CERTIFICATION IN REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY AND INFERTILITY ...
Male Reproductive Endocrinology
-
Upload
roger961 -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
775 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Male Reproductive Endocrinology

BIO 351 Endocrinology, Medgar Evers College
April 3, 2006
Male Reproductive Endocrinology
Kenneth L. Campbell
Prof. of Biology; Assoc. Dean of Science & Mathematics
University of Massachusetts at Boston

This presentation is made possible by a grant entitled
“Shortcourses in Endocrinology at Minority Undergraduate Institutions”
from the National Institute of General Medical
Sciences (NIGMS) to
The Minority Affairs Committee of the Endocrine Society

Are You Interested In:
• Going away for the summer in 2007 to do research for 8 weeks in a cutting-edge endocrine lab in an area of your choice with a caring mentor?
• Receiving a two-year free membership in The Endocrine Society with many benefits, e.g., information about travel grants, scholarships, online journals, etc.?
http://www.endo-society.org/minorityactivities/summer_research.cfm
SUMMER RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES FOR MINORITY STUDENTS

http://www.endo-society.org/minorityactivities/summer_research.cfm
How do I qualify and What should I do?You can apply if you are:
• A full-time minority student beyond your sophomore year or if you are currently enrolled at a minority institution, and
• A U.S. citizen or permanent resident.
For more details on eligibility and requirements, visit The Endocrine Society website at
SUMMER RESEARCH OPPORTUNITIES FOR MINORITY STUDENTS

What are endocrine systems for?
Endocrine Functions
• Maintain Internal Homeostasis
• Support Cell Growth
• Coordinate Development
• Coordinate Reproduction
• Facilitate Responses to External Stimuli

What are feedback systems?
Feedbacks Generate Control Loops
Negative These maintain hormonal balance & are often linked
to homeostatic processes.
If the multiplicative effect of the several links in a control loop is negative, the entire control loop is negative.
Positive These cause physiologic changes in the system
involved.
If the multiplicative effect of the several links in a control loop is positive, the entire control loop is positive.
--+
++

How dynamic are these systems? Hormone, receptor, transducer & effector levels vary with time. Some change over short terms,
others over long terms.
Levels also vary with developmental stage, gender, & health status.
www.antiaging.com/images/ testosterone_decline.gif
After a248.e.akamai.net/.../pubs/mmanual_home/ illus/i232_1.gif

Outline of Male Reproduction
1. Adult anatomy 2. Embryogenesis 3. Sex determination 4. Hormonal controls 5. Puberty 6. Testicular anatomy 7. Meiosis 8. Spermatogenesis 9. Contraception 10. Aging

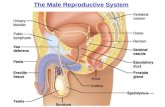
Adult Male Anatomy

Male Embryogenesis

Male Germ Cell Migration
www.med.unc.edu/embryo_images/unit-genital/genital_gifs/genital008-1.gif
www.med.unc.edu/embryo_images/unit-genital/genital_gifs/genital008-
2all.gif


Sex Determination: Genetic

Sex Determination: Gonadal
www.med.unc.edu/embryo_images/unit-genital/genital_gifs/genital010-
1.gif

Sex Determination:Internal Reproductive Tract

Sex Determination:External Reproductive Tract

Pituitary- Hypothalamic Associations
www.cushings-help.com/ anterior-pituitary.gif

How are the gonads controlled? LH
© Kenneth L. Campbell, 1997. All rights reserved.

How are the gonads controlled? FSH
© Kenneth L. Campbell, 1997. All rights reserved.

Inhibin
europe.obgyn.net/nederland/mp/overgang/images/overgang14x.gif
Female
Males lack inhibin A. Inhibin B is inversely correlated with FSH & spermatogenesis
in normal adults.

SteroidSynthesis
arbl.cvmbs.colostate.edu/hbooks/
pathphys/endocrine/basics/
steroidogenesis.gif

Maturation: Hormonal

Leydig Cell Populations
Lejeune, H, R Habert, JM Saez, Origin, proliferation and differentiation of Leydig cells, J Mol Endocrinol 20:1-25, 1998.

Maturation: Tanner Stages
www.cuhk.edu.hk/proj/growthstd/images/
bpuberty.gif
www.cuhk.edu.hk/proj/growthstd/images/gpuberty.gif
a248.e.akamai.net/7/248/430/20020531071032/www.merck.com/pubs/mmanual_home/illus/i258

www.biomedcentral.com/content/figures/1471-2431-2-5-3-
l.jpg
Testosterone in saliva in children & serum SHBG in adolescents & adults. The pubertal decrease in SHBG is less pronounced in women.

Testicular Anatomy
trc.ucdavis.edu/mjguinan/apc100/modules/Reproductive/
mammal/images/testis10.jpg

Meiosis: Males & FemalesMale Female

Spermatogenesis

Sperm Maturation Spermatozoa reach final shape in the testis, but they gain functional maturity while passing through the epididymus & female reproductive tract: activation of full motility, capacitation, in the vagina & cervix; final fertilizing ability after the acrosome reaction, usually near the egg.

Fertilization

Male Contraception
Barrierscondoms
Vasectomy
Hormones peripheral androgens +/- LHRH antagonists or agonists

Male Serum HormoneAge Profiles
www.dpcweb.com/documents/news&views/spring_02/the_aging_male.html
Male Aging & Reproductive Senescence

www.dpcweb.com/documents/news&views/spring_02/the_aging_male.html
The ratio T/SHBGis the FAI, a
Measure of free T.
Adrenal androgenslike DHEAS alsodecline with age.

Low Fertility in Gainj vs Other Groups

How is prolactin controlled?


FSH in Gainj Men

LH in Gainj Men

Many Gainj Men are Infertile

Support from: NSF, Umass/Boston, Sandia National Labs, Hybritech, Quidel, Monoclonal Antibodies Inc.
AcknowledgementsAcknowledgements
Gainj ProjectThe Gainj PeopleRees MidgleyAl HermalinLora MyersJim WoodPat JohnsonIla Maslar Diana LaiSam Refetoff Peter SmousePeter HeywoodMichael AlpersBrian DavisonYan Ren Lynne ShintoDiane DrinkwaterDarryl HolmanBettina Shell
Related StudiesKathy O’ConnorCoralie MunroSusannah Barsom Ellie Brindle Cheryl StroudKai OrtonJodiann ThompsonYefim ProshchitskiyYelena FilipovaMatt LoprestiOliver SchultheissCheryl FrederickSteve MonfortMalcolm PottsDavid McClelland (dec)
Turkana ProjectAll Turkana SubjectsMike LittlePaul LeslieBen CampbellDhanesh DookhranKathy WhitemanAlexandra EvindarWilliam LukasSandra GrayJeanine QuigleyChristine Sekadde -KigonduLeah Kirumbi
(*in the lab at UMB)

www.dpcweb.com/documents/news&views/spring_02/the_aging_male.html
Male Hormone Levels with Age