. Advantage of a half wave rectifier : 1.its cheap, simple and easy to construct. It is cheap because of the low number of components involved. Disadvantages of Half wave rectifier: 2.High ripple factor will result in noises in the input audio signal, which in turn will affect audio quality. Full wave rectifier: Full wave rectifier can be classified as: 1. Centre-tapped Full Wave Rectifier 2. Full Wave Bridge Rectifier 1. Centre-tapped Full Wave Rectifier:

The full wave rectifier circuit consists of two power diodes connected to a single load resistance (RL) with each diode taking it in turn to supply current to the load. When point A of the transformer is positive with respect to point C, diode D1 conducts in the forward direction as indicated by the arrows. When point B is positive (in the negative half of the cycle) with respect to point C, diode D2 conducts in the forward direction and the current flowing through resistor R is in the same direction for both half-cycles. As the output voltage across the resistor R is the phasor sum of the two waveforms combined, this type of full wave rectifier circuit is also known as a “bi-phase” circuit. Advantages of center tapped full wave rectifier: 1.The ripple factor is much less than that of half wave rectifier. 2.The rectification efficiency is twice than that of a half wave rectifier. For a full wave rectifier, the maximum possible value of rectification efficiency is 81.2 % while that half wave rectifier is 40.6 %

3.The DC output voltage and DC load current values are twice than those of a half wave rectifier. Disadvantages of center tapped full wave rectifier : 1.It is expensive to manufacture a center tapped transformer which produces equal voltage on each half of the secondary windings. 2.The output voltage is half of the secondary voltage, as each diode utilizes only one half of the transformer secondary voltage. 3.The PIV (peak inverse voltage) of a diode used twice that of the diode used in the half wave rectifier, so the diodes used must have high PIV. 2.The Full Wave Bridge Rectifier: Another type of circuit that produces the same output waveform as
the full wave rectifier circuit above, is that of the Full Wave Bridge Rectifier. This type of single phase rectifier uses four individual rectifying diodes connected in a closed loop “bridge” configuration to produce the desired output. The four diodes labelled D1 to D4 are arranged in “series pairs” with only two diodes conducting current during each half cycle.

During the positive half cycle of the supply, diodes D1 and D2 conduct in series while diodes D3 and D4 are reverse biased and the current flows through the load as shown below. The Positive Half-cycle:
During the negative half cycle of the supply, diodes D3 and D4 conduct in series, but diodes D1 and D2 switch “OFF” as they are now reverse biased. The current flowing through the load is the same direction as before. The Negative Half-cycle:
As the current flowing through the load is unidirectional, so the voltage developed across the load is also unidirectional the same as

for the previous two diode full-wave rectifier, therefore the average DC voltage across the load is 0.637Vmax. Advantages of Full Wave Bridge Rectifier: 1.The center tap transformer is eliminated. 2.The output is double to that of the center tapped full wave rectifier for the same secondary voltage. 3.The peak inverse voltage across each diode is one-half of the center tap circuit of the diode. Disadvantages of Full Wave Bridge Rectifier: 1.It needs four diodes. 2.The circuit is not suitable when a small voltage is required to be rectified. It is because, in this case, the two diodes are connected in series and offer double voltage drop due to their internal resistance
Filter:
The filter is a device that allows passing the dc component of the load and blocks the ac component of the rectifier output. Thus the output of the filter circuit will be a steady dc voltage. Need of filter: As we know that rectifier converts a.c to d.c but we can’t say it is pure dc rather pulsating d.c as it has some a.c characteristics such periodic nature which indicates that it has some a.c component present in it. This ac component has to be completely removed in order to get pure dc output. So, we need a circuit that smoothens the rectified output into a pure dc signal and that circuit is known as filter

The following figure shows the functionality of a filter circuit.
Filters A filter circuit is constructed using two main components as follows: 1.An inductor allows dc and blocks ac. 2.A capacitor allows ac and blocks dc. X=2*pi*f*l Types of filter: The different types of filter are: 1.Inductor filter 2.Capacitor filter 3.pi filter Series Inductor filter: As an inductor allows dc and blocks ac, a filter called Series Inductor Filter can be constructed by connecting the inductor in series, between the rectifier and the load. The figure below shows the circuit of a series inductor filter.

