By: Emily Drake & Baylie Wilson. Functional: Diarthroses (freely moving) Structural: Synovial...
-
Upload
alexander-phillips -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
2
Transcript of By: Emily Drake & Baylie Wilson. Functional: Diarthroses (freely moving) Structural: Synovial...

KNEE JOINTBy: Emily Drake & Baylie Wilson

Classification
Functional: Diarthroses (freely moving)
Structural: Synovial joint (filled with synovial fluid)
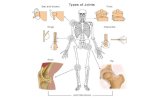
The knee joint is a hinge type synovial joint
Allows for flexion and extension
formed by articulations between the patella, femur and tibia
The shape of the knee joint makes it weak so it relies on muscles and ligaments for stability

Meniscus
Medial and lateral menisci are fibrocartilage structures in the knee that serve two functions:
1. increase stability of the joint.2. To act as shock absorbers.
They are C shaped on both the lateral and the medial condyles
The Menisci keep your knee steady by balancing your weight across the knee
The lateral meniscus is smaller making it fairly mobile

Meniscus Tear A tear in the fibrocartilage
Usually caused by twisting or turning quickly, often with the foot planted and the knee is bent
Minor tear Slight pain and swelling
Usually goes away on its own in 2-3 weeks with rest and ice
Moderate tear Pain at the side or center of your knee
Swelling gets worse over 2 or 3 days
Can heal itself in 1 or 2 weeks with rest and ice
Severe tear Pieces of the meniscus move around in joint
May not be able to straighten it
Swell and become stiff
Surgery may or may not fix the tear

ACL & PCL
Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Posterior Cruciate Ligament cross each other to connect the femur and the tibia
ACL Attached at the anterior region of the tibia and the posterior region of
the femur in the intercondylar fossa It prevents anterior dislocation of the tibia onto the femur.
PCL Attached at the posterior region of the tibia, and anterior of the femur
in the intercondylar fossa It prevents posterior dislocation of the tibia onto the femur.

ACL & PLC Tears A partial or complete tear in the ligament ACL tear
Caused by Twisting your knee with the foot planted Getting hit on the knee Extending the knee too far Jumping and landing on a flexed knee Stopping suddenly when running
Treatment Surgery with ligament graft from the hamstring or Achilles to replace the ACL
PCL tear Caused by
Hitting the knee Falling on the knee while it's bent
Treatment Physical therapy Graft surgery

Collateral Ligaments
Two strap-like ligaments They act to stabilize the hinge motion of the knee,
preventing any medial or lateral movement Tibial (medial) collateral ligament
A wide and flat ligament, found on the medial side of the joint. Proximally, it attaches to the medial epicondyle of the femur, distally it attaches to the medal surface of the tibia.
Fibular (lateral) collateral ligament
Thinner and rounder than the tibial collateral, this attaches proximally to the lateral epicondyle of the femur, distally it attaches to a depression on the lateral surface of the fibular head.

Patellar Ligament
A continuation of the quadriceps femoris tendon distal to the patella. It attaches to the tibial tuberosity.
It holds the knee cap in place

Dislocated Knee Cap
Patellar Subluxation The kneecap slides abnormally or dislocates along the
thigh bone during activity Knee pain around the patella and shifted patella
Causes Sudden change in direction
Direct hit to the patella
Treatment Place knee straight and pop it back in place Surgery is rare Ice and elevate

Sources
Knee Joint. (n.d.). Retrieved March 24, 2015, from http://
www.innerbody.com/image/skel16.htm l
Knee joint. (n.d.). Retrieved March 24, 2015, from http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=8845
(n.d.). Retrieved March 24, 2015, from http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/knee.../picture-of-the-knee