Year 11 GCSE PE Sports Injuries
description
Transcript of Year 11 GCSE PE Sports Injuries

Year 11 GCSE PE
Sports Injuries

Sports InjuriesLearning Objectives:1.Be able to explain how sports injuries are caused2. To develop an understanding of the different types of sports injuries and how to medically treat them.
Starter:1.What is the purpose of a warm up and what are the stages of a warm up? (3 minutes)

A* Answer.
A warm up before taking part in any form of exercise is essential. It is called a warm up because the bodies temperature increases when heat is produced as a by product of muscular action. The range of movement is increased, preventing straining or pulling of the muscles. It is also for Psychological preparation as it helps players prepare mentally for training/competition.

Stages of a Warm Up
1.Pulse raisersIncludes activities like light jogging, which will
increase the HR and therefore the movement of Oxygen and Glycogen stores to the muscles that need energy. This also warms the synovial fluid
and makes joints more mobile.

Stages of a Warm up
2. Flexibility/ stretchingStretching exercises will increase the range of
movement at the joint and help to prevent muscle ligament and tendon damage.

Stages of a Warm Up
3.Skill RehearsalMeans practice of movement skills through the full range of movement. Actual skills of the game are performed. These will work the muscles and help with mental preparation. There should be a gradual increase of pace to full speed.

Is injury part of playing sport?
Agree or Disagree

Prevention of some injuries may be possible if a person does what?
(Discuss in pairs)

Prevention of some injuries may be possible if an athlete:-
• Warms up /cools down correctly• Uses the correct equipment• Knows the rules and regulations• Checks if the surface an facilities are safe to
use.• Does not participate if over tired.• Ensures that a teacher/coach is always
present.





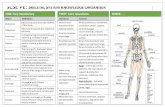
Sports Injuries
Injuries occur in two ways:-
externally or internally

Externally
• An externally caused injury might involve someone bumping into you, impacting on your body to cause a fracture or dislocation.
• The external environment also brings risks, like dehydration in severe heat.

External Force ( sudden stress injuries)
Impact injuries are common in invasion sports There are two types:Impact with someone (tackle, collision, punch, kick) or something (landing hard, running into a post). These cause cuts, bruises, sprains, fractures, dislocations or concussion.The environment – very hot or cold conditions. Heat causes dehydration. Cold causes hypothermia.

Internally
• Internally, very sudden powerful movements can tear and strain muscles, tendons. Something that’s also possible from overuse (Overuse Injuries).

Overuse injuries
Overuse injuries are caused by using a part of the body again and again and can also be brought on by:-• Heavy training Programmes• Insufficient rest between events, training.• Poor technique• Badly designed footwear or equipment

Examples of overuse injuries
Inflammation of the elbow known as golf elbow and tennis elbow .
Football, hockey and basketball players are prone to knee cartilage injuries due to twisting , turning and landing.
Other examples are Stress fractures and Shin splints

Chronic Injuries
• happen when injuries are not treated or given time to heal. These can lead to arthritis.
The type of injury could be mild or severe, for example like an ‘open fracture’,
when bones break and come out
through the skin.

Soft tissue injuries
Sprains - when ligaments are overstretched or torn around a joint, eg twisted or sprained ankle.Strains - when a muscle or tendon is overstretched or torn, eg pulled muscle.Bruises - caused when blood vessels burst under the skin following impact.

Skin Damage
Abrasions small grazes should be cleaned with water and covered to protect against infection.Blisters - caused by friction or rubbing which produces a layer of fluid under the skin. Should be covered with a plaster. Do not burst

Cuts Caused by impact with a sharp object.Need to be treated by stopping bleeding and letting the blood clot ASAP.A clean dressing can be used to apply pressure until bleeding stops.Injured part may need to be raised to slow bleeding down.

RICERICE
is the protocol used for the treatment of soft tissue injuries.
What do It stands for ?

RICE• Rest - Stop playing immediately and take any weight off
the injured area• Ice - Apply ice to the injured area. This helps to slow the
bleeding and swelling by making the blood vessels constrict
• Compression - Using a compression bandage on the area will also help to control swelling. Make sure its not so tight that it cuts off the circulation altogether!
• Elevation - Keeping the injured part raised above the heart helps swelling drain away and reduce blood flow to the area

Fractures
Fracture is an injury that damages the bone.
Closed - when the bone breaks but stays inside the skin.
Open - when the bone breaks and comes out through the skin.

Do you know what a green stick fracture is?

Joint injuries
Dislocation - when the bones of a joint are wrenched apart.Tennis and golf elbow - damage to tendons caused by overuse.Cartilage - which tears in the knee and can 'lock' the joint

Winding
A blow to the abdomen can cause feelings of difficulty when breathing , pain and nausea.
TreatmentTreat this by stopping exercise, leaning forwards and gently rubbing the area

Hyperthermia
This is where the body temperature rises too high and usually occurs following exercising in a hot climate. Signs of this are a weak pulse and pale, clammy skin. TreatmentTo treat this, lay the athlete down in a cool place and give them a drink before seeking medical advice.

Hypothermia
This is the opposite, where body temperature goes too low (below 35 degrees C). Symptoms include an irregular heart rate, stiff muscles and possible unconsciousness.Treatment You must slowly raise the body temperature by removing wet clothing and wrapping in a warm, dry blanket, and giving warm drinks and maybe a warm bath.

Concussion
This is caused by a knock to the head which can cause dizziness, memory loss, disorientation and sometime unconsciousness.Treatment If conscious they should be kept under observation for 24 hours. If unconscious they should be put in the recovery position and an ambulance called.