Synovial Final2
-
Upload
iles-reen-chan-alvarez -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
Transcript of Synovial Final2
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
1/24
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
2/24
I. Physiology & Composition Movable joints (diarthroses) composed of: Bones lined with articular cartilage
Separated by a cavity containing synovial fluid enclosed in asynovial membrane
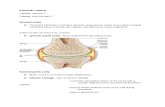
Synovial membrane
synoviocytes: Phagocyticsynthesizes degradative enzymes
Synthesizes hyaluronate
Connective tissue Blood vessels, lymphatics & nerves
Fluid formation Ultrafiltrate of plasma across synovial membrane Non selective
Excludes proteins of high molecular weight
Synoviocytes Secrete mucopolysaccharite which contains:
Hyaluronic acid
protein
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
3/24
Cartilage & fluid function: Reduce friction between bones Lubricates joints Fluid provides nutrients to cartilage
Lessens shock of walking and jogging impactSynovial Fluid Normal ValuesVolume
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
4/24
Collection: arthrocentesisneedle aspiration ofsynovial fluid
Volume: Normal= 3.5 mL
Diseased / inflamed = up to 25 mL
Collect 2 tubes Heparin tube : microbiology
Plain top: chemistry and immunology EDTA (liquid) : hematology
*Avoid all powdered anticoagulantsinterfere with crystalanalysis
Fluid verification
Mucin clot test- Add fluid to dilute acetic acid turbidity (clot formation) due
to hyaluronate
Metachromatic staining Place fluid on filter paper + few drops of toluidine blue
metachromatic staining
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
5/24
Color: Normalclear, pale yellow
Red to brown: indicates trauma of procedure ordisorder Turbidity: associated with presence of WBCs Milky: may indicate presence of crystals
Viscosity:
Measured at bedside by ability to form a string from tipof syringeNormal: 4-6 cm
Ropes test (mucin clot test)measurement ofhyaluronate polymerizationFluid forms a clot surrounded by clear fluid when added to
acetic acidClot quality is reported:Good = solid clot
Fair = soft clot
Poor = friable clot
Very poor = no clot
Test is of questionable precision and seldom used
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
6/24
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
7/24
Cell CountWBCs Method
Use Neubauer counting chamber May pretreat viscous fluids with hyaluronidase & incubate
at 37oC for 5 min. Dilution with hypotonic saline is used to lyse any RBCs OR Dilute with normal saline/methylene blue mixture to
differentiate WBCs from RBCs
Normal =
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
8/24
Other cell abnormalities: Increased eosinophilsrheumatic fever, parasitic
infections, metastatic carcinoma, post radiationtherapy or arthrography
LE cellspatients with lupus erythematosus
Reiter cellsmacrophages with ingested neutrophils
RA cells (ragocytes)precipitated rheumatoid factor
appearing as cytoplasmic granules in neutrophils
Hemosiderin granulesdue to hemorrhagic process
or cases of pigmented villonodular synovitis
Cartilaginous cellsobserved in cases of osteoarthritis
Rice bodiesfound in septic and rheumatoid arthritisand Tuberculosis
Fat dropletsindicate traumatic injury
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
9/24
Synovial lining cell
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
10/24
Neutrophils in synovial fluid
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
11/24
Lymphs in synovial fluid
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
12/24
LE cell in synovial fluid
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
13/24
Crystals Crystal formation may be due to: Metabolic disorders Decreased renal excretion
Cartilage and bone degeneration Medicinal injection (ex: corticosteroids)
Fluid is examined using the wet preparation technique ASAP examination as pH and temperature affect observation Ideally examined prior to WBC disintegration Examine under both direct and compensated polarizing light
*may also be observed in Wright stain preparations Under polarizing light (Direct polarization) Birefringent substances appear as bright objects on a black
background Intensity varies between substances
Under compensated polarizing light
A red compensator plate is placed between the crystal and slide Crystals aligned parallel to the compensator appear yellow
