Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
-
Upload
pratiwi-akbar -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
1/81
The structure and organization
of eukaryotic cell
by:
dr.Sutrisno Darmosumarto, Sp.A
Histology & Cell Biology Department
Gadjah Mada ni!ersity
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
2/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
3/81
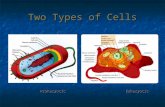
The basic structure of cell
• Cellular membrane, covers
• Cytoplasm, contains nucleus,
organelles and inclusions
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
4/81
Organelles
• Permanent
• Performing cell activities
• E.g. mitochondria, !olgi apparatus,lysosome, smooth and rough endoplasmic
reticulum etc
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
5/81
"nclusions
• Temporary
• #etabolic products
• E.g. glycogen granules, mucinogenglobule, zymogen granule, melanin
granule etc
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
6/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
7/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
8/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
9/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
10/81
$asic activities of cell
• #etabolism, divided into
anabolism and catabolism• Concerning %ith irritability
• &eproduction
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
11/81
C"## C$M%$"'S
• The cell is composed of ' basic parts
(ytoplasm and nu(leus
• "ndividual cytoplasmic components not
clearly visible in (E)stained preparations
• the nucleus intensely stained dark blue
or black
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
12/81
Cell Membrane
• composed of phospholipids, protein, and, to a
lesser e*tent, polysaccharides.
• The functions
selective barrier regulates the passage of certainmaterials into and out of the cell.
facilitate the transport of specific materials through
this limiting barrier
carry out a number of specific recognition andregulatory functions
+. to - nm in thickness visible only in the E#.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
13/81
Cytoplasm
• composed of a matri* embedded
several structures classified into / groups
• organelles
• inclusions
• other components
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
14/81
'he (hara(teristi(s o)
(ytoplasmi( (omponents
-. organelles presents in all eukaryotic cells enclosed in a membrane, and contain enzymesthat participate in cellular metabolic activity permanent components of the cytoplasm 0theendoplasmic reticulum, the mitochondria, the!olgi apparatus, and the lysosome1.
'. The inclusions temporary components,accumulations of pigment, lipids, proteins, orcarbohydrates
/. The other components the centrioles,microtubules, and microfilaments.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
15/81
Mito(hondria*.
• composed of an e*ternal membrane andan internal membrane
• "nternal membrane pro2ects folds the
crista.
• These membranes surround a space
spaium intermembrane
• 3pace bet%een the cristae matri*
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
16/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
17/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
18/81
Mito(hondria
• transform the chemical energy
into available energy stored in
4TP• release energy re5uired to
perform any type of %ork 0be of
osmotic, mechanical, electrical, or
chemical nature1
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
19/81
" + & +ibosomes
• flattened, rounded, or tubular vesicles anastomose %ith one another in a net%orkform
• ' types of E& 6 granular 0rough1 andagranular 0smooth1
• The membranes of the E& continuous
%ith the nuclear envelope membrane.• usually arranged in the form of flattened
cisternae stacked in parallel
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
20/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
21/81
The relevance of E&
• 7ithout E& 8 cytosol is proteinaceous gel
8 traffic of substances by diffusion
the interior of cell
the most difficult to reach
enzymes difficult to be distributed as rapid a neededat appropriate site
%aste product 9 essential building block accumulateat useless:to*ic concentration
• 7ith E& form an intracellular circulatory system for enzyme,
vital substances and secrete:e*crete
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
22/81
&ibosome
• small, electron)dense particles, -6'nm in diameter, attached to the outer
surfaces of the membranes composedof &;4 and protein the basophilia inthe cytoplasm
• &ibosomes can appear as isolatedgranules free in the cytoplasm, or linked ingroups called polysomes.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
23/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
24/81
ifferent intracellular p( values
• #anifestation of cellular heterogenicity
• 3egregation synthesized protein in &E&lumen
• 3upplementary mechanical support for
colloidal structure• 4ctive transport
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
25/81
3mooth E&
• no ribosomes• very abundant in the liver cell• entirely of membranes as profusely
anastomosing tubules or flat cisternae• participates in the contraction of muscle cells• >eto*ification• ?ipid synthesis
• involved in the synthesis of the glycogen in livercells glucose)@)phosphatase found %ithinits membranes
• glycogenolysis
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
26/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
27/81
Golgi Apparatus
• group of piled)up flat vesicles %ith
peripheral dilatations
• occupies a finite and fi*ed area in
the cytoplasm of most cells0supranuclear1
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
28/81
!olgi app=.
• plays a role in the process of synthesis,
concentration, and storage of secretory)
products of most glandular cells.