The rectified output when passed through this filter, the ac components present in the signal are grounded through the capacitor which allows ac components. The remaining dc components present in the signal are collected at the output. Shunt Capacitor Filter: As a capacitor allows ac through it and blocks dc, a filter called Shunt Capacitor Filter can be constructed using a capacitor, connected in shunt, as shown in the following figure.
The rectified output when passed through this filter, the ac components present in the signal are grounded through the capacitor which allows ac components. The remaining dc components present in the signal are collected at the output. Π- Filter: This is another type of filter circuit which is very commonly used. It has capacitor at its input and hence it is also called as a Capacitor Input Filter. Here, two capacitors and one inductor are connected in

the form of π shaped network. A capacitor in parallel, then an inductor in series, followed by another capacitor in parallel makes this circuit.
In this circuit, we have a capacitor in parallel, then an inductor in series, followed by another capacitor in parallel. ➢ Capacitor C1 − This filter capacitor offers high reactance to dc
and low reactance to ac signal. After grounding the ac components present in the signal, the signal passes to the inductor for further filtration.
➢ Inductor L − This inductor offers low reactance to dc
components, while blocking the ac components if any got managed to pass, through the capacitor C1.
➢ Capacitor C2 − Now the signal is further smoothened using this
capacitor so that it allows any ac component present in the signal, which the inductor has failed to block.
Thus we, get the desired pure dc output at the load.
D.C power supply system: Now a days, almost all electronic equipment include a circuit that converts ac supply into dc supply. The part of equipment that

converts ac into dc is called DC power supply. The input of the power supply there is a power transformer. It is followed by a rectifier (a diode circuit)a smoothing filter. Transformer is used to step-up or step-down (usually to step-down) the-supply voltage as per need of the solid-state electronic devices and circuits to be supplied by the dc power supply. It can provide isolation from the supply line-an important safety consideration. It may also include internal shielding to prevent unwanted electrical noise signal on the power line from getting into the power supply and possibly disturbing the load. Rectifier is a device which converts the sinusoidal ac voltage into either positive or negative pulsating dc. P-N junction diode, which conducts when forward biased and practically does not conduct when reverse biased, can be used for rectification i.e. for conversion of ac into dc. The rectifier typically needs one, two or four diodes. Rectifiers may be either half-wave rectifiers or full-wave rectifiers (centre-tap or bridge) type. The output voltage from a rectifier circuit has a pulsating character i.e., it contains unwanted ac components (components of supply frequency f and its harmonics) along with dc component. For most supply purposes, constant direct voltage is required than that furnished by a rectifier. To reduce ac components from the rectifier output voltage a filter circuit is required. Thus filter is a device which passes dc component to the load and blocks I ac components of the rectifier output. Filter is typically constructed from reactive circuit I elements such as capacitors
Transformer
Rectifier
Filter

and/or inductors and resistors.The magnitude of output dc voltage may vary with the variation of either the input ac voltage or the magnitude of load current. Transistor: A transistor is a miniature electronic component that can work either as an amplifier or a switch.It is a three terminal device It is a contraction of "transfer resistor” which implies that it can be used as a resistor that is exactly what it is - a controllable resistance. The resistance is between the collector and emitter - we control it by applying suitable signals to the base. The three terminals of the transistor are: 1.Emitter 2.Base 3.Collector
❖ Emitter – The section that supplies the large section of majority
charge carrier is called emitter. The emitter is alway connected in forward biased with respect to the base so that it supplies the majority charge carrier to the base. The emitter-base junction injects a large amount of majority charge carrier into the base because it is heavily doped and moderate in size.
❖ Collector – The section which collects the major portion of the majority charge carrier supplied by the emitter is called a collector. The collector-base junction is always in reverse bias. Its main function is to remove the majority charges from its junction with the base. The collector section of the transistor is moderately doped, but larger in size so that it can collect most of the charge carrier supplied by the emitter.

