Reproductive Systems 3-D male reproductive System 3-D female reproductive System.
-
Upload
wesley-reeves -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
2
Transcript of Reproductive Systems 3-D male reproductive System 3-D female reproductive System.
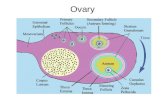
Testes TissueSperm production occurs
in seminiferous
tubules
At puberty, testosterone
production begins
in interstitial cells
See Fig. 46.12
Testes TissueSperm production occurs
in seminiferous
tubules
Sertoli cells regulate
sperm production &
nourish developing
sperm
See Fig. 46.12
Testes TissueSperm production occurs
in seminiferous
tubules
Spermatozoa are
produced by
spermatogonia
See Fig. 46.12
Animation: Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesisproduction of sperms occurs in the
testes in seminiferous tubulesfirst stage of spermatogenesis mitotic
cell divisions of primordial germ cells to produce spermatogonial cells
spermatogonial cells then undergo a period of growth to form primary spermatocytes
each primary spermatocyte then undergo two meiotic cell divisions: meiosis I to produce secondary
spermatocyte & meiosis II to produce spermatids
spermatid cells then undergoes differentiation to form sperm cells
Sperm cells are nourished by Sertoli cells
each primary spermatocyte produce 4 sperm cells with haploid number of chromosomes i.e. 23 chromosomes
Oogenesis oogenesis is process by which female gametes (egg cells) are produced in the ovary
it begins during fetal development when oogonia are formed from primordial germ cells by mitosis
Oogonia undergoes growth to form primary oocytes
primary oocyte begin first meiotic division but stop in Prophase I until on set of puberty
at puberty some follicles develop each month in response to FSH produced by pituitary gland
primary oocyte completes first meiotic division to forms two cells of different sizes due to unequal distribution of cytoplasm
the one with less cytoplasm become the first polar body which eventually degenerates
the larger cell becomes secondary oocyte and proceeds to meiosis II & stops at prophase II
meiosis II is completed if cell is fertilized forming an ovum and second polar body
Animation: Comparison of Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis
Comparison Between spermatogenesis & oogenesis
spermatogenesis oogenesismillions sperms produced
per dayfour sperms of equal
division of the cytoplasm & no polar bodies
begins at puberty i.e. at sexual maturity
occurs throughout adult life
sperms are produced continuously & released during ejaculation
occurs in the testesspermatogenesis involves
meiotic cell divisionproduce haploid cells
one ovum per 28 day menstrual cycle
one ovum, unequal division of the cytoplasm, 2 polar bodies
begins during foetal development
ends at menopauseovum released during
ovulation in the middle of the menstrual cycle
occurs in the ovaries oogenesis involves
meiotic cell divisionproduce haploid cells
Fertilisation sperm cell approach the egg in oviduct
Acrosome of sperm cell releases hydrolytic enzymes which digest jelly layer (zona pellucida) of the egg
sperm cell head (acrosomal process) extends through jelly to vitelline membrane (egg’s plasma membrane)
binding proteins on surface of acrosome attach to receptors on vitelline membrane
sperm plasma membrane fuses with egg plasma membrane
fusion of plasma membranes causes depolarization of egg plasma membrane i.e. cortical reaction which bars other sperm cells from fusing with membrane
sperm nucleus enters egg (secondary oocyte) after dissolution of nuclear membranes resulting in combination of genetic material
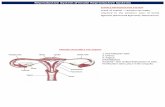
Revision QuestionsDraw a labelled diagram of the
adult female reproductive system. [4]
Draw a labelled diagram of an adult male reproductive system. [6 ]
Explain the processes involved in oogenesis in humans. [9]
Draw the structure of a mature human egg. [4]
Explain the role of hormones in the regulation of the menstrual cycle in human females. [8]
Draw a labelled diagram of a mature sperm. [5]
Outline the process of spermatogenesis in humans. [5]
Compare the process of spermatogenesis and oogenesis. [7]
Describe the process of fertilization in humans. [8]
Describe the development of the early human embryo. [5]
Outline the regulation of pregnancy by two named hormones. [4]