skeleton - F · PDF file• Name the 6 types of synovial joint and give ... achieve a...
Transcript of skeleton - F · PDF file• Name the 6 types of synovial joint and give ... achieve a...

THE SKELETON

Objectives• Identify the bones that articulate at different
joints in the body.• Name the 6 types of synovial joint and give
examples of each.• Describe the structure and function of parts of a
synovial joint.• Be able to classify joints according the
movement they allow.• Use technical language to describe common
joint movements.• Analyse sporting techniques in terms of joint
movements.

• The human skeleton consists of 206 bones. Many of which move or hinge at joints. In conjunction with over 600 muscles these bones enable the human body to achieve a variety of movements.
• The functions of the skeletal system include: -• To provide a lever system against which muscles can
pull.• To provide a large surface area for the attachment of
muscles.• To protect delicate organs such as the brain.• To give shape to the body.• To give support to the body.• To manufacture red blood cells and to store fat calcium
and phosphate. • Click here- label the skeleton and print it out for you file

AXIAL & APPENDICULAR SKELETON
• The bones of the body are grouped into two major divisions.
• The axial skeleton consists of the bones, which lie around the longitudinal axis of the body. These include the SKULL, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, STERNUM & RIBS.
• The appendicular skeletonconsists of the bones of the LIMBS, PECTORAL (shoulder) GIRDLE, & PELVIC (hips) GIRDLE.

JOINTS• Joints are where two or more bones articulate
(move).• Joints are classified according to how much
movement they allow. 1. Fibrous – these are fixed or immovable joints
such as the cranium, sacrum and the coccyx.2. Cartilaginous – these are slightly movable
joints such as the vertebrae.3. Synovial – these are freely movable joints such
as the shoulder and hip.

Synovial joints• In PE these are the most important joints.• There are 6 types of synovial joint. 1. Ball & socket – hip and shoulder.2. Hinge – knee, elbow and ankle.3. Pivot – radio-ulna, atlas/axis.4. Saddle – thumb.5. Condyloid – wrist.6. Gliding – between vertebrae in spine. Click here and complete the matching exercise

Ball & socket joints• The hip joint• The head of the femur fits into a
deep cavity called the acetabulum on the pelvic bone.
• This deep cavity gives the hip joint stability.
• The presence of strong ligaments add to the stability making it difficult to dislocate the hip.

• The shoulder joint• The head of the humerus
fits into a shallow cavity on the scapula called the glenoid fossa.
• The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body but is also fairly unstable because of the shallow cavity.
• Stability is improved by ligaments and muscles.

Hinge Joints
• The knee joint• In the knee joint the femur
articulates with the tibia.• The patella (knee cap)
helps to give a better angle of pull.
• The fibula is not part of the knee joint and so the tibia is the weight bearing bone.

• The ankle joint• In the ankle the talus
articulates with the tibia and fibula.
• Ligaments provide stability to the joint.
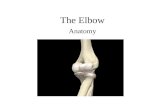
• The elbow joint• In the elbow the
humerus articulates with the radius and the ulna.
• Movement can only occur in one plane.

The pivot joint• The radio-ulna • In this joint the radius
and ulna articulate within the elbow joint.
• This joint allows the elbow some twisting movement (pronation & supination.
• Atlas/axis• In this joint the atlas
and axis bones articulate to allow a rotation movement as in shaking your head.

Condyloid and gliding joints• The wrist• In this joint the
radius and ulna bones articulate with 3 of the carpal bones.
• The spine• The spine has five areas
and has to fulfil many functions such as weight bearing stability and support.
• There are three type of joint in the spine but for A level the main one to know is the gliding joints between the vertebral arches.
What have you learnt?
Click here to complete exercise 1 [Quia]
Click here to open word document
Complete and add to your notes

Features of a synovial joint• Synovial joint have a number of common
features.
•Reduce friction•Nourish cartilage•To get rid of waste from joint
Slippery fluid like egg white which fills joint capsule
Synovial fluid
•To strengthen joint•To secrete synovialfluid
Outer layer – tough & fibrousInner – synovialmembrane covers all internal surfaces
Two layered joint capsule
•Prevents friction between articulating bones
Smooth& spongy covers ends of bones
Hyaline/articularcartilage
FUNCTIONSTRUCTUREFEATURE

FUNCTIONSTRUCTUREFEATURE
•Reduces frictionFluid filled sac found between tendon and bone
Bursae
•Improves fit between bone ends•Increases stability•Reduces wear & tear to joint surfaces
A wedge of tough flexible cartilage
Meniscus
•Increases joint stability•Acts as shock absorber•Reduces friction
Fatty pad found between capsule, bone or muscle
Pads of fat
•Joins bone to bone•Provides stability
A band of strong fibrous connective material
Ligament
Play the matching card game to make sure you know these features

Movements around a joint
• All synovial joints can move freely but the amount and type of movements which occur at each joint varies.
• Many of the movements occur in pairs –they are the opposite of each other.
• Technical terms to describe the movements you need to know include:-

Facing the palm of the hand upSUPINATION
Facing the palm of the hand downPRONATION
Bending the foot upwards towards tibiaDORSIFLEXION
Pointing the foot downwardsPLANTAR FLEXION
Bending sidewaysLATERAL FLEXION
Lower end of bone moves around in a circleCIRCUMDUCTION
Movement of a bone around its axis (can be inward (medial) or outward (lateral))
ROTATION
Movement towards the midline of the bodyADDUCTION
Movement away from the midline of the bodyABDUCTION
An increase in the angle which occurs at a jointEXTENSION
A decrease in the angle that occurs in a jointFLEXIONMEANINGTERM

Dorsiflexion & plantaflexionANKLE
Flexion & extensionKNEE
Flexion & extension, adduction & abduction, circumduction
HIP
Flexion & extension, lateral extension, rotationSPINE
Flexion & extension, adduction & abduction, circumduction
WRIST
Pronation & supinationRADIO-ULNA
Flexion & extensionELBOW
Flexion & extension, adduction & abduction, circumduction, rotation
SHOULDER
POSSIBLE MOVEMENTSJOINT
Click on the link to complete the exercise