Chapter 9: Articulations. Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where 2 bones...
-
Upload
dale-dawson -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 9: Articulations. Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where 2 bones...

Chapter 9:Chapter 9:ArticulationsArticulations

ArticulationsArticulations
• Body movement occurs at Body movement occurs at jointsjoints ((articulationsarticulations) where 2 bones ) where 2 bones connectconnect

Joint StructureJoint Structure
• Determines direction and distance of Determines direction and distance of movement (movement (range of motionrange of motion))
• Joint strength decreases as mobility Joint strength decreases as mobility increasesincreases

What are the major What are the major categories of joints, categories of joints, and the structure and and the structure and function of each function of each category?category?

Functional ClassificationFunctional Classification
Table 9–1

Structural ClassificationsStructural Classifications
• BonyBony
• FibrousFibrous
• CartilaginousCartilaginous
• Synovial Synovial

SynostosisSynostosis
• Fused bones, immovable:Fused bones, immovable:– metopic suture of skullmetopic suture of skull– epiphyseal lines of long bonesepiphyseal lines of long bones

Fibrous JointFibrous Joint
• Gomphosis – periodontal ligamentGomphosis – periodontal ligament
• Syndesmosis – interosseous Syndesmosis – interosseous membranemembrane
• Suture – have fibrous strandsSuture – have fibrous strands

Cartilagenous JointCartilagenous Joint
• Is a rigid cartilaginous bridge Is a rigid cartilaginous bridge between 2 bones:between 2 bones:– epiphyseal cartilage of long bonesepiphyseal cartilage of long bones– between vertebrosternal ribs and between vertebrosternal ribs and
sternumsternum

What is the basic What is the basic structure structure of a synovial joint, and of a synovial joint, and what are the common what are the common accessory structures accessory structures and their functions?and their functions?

Synovial Joints (Diarthroses)Synovial Joints (Diarthroses)
• Also called Also called moveable jointsmoveable joints
• At ends of long bonesAt ends of long bones
• Within Within articular capsulesarticular capsules
• Lined with synovial membrane Lined with synovial membrane

Articular CartilagesArticular Cartilages
• Pad articulating surfaces within Pad articulating surfaces within articular capsulesarticular capsules: : – prevent bones from touchingprevent bones from touching
• Smooth surfaces lubricated by Smooth surfaces lubricated by synovial fluidsynovial fluid::– reduce friction reduce friction

Synovial FluidSynovial Fluid
• Contains slippery Contains slippery proteoglycansproteoglycans secreted by secreted by fibroblastsfibroblasts

Functions of Synovial FluidFunctions of Synovial Fluid
1.1. LubricationLubrication
2.2. Nutrient distributionNutrient distribution
3.3. Shock absorptionShock absorption

Synovial Joints: Synovial Joints: Accessory StructuresAccessory Structures
• CartilagesCartilages
• Fat padsFat pads
• LigamentsLigaments
• TendonsTendons
• BursaeBursae

CartilagesCartilages
• Cushion the joint:Cushion the joint:– fibrocartilage fibrocartilage meniscusmeniscus ( (articular discarticular disc))

Fat PadsFat Pads
• Superficial to the joint capsuleSuperficial to the joint capsule
• Protect articular cartilagesProtect articular cartilages

Accessory LigamentsAccessory Ligaments
• Support, strengthen joints Support, strengthen joints
• SprainSprain: : – ligaments with torn collagen fibersligaments with torn collagen fibers

TendonsTendons
• Attach to muscles around jointAttach to muscles around joint
• Help support jointHelp support joint

BursaeBursae
• Pockets of synovial fluidPockets of synovial fluid
• Cushion areas where tendons or Cushion areas where tendons or ligaments rubligaments rub

Synovial Joints: Synovial Joints: Stabilizing FactorsStabilizing Factors
• Prevent injury by limiting range of Prevent injury by limiting range of motion:motion:– collagen fibers (joint capsule, ligaments)collagen fibers (joint capsule, ligaments)– articulating surfaces and menisciarticulating surfaces and menisci– other bones, muscles, or fat padsother bones, muscles, or fat pads– tendons of articulating bones tendons of articulating bones

InjuriesInjuries
• DislocationDislocation (luxation)(luxation)::– articulating surfaces forced out of articulating surfaces forced out of
positionposition– damages articular cartilage, ligaments, damages articular cartilage, ligaments,
joint capsulejoint capsule
• SubluxationSubluxation::– a partial dislocationa partial dislocation

What are the dynamic What are the dynamic movements of the movements of the skeleton?skeleton?