❖ Base – The middle section of the transistor is known as the base. The base forms two circuits, the input circuit with the emitter and the output circuit with the collector. The emitter-base circuit is in forward biased and offered the low resistance to the circuit. The collector-base junction is in reverse bias and offers the higher resistance to the circuit. The base of the transistor is lightly doped and very thin due to which it offers the majority charge carrier to the base.
There are two types of transistor, namely NPN transistor and PNP transistor. The transistor which has two blocks of n-type semiconductor material and one block of P-type semiconductor
material is known as NPN transistor. Similarly, if the material has one layer of N-type material and two layers of P-type material then it is called PNP transistor. The symbol of NPN and PNP is shown in the above figure. Working principle Usually, silicon is used for making the transistor because of their high voltage rating, greater current and less temperature sensitivity. The emitter-base section kept in forward biased constitutes the base

current which flows through the base region. The magnitude of the base current is very small. The base current causes the electrons to move into the collector region or create a hole in the base region.
The base of the transistor is very thin and lightly doped because of which it has less number of electrons as compared to the emitter. The few electrons of the emitter are combined with the hole of the base region and the remaining electrons are moved towards the collector region and constitute the collector current. Thus we can say that the large collector current is obtained by varying the base region. Different types of transistor configurations: We know that generally the transistor has three terminals – emitter (E), base (B) and collector. But in the circuit connections we need four terminals, two terminals for input and another two terminals for output. To overcome these problems we use one terminal as common for both input and output actions.Using this property we construct the circuits and these structures are called transistor

configurations. Generally there are three different configurations of transistors and they are : 1.Common Base (CB) Configuration 2.Common Collector (CC) Configuration 3.Common Emitter (CE) Configuration 1.Common Base (CB) Configuration
In this configuration we use base as common terminal for both input and output signals. The configuration name itself indicates the common terminal. Here the input is applied between the base and emitter terminals and the corresponding output signal is taken between the base and collector terminals with the base terminal grounded. Here the input parameters are VEB and IE and the output parameters are VCB and IC. The input current flowing into the emitter terminal must be higher than the base current and collector current to operate the transistor, therefore the output collector current is less than the input emitter current. Current gain in common base configuration is given as α = Output current/Input current

α = IC/IE
Input Characteristics Input characteristics are obtained between input current and input voltage with constant output voltage. To obtain the input characteristics the output voltage VCB should be constant and then vary the input voltage VEB for different points then at each point record the input current IE value. With values of VEB and IE the input characteristics is drawn as shown in the figure
Rin = VEB / IE (when VCB is constant) Output characteristics Output characteristics are obtained between output current and output voltage with constant output current. To obtain the input characteristics the output current IE should be constant and then vary the input voltage VEB for different points then at each point record the input current IE value. With values of VEB and IE the input characteristics is drawn as shown in the figure

Rout = VCB / IC (when IE is constant) 2.Common Collector (CC) Configuration In this configuration we use collector terminal as common for both input and output signals. This configuration is also known as emitter follower configuration because the emitter voltage follows the base voltage. This configuration is mostly used as a buffer. These configurations are widely used in impedance matching applications because of their high input impedance.

In this configuration the input signal is applied between the base-collector region and the output is taken from the emitter-collector region. Here the input parameters are VBC and IB and the output parameters are VEC and IE. The common collector configuration has high input impedance and low output impedance. The input and output signals are in phase. Here also the emitter current is equal to the sum of collector current and the base current. Now let us calculate the current gain for this configuration Current gain in common collector configuration is given as γ = Output current/Input current γ = IE/IB
Input Characteristics The input characteristics of a common-collector configuration are obtained between inputs current IB and the input voltage VCB at constant output voltage VEC. Keep the output voltage VEC constant at different levels and vary the input voltage VBC for different points and record the IB values for each point. Now using these values we need to draw a graph between the parameters of VBC and IB at constant VEC.

Output Characteristics The operation of the common collector circuit is same as that of common emitter circuit. The output characteristics of a common collector circuit are obtained between the output voltage VEC and output current IE at constant input current IB. In the operation of common collector circuit if the base current is zero then the emitter current also becomes zero. As a result no current flows through the transistor If the base current increases then the transistor operates in active region and finally reaches to saturation region. To plot the graph first we keep the IB at constant value and we will vary the VEC value for various points, now we need to record the value of IE for each point. Repeat the same process for different IB values. Now using these values we need to plot the graph between the parameters of IE and VCE at constant values of IB. The below figure show the output characteristics of common collector.

3.Common Emitter Configuration:
In this configuration we use emitter as common terminal for both input and output. This common emitter configuration is an inverting amplifier circuit. Here the input is applied between base-emitter region and the output is taken between collector and emitter terminals. In this configuration the input parameters are VBE and IB and the output parameters are VCE and IC.