• The proteins synthesized enclosed by a
membrane to form secretory granules.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
29/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
30/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
31/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
32/81
3ecretory patha%ay
-. ribosomal stage
'. cisternal stage
/. intracellular transportA. concentration of secretory protein
. intracellular storage
@. e*ocytosis
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
33/81
-. &ibosomal stage
• 3ynthesized on polysome attached to E&
• Bolume '
• ++ surface area• Produce protein simultaneously
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
34/81
'. Cisternal stage
• 3egregate by vectorial transport
• 3ignal peptidase on cisternal surface
•
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
35/81
/. "ntracellular transport
-. from &E& to !olgi
'. from !olgi to condensing vacuole
8 connected by membrane tubules,formed intermittenly
8 !E&? e*pand to condensed vacuole
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
36/81
A. concentration
• ' 8 ' folds
• "ntracellular protein gradient forced
concentration
• 3ecretory protein , basic 0D1 charge
• Polyanion macromolecules 0)1 charge
• ?o%er osmotic pressure (' e*it by nonenergy re5uiring process
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
37/81
. "ntracellular storage
• ' 8 -. nm
• Contain all types of inactive enzymes
• &each apical part
microtubulesassistance
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
38/81
@.>ischarge
• Energy dependent process
• (ormonal:neuronal stimulation
• "nvolve 'nd
messenger CaDD
:c4#P• 3ecretory membrane fuse %ith plasma
membrane
• Tight 2unction prevent autodigestion
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
39/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
40/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
41/81
#ysosomes
• membrane)bound vesicles contain lyticenzymes intracytoplasmic digestion
• particularly abundant in cells e*hibiting
phagocytic activity 0eg, macrophages, %hiteblood cells1.
• usually spherical, diameter .' to . :µm
• The enveloping single membrane serves to
separate the lytic enzymes from the cytoplasm prevents the attacking and digestingcytoplasmic organelles.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
42/81
#ysosome*
• ?ysosomal enzymes
synthesized in &E& , transferredto the !olgi apparatus
packaged into vesicular
lysosomes
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
43/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
44/81
MC+$'B#"S, MC+$-#AM"'S, & '"+M"DA'"
-#AM"'S
• "n addition to the membrane)bound organ)
elles, the cytoplasmic matri* e*hibits a
comple* net%ork consisting of
microtubules, microfilaments, andintermediate filaments provide for the
form and shaping of cells , also important
in cytoplasmic and cellular movement.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
45/81
Mi(rotubules
• rod) or pipe)like organelles microtubules.
• outer diameter of 'A nm consisting of adense %all nm thick and a less dense
0possibly hollo%1 core -A nm %ide.
• lengths are variable
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
46/81
#icrotubules=
• Composed of proteinaceous subunits 0 tubulin .
• Tubulin, a heterodimer, is a molecule consisting
of ' non)identical monomers 0 alfa and beta
tubulins1.• $oth tubulins , #7 about @,
• nder appropriate conditions tubulin subunits
polymerize into typical microtubules.• 4 total of -/ protofilaments generally comprise
the %all of a microtubule .
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
47/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
48/81
Cilia and flagella
• motile processes highly organizedmicrotubule core e*tend from the surface ofmany different cell types.
•Ciliated cells
possess a large number of cilia 0' to - :um in length1.
•
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
49/81
ntermediate -ilaments
• kno%n as tonofilaments diameter of F)- nm.
• be involved %ith the Gslo%G component ofa*oplasmic transport, as a smooth muscle
cytoskeletal component, in pigment granulemovement, as a 2unctional comple* structuralelement, and %ith cell spreading.
• possess an actin core follo%ing brief
trypsinization
the filaments bind heavymeromyosin 0 a functional assay normally usedto identify actin1
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
50/81
Cytoplasmi( n(lusions
• transitory components of the cytoplasm
lipid droplets, carbohydrateaccumulations 0glycogen1, secretory
granules, colored substances 0melanin
pigment and lipofuscin1
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
51/81
'H" C#"S
• a rounded or elongated structure in the
center of the cell.• its diameter varies to - :um.
• is composed of the nuclear envelope,
chromatin, the nucleolus, andnucleoplasm .
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
52/81
The functions of nucleus
• &egulate cell activities
• &eproduction
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
53/81
Chromatin
• 4 comple* of >;4 9 histone
Composes of
•>;4 8 /-
• &;4 8
• (istone 8 /@
• ;on histone) 'F
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
54/81
The function of >;4
• >;4 0transcription1 &;4
0translation1 protein
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
55/81
Composition of >;4
• ) PE;TO3E 0deo*yribose1
• ) $43E 8 Purine ) adenine
) guanine
H Pyrimidines ) thymidine
) cytosine
) P(O3P(O&"C 4C"> 0(/POA1
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
56/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
57/81
Composition of &;4
• ) PE;TO3E 0ribose1
• ) $43E
8 Purine ) adenine
) guanosine
8 Pyrimidine
) uracyl
) cytosin
• HP(O3P(O&"C 4C">
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
58/81
Barious &;4
• / ma2or classes
) messenger &;4
) transfer &;4) ribosomal &;4
• ' minor classes
) heterogenous nuclear &;4) small cytoplasmic &;4
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
59/81
The plasma membrane
• "s about F nm thick
• 3urrounds the cell and controls chemical
traffic into and out of the cell
• is selectively permeableI it allo%s some
substances to cross more easily than
others
• (as a uni5ue structure %hich determines
its function and solubility characteristics
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
60/81
?ipid in plasma membrane
• The lipids in the plasma membrane are
chiefly phospholipids like phosphatidyl
ethanolamine and cholesterol.
