Townsend Harris High School Ottoman Empire Safavid Empire Mughal Empire.
The Mughal Empire - MS. CAGGIANOOrigins of the Mughal Empire • The Mughal Empire was founded by...
Transcript of The Mughal Empire - MS. CAGGIANOOrigins of the Mughal Empire • The Mughal Empire was founded by...
The Mughal EmpireFocus Question: How was the Mughal Empire able to gain, consolidate, and
maintain power?
Do-Now:
Take out your anticipation guide on the Ottoman Empire from Friday!
Homework:
Finish Mughal Empire reading.
Quiz on Friday! Quiz will be on the Ottoman Empire, Mughal Empire, and the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan. Extra help tomorrow 9th period and additional
extra help on Thursday 9th period in room D207.
Anticipation Guide: Building the Ottoman Empire• The Byzantine Empire broke away from the Ottoman Empire.
• The Ottomans ruled the Middle East.
• The Ottomans were intolerant of other religions.
• Being a slave in the Ottoman army was viewed as advantageous rather than negative.
• Ottoman wealth came from warfare.
• The Ottoman Empire achieved a golden age under the Suleiman the Magnificent.
Istanbul
Sultans built mansions, rest houses, religious schools, and hospitals throughout the city. Both public and private gardens further beautified the capital. Many Ottoman writers compared Istanbul to paradise. The city and its suburbs stretched along the Bosporus Strait between the Mediterranean and Black Seas.
Hagia Sophia MosqueThe cathedral of Hagia Sophia was converted into a mosque. It was one of the grandest mosques in the Islamic world. Today it is now a museum.
Suleymaniye MosqueBuilt in the reign of Suleiman, the Suleymaniye is one of the largest domed structures in the world, and is one of the greatest engineering achievements of Islamic civilization. The pencil thin minarets were characteristic of Ottoman architecture.
Topkapi PalaceAfter the conquest of Istanbul, construction of the Topkapı Palace was started at the year 1460 and completed at 1478 . The palace was the administrative, educational and art center of the Empire for nearly four hundred years. It was abandoned in the 19th century for the Dolmabahçe Palace.
The Golden HornThe Golden Horn was the ancient harbor of Istanbul during the Byzantine and Ottoman periods. It was crowded with merchant ships from ports throughout the region. During the Ottoman period it was largely inhabited by Jewish immigrants from Spain. The mixtures of Armenians, Greeks, Gypsies, and Turks living along its shores reflected the city's colorful ethnic mosaic.
Grand BazaarThe Grand Bazaar in Istanbul is one of the largest and oldest covered markets in the world, with 61 covered streets and over 4,000 shops which attract between 250,000 and 400,000 visitors daily. During Ottoman times, the bazaars were filled with merchants and travelers from as far away as England and present-day Malaysia. Spices from the Indies were offered, ivory from Africa, forest products from Russia, rugs from Persia, and many other goods were offered.
Selim I (Selim the Grim)
• Gained control of Mecca and Medina, 2 of the most holy Islamic cities.
• Captured the Mamluk Empire in Egypt and gained control of Cairo which was the intellectual center of the Islamic world.
Origins of the Mughal Empire
• The Mughal Empire was founded by Babur, a Muslim descendent of one of the Mongol khans.
• His motives for building an empire were to gain money and win back his homeland in Central Asia.
• Unable to win back his homeland, Babur turned his efforts to conquering parts of present-day Pakistan and Northern India.
• Within two years, his armies had conquered large portions of the Indus and Ganges plains. He was a great military strategist and fierce fighter who went into battle alongside his troops.
• He designed a new capital city at Delhi where he developed a taste for the arts and music and wrote one of the great histories of India.
Chunked Reading: The Mughal Empire
Directions: As you read through each chunk, summarize each chunk in 2-3 sentences. Be sure to define any important vocabulary and individuals in addition to your summaries.
As Babur laid the foundations for the Mughal Empire, he needed to make sure that he was able to consolidate and maintain power. The majority of people living in the newly acquired territory practiced Hinduism, whereas Babur and the Mughals practiced Islam. In order to maintain control of the empire, Babur tolerated the practice of Hinduism along with allowing the construction of new Hindu temples. He encouraged trade with the rest of the Islamic world which helped the economy of the empire. After the death of Babur, his son, Humayan, ruled for a brief time. After Humayan’s death, Babur’s grandson, Akbar, took the throne at thirteen years old. Historians have regarded Akbar as one of history’s greatest rulers.
The Mughal Empire under Akbar
Akbar wanted to unite India under his rule. He created a strong military to extend the empire along with expanding the bureaucracy to maintain control of the empire and new territories. Akbar eliminated the tax on non-Muslims to promote religious toleration and Hindus were allowed to govern with their own laws and have control over their institutions. Hindus were appointed to the government and Muslims were ordered to respect cows, which Hindus viewed as sacred. The Ibadat Khana was built which was a meeting house where Akbar would converse with scholars from all over the world to learn about various religions and cultures. In addition to promoting religious toleration, Akbar pushed for social and economic reforms. He welcomed international trade which resulted in strong trading relationships with the Ottoman Empire and Europeans. His rule brought peace and prosperity to India, which helped art, literature, and architecture flourish.
The Mughal Empire under Jahangir and Shah Jahan
After the death of Akbar, his son Jahangir took the throne. Following the reforms of his father, Jahangir continued appointing Hindus and Muslims to the court. Urdu which was a blend of Arabic, Persian, and Hindi became the official language of the empire. Further trading contacts with Europe were established which made India become a major trading destination known for its cotton textiles. Art and architecture continued to flourish with monuments, gardens, and palaces being built throughout the empire. His son, Shah Jahan, followed in his father’s footsteps and is most remembered for the Taj Mahal. After the death of his wife, Shah Jahan commissioned the tomb to be built “as beautiful as she was beautiful”. Shah Jahan eventually became ill and his four sons battled for power. The third son, Aurangzeb, took control of the empire.
The Mughal Empire under AurangzebAurangzeb was an excellent military tactician and expanded the Mughal Empire to its greatest extent. He maintained control for half a century in which he was both respected and feared. One of his major goals was to purify Islam in India and rid it of Hindu influences. He imposed Sharia law, and prohibited the building of Hindu temples and celebration of Hindu festivals. This resulted in a series of revolts, but Aurangzeb was still able to maintain control until his death. This led to the decline of the empire as weak emperors were unable to maintain control. The Portuguese, Dutch, French, and English all had an established trading presence in India for over two centuries. With the declining empire, European powers were able to take advantage of the situation and establish political and economic control.
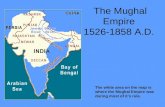
The Mughal Empire in India
Using your notes from the reading and do-now, how were the Mughals able to gain, maintain, and consolidate power? In your opinion, did these actions help or hurt the empire? Write your answer in the box below using at least three pieces of evidence.