This type of configuration is mostly used in the applications of transistor based amplifiers. In this configuration the emitter current is equal to the sum of small base current and the large collector current. i.e. IE = IC + IB. We know that the ratio between collector current and emitter current gives current gain alpha in Common Base configuration similarly the ratio between collector current and base current gives the current gain beta in common emitter configuration. Current gain in common emitter configuration is given as β= Output current/Input current β= IC/IE
Input Characteristics The input characteristics of common emitter configuration are obtained between input current IB and input voltage VBE with constant output voltage VCE. Keep the output voltage VCE constant and vary the input voltage VBE for different points, now record the values of input current at each point. Now using these values we

need to draw a graph between the values of IB and VBE at constant VCE. The equation to calculate the input resistance Rin is given below. Rin = VBE/IB (when VCE is at constant) Output Characteristics Output characteristics are obtained between output current and output voltage with constant output current. To obtain the input characteristics the output current IB should be constant and then vary the input voltage VCE for different points then at each point record the input current IC value. With values of VCE and IC the output characteristics is drawn as shown in the figure
Rout = VCE/IC (when I B is at constant) Biasing: Biasing is the process of providing DC voltage which helps in the functioning of the circuit. A transistor is based in order to make the emitter base junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased, so that it maintains in active region, to work as an amplifier.

Need of biasing: Transistor Biasing is the process of setting a transistors DC operating voltage or current conditions to the correct level so that any AC input signal can be amplified correctly by the transistor.So if the transistor is to operate correctly as a linear amplifier, it must be properly biased around its operating point. Methods of transistor biasing: The following are the most commonly used methods of obtaining transistor biasing :
1. Base resistor method 2. Emitter biasing method 3. Biasing with collector feedback resistor 4. Voltage divider bias
1.Base resistor method
In this method a high resistance RB is connected between the base and positive end of supply for npn transistor.Here the required zero signal base current is provided by Vcc and it flows through RB .Now the base is positive w.r.t emitter that means

base emitter junction is forward biased.The required value of zero signal base current IB can be made to flow by selecting the proper value of base resistor.
As we know, IB = IC/ β Applying KVL to the loop ABENA, Vcc = IB RB + VBE IB RB = Vcc — VBE
RB =(Vcc — VBE)/ IB
Since VBE is quite small as compared to Vcc so it is neglected RB =Vcc/ IB
It may be observed that Vcc is a fixed known quantity and IB is chosen also e suitable value.So we can directly find the value of RB and because of this reason, this method is also known as fixed bias method. 2.Emitter biasing method:

In the emitter bias method two separate and equal d.c voltage sources are provided along with a resistor RE in the emitter circuit. Applying KVL to base emitter circuit IBRB+VBE+IERE=VEE
As we know that, IC=IE and IC= βIB. Therefore IB = IE/ β. ———-(1) Substituting eq 1 in loop eq (IE/ β) RB+VBE+IERE=VEE
So , IE=( VEE— VBE)/( RE+RB/β)= IC
It is clear that IC is dependent VBE and β,both of which change with temperature. If RE>> RB/β then IC=( VEE— VBE)/ RE
This condition makes IC independent of β. If VEE >>VBE then IC=( VEE)/ RE
This condition makes IC independent of β and VBE the Q point is not affected appreciably by the variations in these parameters. 3.Biasing with collector feedback resistor:

In this method one end of RB is connected to the base and other end to the collector.Here the required zero signal base current is determined by collector base voltage VCB. If VCB forward biases the base emitter junction then base current flows through RB.
VCC= ICRC+IBRB+VBE
IC=( VCC— VBE)/(( RB/ β) +RC) IC dependent on β, which is a temperature dependent factor.

4.Voltage divider bias: In this method two resistances R1 and R2 are connected across the supply voltage VCC and provide biasing.The name “voltage divider” comes from the voltage divider formed by R1 and R2.The voltage drop across R2 forward biases the base emitter junction. This causes the base current and hence collector current flow in the zero signal conditions.
I1=Vcc/(R1+R2) Voltage across resistance R2 V2 Applying KVL to base circuit,

So Ic doesn’t depend on β but depends on VBE and V2>>VBE so Ic is practically independent of VBE.Thus Ic is almost independent of transistor parameters and has good stabilisation.

