Chapter 9 Articulations. Joint Functional Classification Synarthroses: immovable Amphiarthroses:...
-
Upload
lionel-obrien -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
5
Transcript of Chapter 9 Articulations. Joint Functional Classification Synarthroses: immovable Amphiarthroses:...

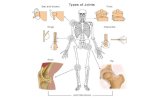
Chapter 9 Chapter 9 ArticulationsArticulations

Joint Functional ClassificationJoint Functional Classification
Synarthroses: immovableSynarthroses: immovable
Amphiarthroses: slightly movableAmphiarthroses: slightly movable
Diarthroses: freely movableDiarthroses: freely movable


Fibrous Joints (Synarthroses)Fibrous Joints (Synarthroses)
Syndesmoses
•Fibrous bands connect 2 bones
•Joints between distal and radial end of ulna
Sutures
Teethlike projection interlock
Found in the skull
Gomphoses
Occurs between the root of tooth and alveolar process

Cartilaginous Joints (Amphiarthroses)Cartilaginous Joints (Amphiarthroses)
Synchondroses
•Has hyaline cartilage between articulating bones
•Articulation between first rib and sternum
•Also during growth years between epiphysis and diaphysis
Symphysis
Pad of disk of fibrocartilage connects 2 bones
Vertebral disc

Synovial Joints (Diarthroses)Synovial Joints (Diarthroses)
Majority of joints between bones in Majority of joints between bones in the appendicular skeleton are the appendicular skeleton are synovial jointssynovial joints

Structure of Synovial JointsStructure of Synovial Joints
Sleeve-like extension of periosteum of articulating bones. Forms casing around bone end
Moist membrane that lines inner surface of joint capsule
Thin layer of hyaline cartilage cushioning articulating surface of bone
Ligament
Cords of dense fibrous tissue. Lash bones firmly together
Pillow-like structure filled with synovial fluid. Function to cushion joint at bony prominances

Types of Synovial JointsTypes of Synovial JointsUniaxial permit movement around only Uniaxial permit movement around only one axis and in only one planeone axis and in only one plane– Hinge jointHinge joint– Pivot jointsPivot joints
Biaxial permit around 2 perpendicular Biaxial permit around 2 perpendicular axes and planesaxes and planes– Saddle jointsSaddle joints– Condyloid jointsCondyloid joints
Multiaxial permit movement around 3 or Multiaxial permit movement around 3 or more axes and planesmore axes and planes– Ball and socket jointsBall and socket joints– Gliding jointsGliding joints


Types of Synovial JointsTypes of Synovial JointsHinge Joint: distal bone can move only in one plane, flexion and extension (forward and backward).
pivot joint´s movement is limited to rotation.
Ball and SocketDistal bone can move around a center in an indefinite number of axes.
CondyloidDistal bone has an ovoid articular surface and is received into an elliptical cavit, which makes it impossible for the bones to perform axial rotation.
GlidingThe main movements are flexion-extension and rotation.
saddle joint consists of two opposing surfaces that are reciprocally concave-convex, wich allows flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction, but no axial rotation.

Types of Synovial JointsTypes of Synovial Joints


Humeroscapular Joint / Shoulder Humeroscapular Joint / Shoulder Joint Joint

Humeroscapular Joint / Shoulder Humeroscapular Joint / Shoulder Joint Joint

Elbow Joint Elbow Joint

Elbow Joint Elbow Joint Helps cushion joint
Medially cubital vein
Ulnar nerve

Forearm and Wrist JointsForearm and Wrist Joints
Proximal radioulnar: pivot joint between Proximal radioulnar: pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular notch of the ulna and the annular ligament.ligament.
Distal radioulnar:pivot-joint formed Distal radioulnar:pivot-joint formed between the head of the ulna and the between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch on the distal radiusulnar notch on the distal radius. .
Proximal radioulnar: pivot joint between Proximal radioulnar: pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular notch of the ulna and the annular ligament.ligament.
Distal radioulnar:pivot-joint formed Distal radioulnar:pivot-joint formed between the head of the ulna and the between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch on the distal radiusulnar notch on the distal radius. .
Proximal radioulnar: pivot joint between Proximal radioulnar: pivot joint between the circumference of the head of the the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular notch of the ulna and the annular ligament.ligament.
Distal radioulnar:pivot-joint formed Distal radioulnar:pivot-joint formed between the head of the ulna and the between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch on the distal radiusulnar notch on the distal radius. .