• Phospholipids are amphiphilic %ith the
hydrocarbon tail of the molecule being
hydrophobicI its polar head hydrophilic.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
61/81
?ipid bilayer
• Cell membrane is made of a phospholipidbilayer sand%ichedbet%een t%o layers of globular protein.
8 The polar 0hydrophilic1 heads of phospholipidsare oriented to%ards the protein layersforming a hydrophilic zone.
8 The nonpolar 0hydrophobic1 tails of
phospholipids are oriented in bet%een polarheads forming a hydrophobic zone.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
62/81
&ole of membrane protein
• transport of molecules:ions into or out of cells.
Three methods of doing this are through active,
facilitated or passive transport.
• cell recognition• enzymatic activity
• receptors
• cell to cell communication• attachment to the cytoskeleton and e*tracellular
matri*
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
63/81
&ole of membrane protein
• transport of molecules:ions into or out of cells.
Three methods of doing this are through active,
facilitated or passive transport.
• cell recognition,• enzymatic activity
• receptors,
• cell to cell communication,• attachment to the cytoskeleton and e*tracellular
matri*
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
64/81
Transport ion:molecule
• T%o %ays that molecules pass through
transmembrane proteins
8 uniport ) %hich is %here one molecule is transported,
8 cotransport ) %here ' molecules are transferred. t%obasic types of cotransport
• symport, %hich is %here t%o molecules are transported
in the same direction and
• antiport, %here the molecules are transported opposite
directions through the membrane 0%hich %ill be sho%n
by the ;a ) J 4TPase pump1.
http://www.cbc.umn.edu/~mwd/cell_www/glossary.htmlhttp://www.cbc.umn.edu/~mwd/cell_www/glossary.html
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
65/81
Types of transport
• Passive Transport
8 uncharged small molecules can move directly
through the membrane in the direction of high
concentration to lo% concentration. 8 charge molecule 0positive or negative1 tend
to move to the side of the membrane that
have the opposite electrical potential.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
66/81
Types of transport=
•
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
67/81
Types of transport=
• 4ctive Transport 0these can be either
uniport or cotransport1
8 re5uire energy, is going
8 against the electro)chemical gradient. 4ne*ample of this can be found in the ;a ) J
4TPase 0The 3odium)Potassium 4TPase
pump1, this is important especially in thenerves of all animals. This is commonly used
to generate a membrane potential
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
68/81
Transport of large molecules
• "ndo(ytosis
• "/o(ytosis
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
69/81
Cell division
• #itotic division• #eiotic division
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
70/81
Mitoti( di!ision
• >uring mitosis the mother cell divides
and each of the daughter cells receives achromosomal karyotype identical to that of
the mother cell
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
71/81
Prophase
• characterized by the gradual coiling up ofchromatin of the nucleus giving rise to severalindividualized rod)shaped or hairpin)shapedbodies that stain intensely 0the (hromosomes
• The nuclear envelope remains unaltered, and thechromosomes appear coiled in the nucleus. Thecentrioles duplicate and separate, and a pairmigrates to each pole of the cell.
• 3imultaneously, the microtubules of the mitoticspindle appear bet%een the ' pairs of centrioles .
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
72/81
#etaphase
• the nuclear envelope and the nucleolusdisappear.
• The chromosomes migrate to the
e5uatorial plane of the cell, %here each di)• vides longitudinally to form ' chromatids.
• These attach to the microtubules of the
mitotic spindle at a special pla5uelike,electron)dense region, the (entromere01ineto(hore .
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
73/81
4naphase
• the sister chromatids separate from
each other and migrate to%ard the
opposite poles of the cell, follo%ing the
direction of the spindle microtubules.• Throughout this process, the centromeres
move from the center, pulling along the
remainder of the chromosome .
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
74/81
Telophase
• characterized by the reappearance of nuclei inthe daughter cells.
• The chromosomes revert to their semidispersedstate and the nucleoli, chromatin, and nuclear
envelope reappear.• a constriction develops at the level of the
e5uatorial plane of the mother cell andprogresses until it divides the cytoplasm and itsorganelles in half .
• 4n accumulation of microfilaments occursbeneath the cell membrane in the region ofmitotic constriction.
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
75/81
#eiotic division
• !erminal cells 0spermatogonium or
oogonium1
• !oes through ' successive divisions
• &eduction by half of the number of
chromosomes and amount of >;4 per cell
producing spermatid
• Through an elaborate process of
cytodifferentiation spermatozoon
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
76/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
77/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
78/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
79/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
80/81
-
8/17/2019 Bio sel - The structure and organization of eukaryotic cell.ppt
81/81