Amplifier: An amplifier is an electronic device or circuit which is used to increase the magnitude of the signal applied to its input. Working principle of single phase CE amplifier:
The common emitter configuration can acts as an amplifier. In the above circuit, capacitors C1 and C2 are used as Coupling Capacitors to separate the AC signals from the DC biasing voltage. This ensures that the bias condition set up for the circuit to operate correctly is not affected by any additional amplifier stages, as the capacitors will only pass AC signals and block any DC component. The output AC signal is then superimposed on the biasing of the following stages. Also a bypass capacitor, CE is included in the Emitter leg circuit, which increases its gain considerably by short-circuiting the emitter resistance RE for high frequency signals, which results in the reduction of the overall transistor load. The circuit consists of voltage divider biasing, used to supply the base bias voltage as per the necessity. The voltage divider biasing has a potential divider with two resistors are connected in a way that the midpoint is used for supplying base bias voltage.One is the resistor R1 that is the one to

make the transistor to function in the forward biasing mode. The R2 is responsible to make the biasing possible. There is the load resistor and the resistor that is connected at the emitter so that it controls the stability related to thermal issue. Hence to the smaller or the weaker signals that are applied to the base gets amplified at the obtained output signals. Therefore this is the reason it is known as CE amplifier.

Oscillator: An electronic circuit used to generate the output signal with constant amplitude and constant desired frequency is called as an oscillator. It is also called as a waveform generator which incorporates both active and passive elements. There are two main types of electronic oscillator –
1. linear or harmonic oscillator 2. nonlinear or relaxation oscillator.
Linear or harmonic oscillator: The harmonic, or linear, oscillator produces a sinusoidal output. There are two types:
a) Feedback oscillator-Eg. RC oscillator,LC oscillator,Crystal oscillator
b) Negative-resistance oscillator.Eg. Ring oscillator Nonlinear or relaxation oscillator: A nonlinear or relaxation oscillator produces a non-sinusoidal output, such as a square, sawtooth or triangle wave. It consists of an energy-storing element (a capacitor or, more rarely, an inductor) and a nonlinear switching device (a latch, Schmitt trigger, or negative-resistance element) connected in a feedback loop. The switching device periodically charges and discharges the energy stored in the storage element thus causing abrupt changes in the output waveform. Working principle of basic oscillator: An oscillator does not require any external input signal to produce sinusoidal or other repetitive waveforms of desired magnitude and frequency at the output and even without use of any mechanical moving parts.

The above figure shows the block diagram of an oscillator The output oscillations are produced by the tank circuit components either as R and C or L and C. For continuously generating output without the requirement of any input from preceding stage, a feedback circuit is used. From the above block diagram, oscillator circuit produces oscillations that are further amplified by the amplifier. A feedback network gets a portion of the amplifier output and feeds it the oscillator circuit in correct phase and magnitude. Therefore, undamped electrical oscillations are produced , by continuously supplying losses that occur in the tank circuit. The main statement of the oscillator is that the oscillation is achieved through positive feedback which generates the output signal without input signal. Also, the voltage gain of the amplifier increases with the increase in the amount of positive feedback.

In order to understand this concept, let us consider a non-inverting amplifier with a voltage gain ‘A’ and a positive feedback network with feedback gain of β as shown in figure. Let us assume that a sinusoidal input signal Vs is applied at the input. Since the amplifier is non-inverting, the output signal Vo is in phase with Vs. A feedback network feeds the part of Vo to the input and the amount Vo fed back depends on the feedback network gain β. No phase shift is introduced by this feedback network and hence the feedback voltage or signal Vf is in phase with Vs. A feedback is said to be positive when the phase of the feedback signal is same as that of the input signal. The open loop gain ‘A’ of the amplifier is the ratio of output voltage to the input voltage, i.e., A = Vo/Vi

By considering the effect of feedback, the ratio of net output voltage Vo and input supply Vs called as a closed loop gain Af (gain with feedback). Af = Vo/Vs Since the feedback is positive, the input to the amplifier is generated by adding Vf to the Vs, Vi = Vs + Vf Depends on the feedback gain β, the value of the feedback voltage is varied, i.e., Vf = β Vo Substituting in the above equation, Vi = Vs + β Vo Vs = Vi – β Vo Then the gain becomes Af = Vo/ (Vi – β Vo) By dividing both numerator and denominator by Vi, we get Af = (Vo / Vi)/ (1 – β) (Vo / Vi) Af = A/ (1- A β) since A = Vo/Vi Where Aβ is the loop gain and if Aβ = 1, then Af becomes infinity. From the above expression, it is clear that even without external