(negative birefringence) Crystals aligned perpendicular to the compensator appear blue
(positive birefringence)
M di U t C t l (MSU)
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
14/24
Monosodium Urate Crystals (MSU)
Indicate gouty arthritis due to: Increased serum uric acid
Decreased renal excretion of uric acid
Impaired metabolism of nucleic acid
Exhibit negative birefringence Intracellular (acute stages) & extracellular location
Polarized lightstrongly birefringent
Compensated polarized lightyellow when parallel
blue when perpendicular
Needle shaped Calcium pyrophosphate (CCPD) Indicates pseudogout due to: Degenerative arthritis
Endocrine disorders with increased serum calcium
Calcification of cartilage
Exhibit positive birefringence Seen intracellular- and extracellularly
Polarized lightweakly birefringent
Compensated polarized lightblue when parallel (yellow whenperpendicular)
Blunt rods or rhombic shapes
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
15/24
Acute gout (uric acid crystals)
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
16/24
Uric acid crystals
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
17/24
Cholesterol
Nonspecific indications Associated with chronic inflammation
Exhibit negative birefringence (compensated polarized light)
Usually seen extracellularly Polarized lightstrongly birefringence
Rhombic plates
Hydroxyapatite (HA) (Calcium phosphate)
Associated with calcific deposition conditions
May produce an acute inflammatory reaction
Intracellular
Not birefringent
Require an electron microscope to examine
Small, needle shaped
Corticosteroid Associated with intra-articular injections; NO clinical significance
Primarily intracellular
Exhibit positive and negative birefringence Can closely resemble MSU and CCPD
Flat, variable shaped plates
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
18/24
Calcium Oxalate
Following renal dialysis
Birefringent Artifacts:
Anticoagulant crystals (calcium oxalate, lithiumheparin)
Starch granules
Prosthesis fragments
Collagen fibers
Fibrin
Dust particles
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
19/24
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
20/24
Glucose Done simultaneously with blood sample (prefer 8 hour
fast)
Difference between blood and synovial glucose valuesis evaluated Normal = < 10 mg/dL Inflammatory conditions = > 25mg/dL Sepsis = >40 mg/dL Considered low if < serum plasma glucose value
Should be run within 1 hour of collection Draw in sodium fluorideprevents glycolysis
Total protein Not routinely performed Normal = < 1/3 of serum value (~3g/dL)
Large molecule, not easily filtered by membrane Increased protein Changes in membrane permeability Increased joint synthesis Indicates an inflammatory process
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
21/24
Uric Acid
Alone, not diagnostic
May determine gout in conjunction with plasma uric
acid, esp. when crystals are undetectable Normal = serum level
Lactate
May differentiate between inflammatory and septicarthritis
Septic arthritis = >250 mg/dL
Gonococcal arthritis = normal to low levels
Production results from :
Increased demand for energy
Tissue hypoxia Severe inflammatory conditions
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
22/24
Gram stain
Performed on all specimens Most infections are bacterial:
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
S. pyogenes
S. pneumoniae Hemophilus
Neisseria gonorrhea
Fungal, viral and tubercular agents may also beobserved
Culture Routine culture
Enrichment medium (chocolate agar
Specialty media depending on clinician orders and
indications
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
23/24
Autoantibody detection (same as
found in serum)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Lupus erythematosus (LE)
Antibody detection in patients serum
Borrelia burgdorferi
Causative agent of Lyme disease Cause of arthritis
-
7/28/2019 Synovial Final2
24/24
Group Classification SignificanceI. Noninflammatory Degenerative joint disorders
II. Inflammatory Immunologic problems (RA,LE)Gout&pseudogout(crystal induced)
I. Septic Microbial infectionII. Hemorrhagic Traumatic injury
Coagulation deficiency
Note:
* categories overlap* multiple conditions can occur simultaneously* disease stage can vary laboratory results
*see text for details of associated abnormal laboratoryfindings