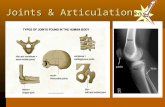
Skeletal System Articulations. Articulation (joint): a point of contact between bones. Some allow...
-
Upload
francis-liverpool -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
1
Transcript of Skeletal System Articulations. Articulation (joint): a point of contact between bones. Some allow...

Skeletal System
Articulations

Articulations
• Articulation (joint): a point of contact between bones.
• Some allow movement, others are immovable (sutures).
• Most joints allow considerable movement as a result of muscle contractions.

Classification of Joints
• Categories– Structural (by connective tissue or fluid)
• Fibrous• Cartilaginous• Synovial
– Functional• Synarthrosas• Amphiarthrosis• diarthrosis
Table 9-1 pg 256 classifies Each joint. Refer to it
Often.

Fibrous Joints (Synarthroses)
• Fibrous joints fit close.
• Connective tissue permit limited movement; most joints are fixed (immovable.)
• 2 sub types– Syndesmoses– Sutures– Gomphoses

Syndesmoses
• Joints in which fibrous tissue connect two bones.
• Some movement possible because of ligament flexibility.– Example: Distal ends of radius and ulna

Sutures
• Found only in skull.
• Thin layer of fibrous tissue between bones.
• Immovable.

Gomphoses
• Unique joints between root of teeth and mandible or maxilla.

Cartilaginous Joints (Amphiarthrosis)
• Bones joined by hyaline or fibrocartilage.
• Hyaline joints- Synchondroses
• Fibrocartilage joints- symphyses
• Joints are slightly movable in certain circumstances.

Synchondroses
• Hyaline cartilage between articulating bones
• Examples: Articulation between first rib and sternum.

Symphyses• Fibrocartilage pads bones
• Slight movement possible when pressure is applied.
• Example: Symphysis pubis opens pelvis during childbirth.
• Other examples of symphysis joints: vertebrae.

Synovial Joints (diarthroses)• Freely movable.
• A majority of joints are synovial.
• Ex: knee, hip
• Subcatagories:– Uniaxial– Biaxial– Muliaxial

Flashcards: Will be used during first dissection• Requirements:
– Front of card• Name of the joint
type.– Back of card
• Definition of joint• Example of the
joint.• Picture of the joint
• Required Cards:– Synarthroses: Syndesmoses– Synarthroses: Sutures– Synarthroses: Gomphoses– Amphiarthrosis: Synchondroses– Amphiarthrosis: symphyses– Diarthroses
DiarthrosesThese joints are freelyMovable.
Examples: Hip & knee

Types of Synovial Joints (Diarthroses)
• 3 main groups:– Uniaxial
• Hinge• Pivot
– Biaxial• Saddle• Condyloid
– Multiaxial• Ball and socket• Gliding

Uniaxial Joints
• Synovial joints that permit movement around one axis and in one plane.
• Hinge: Hinge shape; only back and force movement.– Example: Knee; ulna & humerus
• Pivot: Projection articulates with a ring or notch of another bone.– Example: 2nd & 1st cervical vertibrae.


Biaxial Joints
• Movement around 2 perpendicular axes in two perpendicular planes.
• Saddle: Joint resembles a saddle.– Example: Thumbs are the only 2 saddle joints
in the body.
• Condyloid: Where a condyle (rounded projection) fits into a socket.– Example: Occipital condyles & cervical
vertebrae; Distal end of radius into carpal bones.

Saddle
Condyloid Condyle

Multiaxial Joint
• Joints that allow movement around multiple axes & around multiple planes.
• Ball & socket: Most moveable joint; ball shaped head fits into circular depression.– Example: Should; hip
• Gliding joints: Flat articulating surfaces that allow limited gliding along various axes; least moveable synovial joint.– Example: Vertebrae; carpals & tarsals.

Gliding
Ball & Socket

Flashcards: Will be used during first dissection• Requirements:
– Front of card• Name of the joint
type.– Back of card
• Definition of joint• Example of the
joint.• Picture of the joint
• Required Cards:– Uniaxial: Hinge– Uniaxial: Pivot– Biaxial: Saddle– Biaxial: Condyloid– Multiaxial: Ball & socket– Multiaxial: Gliding
Uniaxial: HingeOnly back and forcemovement
Examples: knee

Structure of synovial joints
• Joint capsule
• Synovial Membrane
• Articular cartilage
• Joint cavity
• Menisci (articular Disks)
• Ligaments
• Bursae

Joint Capsule
• Sleeve-like extension of periosteum (bone membrane)
• Forms a casing around ends of bones, binding them.

Synovial Membrane
• Membrane that lines joint capsule and attaches to margins of articular cartilage.
• Secretes synovial fluid.

Articular Cartilage
• Thin layer of hyaline cartilage.
• Cushions articular (connecting) ends of bone.

Joint cavity
• Space between articulating bones.
• More space More movement.

Menisci (articulating disks)
• Pads of fibrocartilage between articulating ends of some diarthroses.
• Usually divide joint cavity into two separate spaces.
• Knee joint has 2 menisci.

Ligaments
• Strong cords of dense fibrous tissue.
• Keep bones together.

Bursae• Closed pillow like
structure.
• Filled with synovial fluid.
• Cushion joint and facilitate movement of tendons.
• Bursitis- Inflammation of bursae.

Disorders of the Joints• Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease; wear
& tear of articular cartilage. Cartilage thins, bony spurs form at articulations, ligaments calcify. Symptoms: stiffness, pain, limited mobility.

Disorders of the Joints• Traumatic Injuries:
– Dislocations- damages nerve & blood vessels.– Damage to cartilage- tears produce edema, pain,
instability, & limited motion.– Sprain- injury to ligaments surrounding a joint,
disrupting synovial membrane. Bruising and swelling may result from ruptured blood vessels.

Disorders of the Joints• Arthritis: inflammatory joint disease.
Inflammation of synovial membrane, destruction of cartilage, erosion of bone. Can be crippling and cause deformities.– Juvenile arthritis: Onset during childhood.– Gouty arthritis: Arthritis caused by a metabolic
disorder- excess uric acid deposit into synovial fluid.