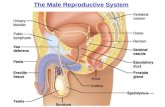
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System cowper’s gland.
-
Upload
ira-parrish -
Category
Documents
-
view
258 -
download
4
Transcript of The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System cowper’s gland.
Sperm Cells
Sperm cells come in two sizes.
Males = smaller head and longer tail.
23 chromosomes. As sperm travel,
various fluids are added.
Spermatazoan.
Scrotum - Sac like structure which holds the testes. Regulates the temperature of the testes for sperm production.
Testes - Two oval structures found in the scrotum. Testicles produce sperm and testosterone.
Structure that rests on top of the testes. It is 18-20 feet of coiled tubing for storage of mature sperm.
Epididymis
Vas Deferens
Long thin duct that runs from the epididymis to the urethra. It carries sperm. This duct is what is severed and tied during vasectomy.
Cowper’s Gland
Produces fluid to neutralize the acid in the male urethra.
a.k.a. Bulbourethral Gland.
Penis The external
structure, which is made up of three adjoining tubes that contain sponge like tissue.
During sexual excitement blood flows into this tissue causing the penis to become stiff and erect.
Urethra
Tube which carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body
In the male this tube also carries semen from the vas deferens to the outside of the body.
Foreskin
A flap of skin that covers the head of the penis. This is often removed during circumcision.
Common Disorders
Sterility – unable to reproduce. Can be caused by environmental factors, Mumps, etc.
Undescended Testes – one of the testes does not descend into the scrotum at birth.
Inguinal Hernia – part of the intestine pushes into the scrotum through a weak spot…Surgery usually always needed to correct problem.
Continued… Enlarged Prostate – Common at middle
age. Not necessarily indicative of disease. Surgery is almost always necessary.
Cancer of Prostate and Testes – uncontrolled cell growth that invades surrounding tissue and destroys it. Testicular Cancers most common between 18 and 36. Usually 100 % curable if detected early.
Testicular Self Exam
(TSE)
Hold the penis out of the way and examine each testicle separately.
Hold the testicle between the thumbs and fingers with both hands and roll it gently between the fingers.
Look and feel for any hard lumps or nodules (smooth rounded masses) or any change in the size, shape, or consistency of the testes.