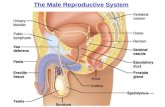
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Epididymis.
Reproductive organ of male
-
Upload
reezali-foundation -
Category
Technology
-
view
652 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Reproductive organ of male

Reproductive Organ of Male
HumanReproduction System
crazy-sains.blogspot.com
The Outlinefor middle and high school

You will learn about:
• The internal and external genital of men.• The function of part of genital.• Spermatogenesis• The related hormone for reproduction system
in men.

The internal genitalia
• Testes• Reproduction ducts• gonad

(1)testes
The testes consist of :• Seminiferous tubule• Interstitial cell/ leydig cell• Sertoli cellThere are three parts of testis that you have to
know, of course those placed in the testis-see figure-


Seminiferous tubule
Seminiferous tubule is the place for forming spermatozoa.
This is long and forming rolled in the testis –see the figure in the previous slide-

Interstitial cell/ leydig cell
This sel can produce testosteron, and the testosteron is used to:
• Increase the spermatogenesis process.• Sperm maturation.• Forming some secondary characteristics.Note:Leydig cell are found among seminiferous
tubule.

Sertoli cellThis sel is placed in semineferus tubule, this sel is used to:• Feed nutrition to sperm during spermatogenesis take place.• Maintain the environment necessary for development and maturation via
the blood-testis barrier• Secrete substances initiating meiosis• Secrete supporting testicular fluid• Secrete androgen-binding protein, which concentrates testosterone in close
proximity to the developing gametes – Testosterone is needed in very high quantities for maintenance of the reproductive
tract, and ABP allows a much higher level of fertility• Secrete hormones affecting pituitary gland control of spermatogenesis,
particularly the polypeptide hormone.• Phagocytose residual cytoplasm left over from spermiogenesis• They release Antimullerian hormone,which prevents formation of the
Mullerian Duct / Oviduct.• Protect spermatids from the immune system of the male.<from wikipedia>

(2)Reproduction ducts
• Epididimis for saving immature sperm• Vas deferens ductto flow sperm from
epididimis to seminalis vesicle• Ejaculatory ductthe short duct that flow
sperm from vas deferens to uretra• Uretrathe last duct(to issue urine and sperm)

Vas deferens
uretra

(3)gonad
• Seminal vesicle• Prostate gland• Cowper gland/bulbouretral gland

Seminalis vesicle
• Is the fluid-producing reserve of food, in the form of fructose, it helps spermatozoid move easily.
• There are two seminalis vesicle/ only one pair –see the figure-

Prostate gland
• There’s only one.-see figure in the next slide-• Produce alkaline sap that flow to the sperm
duct. It uses for neutralizing the acidity of vaginal tract.
• The prostate sap that expelled with semen have better motility,longer survival, and better protection of DNA.


Cowper/bulbouretrhal gland
• There’s only one pair-see the previous slide-• Produce sap that flow to the urethra, so that
produce semen*(together with sperm)• Cowper gland have functions to lubricate the
urethra,neutralize traces of acidic urine in urethra, and flush out remaining sperm in theurthral bulb,residual urine,and also foreign matter.
*)it consists of sperm sel and a fluid/sap.

The external genitalia / penis
• Glans penis• Cavity/erectile tissue-see the figure in the next slide-
Note:Penis uses for copulation.



Erectile tissue
The cavity has erectile tissue, there are three cavities in the penis,but only two kinds of cavities.
These are the cavities:1)Corpus cavernosa(amounted to two).2)Corpus spongiosum(only one) it’s longer than corpus
cavernosa, it reaches to glans penis.The erectile tissue that placed in the cavities, consist of: blood
vessels and nerves of taste.Because, the erectile tissue has blood vessel and nerves of
taste, the penis can stiffen. –learn the erection process in the next slide-

erection
It is the process how the penis can stiffen:Stimulationthe blood vessel in the cavity that
consists of erectile tissue are filled much more by the bloodthe erection(penis is stiffening)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HaWemCSD7dY

spermatogenesis
• Take place for 16 days at seminiferous tubule• Spermatogenesis has 3 stages:
spermatocytogenesisspermatidogenesis spermiogenesis


The explaination:Spermatocytogenesis:• The forming-Process of spermatocyt• The certain spermatogonium (type Ap)will be type B,
this type B spermatogonium will divide mitotically to be two diploid intermediate cells called primary spermatocytes. Two primary spermatocytes moves into the adluminal compartment of the seminiferous tubules and duplicates its DNA and subsequently undergoes meiosis I to produce two haploid secondary spermatocytes.
• The other certain type spermatogonium(type Ad) will divide to produce copies of themselve, so the supply would not run out.
Cited from WIKIPEDIA

Spermatidogenesis:• The process to produce spermatids• The two secondary spermatocyte can produce four
haploid spermatids with undergoing meiosis II.
• The process to produce spermatozoa.• Each spermatid produces one spermatozoa.• The golgi aparatus creates enzyms and will become acrosome.• The golgi surrounds condensed nucleus and become
acrosomal cap• The mid-piece(the mitochondria gahter and the distal centriol
form an axoneme)• One of the centriol elongates to be the tail of the sperm.• Sertoli cell phagocytoses the excess cytoplasm and organelles.
Spermiogenesis:

spermiation
Spermiation is the releasing-process of mature spermatozoa from sertoli cells into the lumen seminiferous tubule. It renders the cell losses cytoplasm and organelle.
This formed spermatozoa is mature,but lack motility. It renders them sterile. And the non-motile spermatozoa are transported to epididymis from sertoli. This work uses peristaltic contraction

hormone
• The reproductive system in human is controlled by hormone, the function of testes is influenced by hormone, hipothalamus is the controller of all.
Learn this :HipothalamusGnRHstimulate to pituitaryFSH(for
increasing spermatogenesis) and LH (for producing testosteron)
From above and previous slide, we can infer that increasing spermatogenesis is controlled by testosteron and FSH

The explanation for hormone
• GnRH is gonadotropin-releasing hormone• FSH is follicle stimulating hormone• LH is luteinizing hormone, this is commonly
called ISCH(interstitial cell stimulating hormone)

crazy-sains.blogspot.com
We are not prolix to give lessons!