input (Vs = 0), the circuit can generate the output just by feeding a part of the output as its own input. And also closed loop gain increases with increase in amount of positive feedback gain. The oscillation rate or frequency depends on amplifier or feedback network or both. The circuit will oscillate when two conditions, called as Barkhausen’s criteria are met. These two conditions are 1. The loop gain must be unity or greater 2. The feedback signal feeding back at the input must be phase shifted by 360 degrees (which is same as zero degrees). In most of the circuits, an inverting amplifier is used to produce 180 degrees phase shift and additional 180 degrees phase shift is provided by the feedback network. Important questions Short type questions: 1.Define rectifier and it’s uses. 2.Explain the need of a filter. 3.Draw the basic block diagram unregulated power supply. 4.Why biasing is needed in a transistor circuit? 5.Define amplifier and oscillator. 6.What are types of oscillator? Long type questions: 1.Describe different types of filter. 2.Explain the input and output characteristics of CE configuration. 3.Explain the working of an oscillator. 4.Explain the working principle of single phase CE amplifier.

Chapter 3 Communication system
Communication is the transfer of information from one point in space and time to another point.
1.Information source :- The objective of any communication system is to convey information from one point to the other. The information comes from the information source, which originates it..It converts this information into physical quantity.The physical manifestation of the information is termed as message signal. 2.Transmitter :- The objective of the transmitter block is to collect the incoming message signal and modify it in a suitable fashion (if needed), such that, it can be transmitted via the chosen channel to the receiving point.The functionality of the transmitter block is mainly decided by the type or nature of the channel chosen for communication.

3.Channel :- Channel is the physical medium which connects the transmitter with that of the receiver.The physical medium includes copper wire, coaxial cable, fibre optic cable, wave guide and free space or atmosphere.The choice of a particular channel depends on the feasibility and also the purpose of the communication system. 4.Receiver:- The receiver block receives the incoming modified version of the message signal from the channel and processes it to recreate the original (non-electrical) form of the message signal. There are a great variety of receivers in communication systems, depending on the processing required to recreate the original message signal and also final presentation of the message to the destination. 5.Destination/User of information:- The destination is the final block in the communication system which receives the message signal and processes it to comprehend the information present in it. The transmission of information and reception of meaningful information can be successfully achieved with the help of two processes. The two processes are 1. Modulation 2. Demodulation Modulation : Modulation is the process of combining the low-frequency audio waves with a very-high frequency radio waves. The low-frequency wave is called Modulating Wave. The very-high frequency radio wave which carries the low frequency audio wave information is called a Carrier Wave. The resultant wave obtained is called Modulated Carrier. Demodulation : Demodulation involves recovering the low-frequency audio wave from the ModulatedCarrier Wave. This

process is performed at the receiving end. It is the reverse process of modulation.
Sl no. Modulation Demodulation
1. Influencing data Recovering data
2. At transmitter side At receiver side
The modulation is divided into following types: 1.Amplitude modulation 2.Frequency modulation 3.Phase modulation Amplitude modulation: Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. When the amplitude of high frequency carrier wave is changed in accordance with the intensity of the signal, it is called amplitude modulation. In this modulation, only the amplitude of the carrier wave is changed in accordance with the intensity of the signal and the frequency of the modulated wave remains the same i.e. carrier frequency. Amplitude modulation was the earliest modulation technique used to transmit voice signals by radio signals. Amplitude modulation is still used in many forms of communication; for example, it is used in portable two-way radios, citizens band radio, VHF aircraft radio, and in computer modems in the form of QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation).

Frequency modulation: When the frequency of carrier wave is changed in accordance with the intensity of the signal, it is called frequency modulation (FM). In frequency modulation, only the frequency of the carrier wave is changed in accordance with the signal and the amplitude of the modulated wave remains the same i.e. carrier wave amplitude.

Phase modulation: In this modulation technique, the phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. It is a form of modulation that can be used for radio signals used for a variety of radio communications applications. As will be seen later, phase modulation, and frequency modulation are closely linked together and it is often used in many transmitters and receivers used for a variety of radio communications applications from two way radio communications links, mobile radio communications and even maritime mobile radio communications.