Forearm and Wrist JointsForearm and Wrist JointsRadiocarpal (wrist): Condyloid joint Radiocarpal (wrist): Condyloid joint formed by the radius and the formed by the radius and the articular disk proximally and the articular disk proximally and the proximal row of carpal bones distally. proximal row of carpal bones distally.

Hand and Finger JointsHand and Finger Joints

Hand JointsHand JointsIntercarpal: Articulations between Intercarpal: Articulations between the individual carpal bones. They are the individual carpal bones. They are plane synovial joints. The small plane synovial joints. The small amount of movement between the amount of movement between the carpal bones at these joints carpal bones at these joints contributes to total wrist mobility. contributes to total wrist mobility.

Hand and Finger JointsHand and Finger Joints
Synovial Joints
Interphalageal

Hip Joint Hip Joint synovial joint formed by the articulation of the synovial joint formed by the articulation of the rounded head of the femur and the cup-like rounded head of the femur and the cup-like acetabulum of the pelvis. It forms the primary acetabulum of the pelvis. It forms the primary connection between the bones of the lower connection between the bones of the lower limb and the axial skeleton of the trunk and limb and the axial skeleton of the trunk and pelvis.pelvis.
surfaces are covered with a strong but surfaces are covered with a strong but lubricated layer called articular hyaline lubricated layer called articular hyaline cartilage.cartilage.

Hip Joint Hip Joint


Knee Joint (tibiofemoral) HingeKnee Joint (tibiofemoral) Hinge
Concavity of tibia forms a shallow socket for condyle of femur
Has several ligamentsHas several ligamentsHas several ligamentsHas several ligamentsHas several ligaments

Knee JointKnee Joint

Ankle JointAnkle Joint synovial hinge joint that connects the synovial hinge joint that connects the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the distal ends of the tibia and fibula in the lower limb with the proximal end of the lower limb with the proximal end of the talus bone in the foottalus bone in the foot
Most common injury sprained ankle is Most common injury sprained ankle is caused by internal rotation to anterior caused by internal rotation to anterior talofibular ligamenttalofibular ligament

Vertebral JointsVertebral Joints

Vertebral JointsVertebral JointsCaliginous joints between bodies of Caliginous joints between bodies of adjacent vertebra classified adjacent vertebra classified symphysessymphyses
Permit only slight movementPermit only slight movement
Synovial joints between articulating Synovial joints between articulating surfaces of vertebral processes are surfaces of vertebral processes are classified as glidingclassified as gliding

ROMROM

Measuring ROMMeasuring ROMROM is measured with a goniometerROM is measured with a goniometer

Measuring ROMMeasuring ROM

Types of MovementTypes of MovementSynovial joints permit one or more of Synovial joints permit one or more of the following movements:the following movements:– Angular: change the size of angle Angular: change the size of angle
between articulating bonesbetween articulating bones– Circular: results in arclike rotation Circular: results in arclike rotation
around axisaround axis– Gliding: moves over articulating Gliding: moves over articulating
surfaces without angular or circular surfaces without angular or circular movementmovement
– Special: Don’t fit in any movement Special: Don’t fit in any movement categorycategory

Angular Movements Angular Movements Flexion: Decrease angle, bends or Flexion: Decrease angle, bends or folds one part to anotherfolds one part to another
Extension: Increase angle between Extension: Increase angle between bonesbones
Hyperextension: Stretching part Hyperextension: Stretching part beyond anatomical positionbeyond anatomical position
Flexion: Decrease angle, bends orFlexion: Decrease angle, bends orFlexion: Decrease angle, bends orFlexion: Decrease angle, bends or


Angular Movements Angular Movements Plantar Flexion: foot is stretched Plantar Flexion: foot is stretched down and back. Increases angle down and back. Increases angle between top of foot and front of legbetween top of foot and front of leg
Dorsiflexion: foot is tilted upward Dorsiflexion: foot is tilted upward decreasing angledecreasing angle

Angular Movements Angular Movements Abduction: moves part away from Abduction: moves part away from median body planemedian body plane
Adduction: Moves toward median Adduction: Moves toward median body planebody plane