Types of Dynamic MotionTypes of Dynamic Motion
• Linear motion (gliding)Linear motion (gliding)
• Angular motionAngular motion
• RotationRotation

Linear MotionLinear Motion
• Pencil maintains Pencil maintains vertical orientation, vertical orientation, but changes but changes positionposition
Figure 9–2a, b

Angular MotionAngular Motion
• Pencil maintains Pencil maintains position, but changes position, but changes orientationorientation
Figure 9–2c

CircumductionCircumduction
• Circular angular motion Circular angular motion
Figure 9–2d

RotationRotation
• Pencil maintains position Pencil maintains position and orientation, but spinsand orientation, but spins
Figure 9–2e

Planes (Axes) of Dynamic Planes (Axes) of Dynamic MotionMotion
• MonaxialMonaxial (1 axis) (1 axis)
• BiaxialBiaxial (2 axes) (2 axes)
• TriaxialTriaxial (3 axes) (3 axes)

AbductionAbduction
Figure 9–3b, c

AbductionAbduction
• Angular motionAngular motion
• Frontal planeFrontal plane
• Moves Moves away fromaway from longitudinal axis longitudinal axis

AdductionAdduction
• Angular motionAngular motion
• Frontal planeFrontal plane
• Moves Moves towardtoward longitudinal axis longitudinal axis

CircumductionCircumduction
• Circular motion Circular motion without rotationwithout rotation
• Angular motionAngular motion
Figure 9–3d

RotationRotation
Figure 9–4

RotationRotation
• Direction of rotation from anatomical Direction of rotation from anatomical positionposition
• Relative to longitudinal axis of bodyRelative to longitudinal axis of body

RotationRotation
• LeftLeft or or right rotationright rotation
• Medial rotationMedial rotation ( (inward rotationinward rotation): ): – rotates toward axisrotates toward axis
• Lateral rotationLateral rotation ( (outward rotationoutward rotation): ): – rotates away from axisrotates away from axis

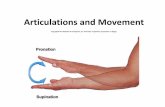
Pronation and SupinationPronation and Supination
• PronationPronation::– rotates forearm, radius over ulnarotates forearm, radius over ulna
• SupinationSupination::– forearm in anatomical positionforearm in anatomical position

Inversion and EversionInversion and Eversion
Figure 9–5a

Inversion and EversionInversion and Eversion
• InversionInversion::– twists sole of foot mediallytwists sole of foot medially
• EversionEversion::– twists sole of foot laterallytwists sole of foot laterally

Dorsiflexion and Plantar Dorsiflexion and Plantar FlexionFlexion
Figure 9–5b

Dorsiflexion and Plantar Dorsiflexion and Plantar FlexionFlexion
• DorsiflexionDorsiflexion: : – flexion at ankle (lifting toes)flexion at ankle (lifting toes)
• Plantar flexionPlantar flexion::– extension at ankle (pointing toes)extension at ankle (pointing toes)

OppositionOpposition
• Thumb movement Thumb movement toward fingers or palm toward fingers or palm (grasping)(grasping)
Figure 9–5c

Protraction and RetractionProtraction and Retraction
Figure 9–5d

Protraction and RetractionProtraction and Retraction
• ProtractionProtraction: : – moves anteriorlymoves anteriorly– in the horizontal plane (pushing forward)in the horizontal plane (pushing forward)
• RetractionRetraction: : – opposite of protractionopposite of protraction– moving anteriorly (pulling back)moving anteriorly (pulling back)

Elevation and DepressionElevation and Depression
Figure 9–5e

Elevation and DepressionElevation and Depression
• ElevationElevation: : – moves in superior direction (up)moves in superior direction (up)
• DepressionDepression::– moves in inferior direction (down)moves in inferior direction (down)

Lateral FlexionLateral Flexion
• Bends vertebral Bends vertebral column from column from side to sideside to side
Figure 9–5f

What are the types of What are the types of synovial joints, and the synovial joints, and the relationship relationship of motion to structure?of motion to structure?

Classification of Classification of Synovial Joints by ShapeSynovial Joints by Shape
• GlidingGliding
• HingeHinge
• PivotPivot
• EllipsoidalEllipsoidal
• SaddleSaddle
• Ball-and-socketBall-and-socket
A Functional Classification of Synovial JointsPLAYPLAY