Important questions: Short questions 1.What are elements of a communication system? 2.Define modulation and demodulation. 3.What are types of modulations? 4.Define amplitude and frequency modulation. 5.What do you mean by phase modulation. Long questions 1.Explain the communication system with the help block diagram. 2.Describe different types of modulation methods. 3.Differentiate between different types of modulation methods.
Chapter 4 Transducers and measuring instruments
Transducer: It is a device that converts variations in a physical quantity, such as pressure or brightness, into an electrical signal, or vice versa.
(Or) A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Sensors: It is a device which detects or measures a physical property and records, indicates, or otherwise responds to it. Difference between sensor and transducer The primary function of the sensor is to sense the physical changes, whereas the transducer converts the physical quantities into an electrical signal. The accelerometer, barometer, gyroscope are the examples of the sensors whereas the thermistor, and thermocouple is the examples of the transducer.

The transducers can be classified as: 1.Active and passive transducers. 2.Analog and digital transducers. On the basis of transduction principle used: 1. Primary and secondary transducer 2.Transducers and inverse transducers. Active transducers: Active transducers are those which do not require any power source for their operation. They work on the energy conversion principle. They produce an electrical signal proportional to the input (physical quantity). For example, a thermocouple is an active transducer. Passive transducer: Passive transducer is a device which converts the given non-electrical energy into electrical energy by external force. Resistance strain gauge, Differential Transformer are the examples for the Passive transducers. Photoemissive cell: A photoemissive cell, commonly known as a phototube, makes use of the photoelectric effect, the phenomenon whereby light-sensitive surfaces give off electrons when struck by light. Photoemissive cells are sometimes called photocells or electric eyes. A phototube consists of a vacuum tube, housed in glass or quartz, containing two electrodes: a curved surface called a cathode and a slender rod called an anode. The cathode is made of a photoemissive material, so that when light strikes the cathode, it emits electrons. In a vacuum phototube, the brighter the light that strikes the cathode, the greater the number of electrons that are released and the greater the current that flows through the tube. Thus any change in the brightness, or intensity, of the light falling on the tube instantly results in a change in the flow of electric current. Many

photoelectric devices depend on a changing light intensity to operate. The electric current may be increased if the tube is filled with an inert gas, such as helium or argon. The response of a gas-filled phototube, however, is not uniformly proportional to the light intensity. As a result, such units may be unsuitable for certain applications.
Photoconductive cell: These cells, also known as photo-resistors, contain a thin film of certain semiconductor materials deposited over a ceramic. When these semiconductor materials are exposed to light, their electrical conductivity is increased. Typically the film is made of lead or calcium sulphides or tellurides.The materials used to make the films in photoconductive cells are generally poor electrical-current conductors because their electrons are unable to move freely within the material when an electrical voltage is applied.

When these semiconductor materials are exposed to light, their electrical conductivity is increased. Typically the film is made of lead or calcium sulfides or tellurides. The materials used to make the films in photoconductive cells are generally poor electrical-current conductors because their electrons are unable to move freely within the material when an electrical voltage is applied. Light directed on such materials is absorbed by some electrons, however, freeing them to pass more easily from one atom to the next. When photoconductive materials are removed from the light, the freed electrons return to their more tightly bound state.
Photovoltaic cell: In photovoltaic cells a small voltage is generated when light strikes the junction between a metal and a semiconductor or a junction

between two different semiconductors. These devices are also called solar cells when they operate with light from the sun. The term photovoltaic effect is given to this process in which two dissimilar materials in close contact act as an electric cell when struck by light. As with the materials used in photoconductive devices, the electrons in the photovoltaic materials are usually not free to move from atom to atom. It has been proven with experiments that when light strikes electrons, however, it provides the energy needed to free some of them from their bound condition.
Multimeter: A multimeter or a multi-tester, also known as a VOM (volt-ohm-milliammeter), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. Application of multimeter: ➢ Testing voltage ➢ Testing current ➢ Testing resistance