Circular MovementCircular MovementRotation: pivoting bone on own axis. Rotation: pivoting bone on own axis. Moving head side to side (NO)Moving head side to side (NO)
Circumduction: distal ends move in Circumduction: distal ends move in circle. Such as pitchingcircle. Such as pitching
Supination: turns palms side upSupination: turns palms side up
Pronation: turns palms side downPronation: turns palms side down


Special MovementSpecial MovementInversion: turn sole of foot inwardInversion: turn sole of foot inward
Eversion: Turn sole of foot outwardEversion: Turn sole of foot outward
•Protraction: moves part forward
•Retraction: Moves part back

Special MovementSpecial Movement
Elevation: moves part upElevation: moves part up
Depression: Moves part downDepression: Moves part down

BursitisBursitis

Joint DisordersJoint Disorders
Noninflammatory: Noninflammatory: – Does not involve inflammation of Does not involve inflammation of
synovial membrane.synovial membrane.– Doesn’t produce systemic signs or Doesn’t produce systemic signs or
symptoms such as fever or damage symptoms such as fever or damage other organsother organs
Inflammatory Inflammatory

Noninflammatory Noninflammatory
Osteoarthritis/degenerative joint disease.Osteoarthritis/degenerative joint disease.– Most common noninflammatory disorderMost common noninflammatory disorder– Wear and tear degenerationWear and tear degeneration– Fracturing of articulating cartilageFracturing of articulating cartilage– Abnormal formation of new bone such as bone Abnormal formation of new bone such as bone
spursspurs– Cause unknown but attributed to obesity, aging Cause unknown but attributed to obesity, aging
and wear and tearand wear and tear– Symptoms are treated with NSAIDS, Symptoms are treated with NSAIDS,
glucosamine, chondriton or injections of glucosamine, chondriton or injections of gelatinous type lubricating fluid, and surgerygelatinous type lubricating fluid, and surgery

OsteoarthritisOsteoarthritis

Swelling deformities of the distal interphalangeal joints
Swelling deformities of the distal interphalangeal joints

NoninflammatoryNoninflammatoryDislocation (subluxation)Dislocation (subluxation)– Usually resulting from traumaUsually resulting from trauma– Can be an emergency due to association Can be an emergency due to association
with blood vessels and nerveswith blood vessels and nerves– Articulating surfaces no longer in proper Articulating surfaces no longer in proper
contactcontact


ArthroscopyArthroscopy
Surgical procedure orthopaedic Surgical procedure orthopaedic surgeons use to visualize, diagnose, surgeons use to visualize, diagnose, and treat problems inside a joint. and treat problems inside a joint.



Inflammatory Joint Inflammatory Joint DiseasesDiseases

ArthritisArthritis
General term for many different General term for many different inflammatory joint diseasesinflammatory joint diseases
Can be caused by variety of factors Can be caused by variety of factors such as infection, injury, genetics such as infection, injury, genetics and autoimmunity and autoimmunity

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)Systemic autoimmune diseaseSystemic autoimmune diseaseInvolves chronic inflammation of Involves chronic inflammation of many tissues and organs, generally many tissues and organs, generally starting with the jointsstarting with the jointsPannus is granulation tissue that is Pannus is granulation tissue that is formed within the synovium by formed within the synovium by proliferating fibroblasts and proliferating fibroblasts and inflammatory cellsinflammatory cellsPannus adheres to cartilage, Pannus adheres to cartilage, destroying it and eventually fusing destroying it and eventually fusing bonesbones

Rheumatoid ArthritisRheumatoid ArthritisDeformity of the fingers known as ulnar Deformity of the fingers known as ulnar deviation is commondeviation is common
Treated with NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and Treated with NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and other antirheumatic medsother antirheumatic meds
New drugs that alter immune response New drugs that alter immune response such as TNF blockers are showing promisesuch as TNF blockers are showing promise

Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisJuvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
appears between the ages of 6 appears between the ages of 6 months and 16 years. months and 16 years.
first signs often are joint pain or first signs often are joint pain or swelling and reddened or warm joints swelling and reddened or warm joints

Gouty arthritisGouty arthritisMetabolic disorderMetabolic disorder
Excess blood levels of uric acid are Excess blood levels of uric acid are deposited as sodium urate crystals within deposited as sodium urate crystals within synovial fluid of joints (tophi) synovial fluid of joints (tophi)
Can lead to very swollen and painful jointsCan lead to very swollen and painful joints
Treated with Allopurinol (inhibits synthesis Treated with Allopurinol (inhibits synthesis of uric acid)of uric acid)