Analog multimeter: An analog multimeter is a PMMC meter. It works based on the d'Arsonval galvanometer principle. It consists a needle to indicate the measured value on the scale. A coil moves in a magnetic field when current passes through it. Digital multimeter: A digital multimeter is a test tool used to measure two or more electrical values—principally voltage (volts), current (amps) and resistance (ohms). It is a standard diagnostic tool for technicians in the electrical/electronic industries. COMPARISON BETWEEN ANALOG AND DIGITAL MULTIMETER
Analog multimeter Digital multimeter
Analog multimeter use a needle and calibrated scale to indicate values
digital multimeters display those values in a digital display.
It is little complicated to read and adjust proper range than digital multimeter.
Digital meters are easier to read and adjust to a proper range required for the circuit or device.
It has low impedance than digital voltmeter.
It has 50 times more impedance than analog voltmeter.
It is less accurate. digital meters are more accurate
It is difficult to measure smaller values.
Digital meters are often capable of measuring smaller current in microamperes and easier than analog ammeters.
Many analog ohmmeter will, when switched to the ohm function, reverse the polarity of the tested leads.
This problem is not happened in digital ohmmeter.

Digital multimeter

Analog multimeter

Working principle of multimeter: Input signal: It is basically the signal i.e. voltage to be measured. Pulse generator: Actually it is a voltage source. It uses digital, analog or both techniques to generate a rectangular pulse. The width and frequency of the rectangular pulse is controlled by the digital circuitry inside the generator while amplitude and rise and fall time is controlled by analog circuitry. AND gate: It gives high output only when both the inputs are high. When a train pulse is fed to it along with rectangular pulse, it provides us an output having train pulses with duration as same as the rectangular pulse from the pulse generator
CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope): The cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) is a type of electrical instrument which is used for showing the measurement and analysis of waveforms and others electronic and electrical phenomenon. It is a very fast X-Y plotter shows the input signal versus another signal or versus time.It is basically a graph displaying device. It draws a graph of an electric signal. It is an electronic test instrument, which is used to obtain waveforms when the differential input signals are given.

The major blocks in general-purpose CRO are 1.Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) 2.Horizontal Deflection System 3.Vertical Deflection System 4.Power Supply 1.Cathode Ray Tube (CRT): CRT is an essential part of CRO. This is also used in the Monochrome picture tube. CRT consists of an electron gun that produces an electron beam. This is a narrow beam that passes through the tube and falls on the screen. The point at which the electron beam will strike that point will glow due to the coating of fluorescent material on the screen.

Main parts of CRT are – ➢ Electron Gum Assembly ➢ Deflection plate assembly ➢ Fluorescent Screen ➢ Glass Tube
Block diagram of CRT
2. Horizontal Deflection System: It has the following blocks: ❖ Time Base Generator ❖ Trigger Circuit ❖ Horizontal Amplifier
Time Base Generator: Time Base Generator is used to generate a sawtooth voltage which is applied to horizontal deflection plates. Which is generated due to the voltage decrease to zero must be fast so the beam can very rapidly move from right to left.

Trigger Circuit:Trigger Circuit triggers the time base generator to generate a sawtooth waveform when the vertical input signal is present. It is used to convert the incoming signal into a trigger pulse so that the input signal and the sweep frequency can be synchronised. Horizontal Amplifier:A horizontal Amplifier is used to amplify the sawtooth voltage before it is applied to horizontal deflection plates. 3. Vertical Deflection System: It consists of the following parts Attenuator Vertical Amplifier Delay Line Attenuator An attenuator is a voltage divider network consisting of a number of resistors. By selecting the proper resistor, the corresponding voltage is obtained. Vertical Amplifier Vertical Amplifier is a wideband amplifier used to amplify the signal in the vertical section of the signal. Delay Line Delay Line is used to delaying signals for some time in the vertical section. 4. Power Supply: There are two power supplies- a) Negative high voltage (HV) Supply b) Positive low voltage supply (LV). The +ve voltage supply is from +300V to 400V, the negative voltage supply is from -1000 V to -1500 V.

Important questions: Short type questions: 1.Define transducer and sensors. 2.Give some examples of transducers 3.What are different types of transducers? 4.What do you mean by active and passive transducer? 5.Define multimeter. Long type questions: 1.Explain the working principle of photo emissive, photoconductive transducer. 2.Describe CRO with neat block diagram. 3.Differentiate between analog and digital multimeter.










![$$ 5 - . 1 ) $ · ... PN junction, Junction Theory, VI characteristics of PN junction diode, Ideal diode, Static and Dynamic Resistance [1][2], Diode current equation[2],Diode notations](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ae6f8997f8b9a29048e3147/-5-1-pn-junction-junction-theory-vi-characteristics-of-pn-junction.jpg)

