Protein Synthesis
description
Transcript of Protein Synthesis
Protein Synthesis
Protein SynthesisReviewWhat is RNA and Why is it Important?Types of RNACodons & AnticodonsTranscriptionTranslationAmino Acids and The Codon ChartReviewDNARNASugarDeoxyriboseRiboseNitrogen BasesAdenine = ThymineGuanine CytocineAdenine = UracilGuanine CytosineShapeDouble StrandedSingle StrandedReviewRemember how the bases bond in DNA?
DNA: ATGCTTAG
RNA is similarly complimentary:
DNA: ATGCTTAGRNA:TACGAATC
UACGAAUC
Protein SynthesisProtein Synthesis is the final part of the process of making proteins from a DNA templateBut wait a minute-Where is DNA?Where are proteins made?
How do we get proteins from DNA if the DNA cant leave?We make RNA from the DNA template!In the nucleusAt the ribosomeProtein SynthesisWhy is RNA important?It uses the code from DNA in the nucleus to order (sequence) amino acids in the cytoplasmAmino acids bond together (dehydration synthesis!) to make proteins
What is a protein?PolypeptideMade from amino acids linked togetherThe amino acids are held together with covalent peptide bondsThe long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptideThe polypeptide chain twists up into a complex shape called a protein.
Amino AcidsThere are 20 different amino acids3 different RNA nucleotides code for 1 amino acidExample: UAC = tyrosine (1 amino acid)AAU = asparginine ( 1 amino acid)GUU = valine (1 amino acid)Linking amino acids creates a protein:Example: tyrosine + asparginine + valine = 1 protien!
Amino AcidsThe order of the amino acids determine the proteins shape The proteins shape determines its function.
If the protein has the wrong shape, it wont work right!!!!!So its really, really important that the amino acids get put in the right order
Protein SynthesisBefore we learn the process of protein synthesis, we need to learn the places:Places:NucleusHas the DNA template (a section of the DNA called a gene)CytoplasmThe fluid within the cellAmino acids are floating in the cytoplasmRibosomeOrganelle where amino acids are linked togetherPutting together amino acids = making a protein
Protein SynthesisBefore we learn the process of protein synthesis, we need to learn the parts:Parts:rRNA = ribosomal RNAHelps make up the ribosome (rRNA and protein make up the ribosome)aids in bonding mRNA to tRNAmRNA = messanger RNACreated in the nucleus, travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosomeCarries the messageCodon (more on this later)
tRNA = transfer RNAMoves amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomeAnticodon (more on this later)
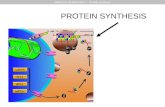
NucleusmRNADNAtRNARibosomeCytoplasmAmino AcidsNew ProteinThe CellEEEE
Protein SynthesisTwo step processTranscription- mRNA synthesisHappens in the nucleus with mRNADNA mRNA
Translation- protein synthesisHappens in the cytoplasm at the ribosome with the mRNA, tRNA and amino acidsProtein SynthesisPart One: TranscriptionSegments of DNA are separated by RNA polymeraseOne of the detached strands is used as the template to make mRNARNA polymerase adds mRNA nucleotides to the exposed DNA strandThis creates mRNA
Protein SynthesisTranscription- Lets Practice!(remember, in RNA there are no Ts; use Us!)
DNA = AGCTTAmRNA = (codon)
*Codon: every three nitrogen bases (also called bases, RNA nucleotides, nucleotides or just the letters)(3 nucleotides = 1 codon = 1 amino acid)How many codons are above? CodonCodonUCGAAU2Codon QuestionA piece of mRNA is made of 15 nucleotides (bases)How many codons does it have?
A piece of mRNA is made of 30 nucleotides (bases)How many codons does it have?
A piece of mRNA is made of 60 nucleotides (bases)How many codons does it have?
Part Two: TranslationWhen something is translated, it is converted from one language to another. In this case, we are converting from the language of nucleotides to the language of amino acids
Protein SynthesisProtein SynthesisTranslation contThe newly formed mRNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosomeThe mRNA translates the DNA code to the tRNA that is in the cytoplasm.Each mRNA codon is paired with a complementary tRNA that is in the cytoplasmThe tRNA has a specific amino acid attached to itThe tRNA anticodon carrying the amino acid attaches to the mRNA codon
Protein SynthesisPart Two: Translation continuedThe tRNA has a specific amino acid attached to itThe tRNA anticodon carrying the amino acid attaches to the mRNA codonPractice:DNA: ATGCAT
mRNA: (codon) tRNA: (anticodon)
AntiCodonAntiCodonUACGUAAUGCAUTranslation ContinuedOnce two amino acids are present at the ribosome, a peptide bond forms that hold the amino acids togetherMultiple amino acids bonded together = a protein (a polypeptide)
The process of matching tRNA to mRNA continues until all mRNA codons are matched to their anticodons and a STOP codon is read.- The end result is a polypeptide (a protein)
Amino AcidsIf I were to give you a strand of DNA, you should be able to tell me:The complimentary mRNA strand (codon)The amino acid the mRNA is coding forThe tRNA strand (anticodon) that brings the amino acid to the ribosomeTo determine the amino acid the mRNA is coding for, you can use an mRNA codon tableIf mRNA isUCGFind U for the first baseC for the second baseAnd G for the third base
-UCG codes for the amino acid Serine- The anticodon AGC is on the tRNA that brings serine to the ribosome
Practice!DNA: GACTTAmRNA: (codon)
What amino acid are the mRNA codons code for?
CUGAAUCUG=
AAU =
DNA: GACTTA
mRNA: (codon)
Amino Acids:
What must the tRNA anticodons be to attach those amino acids?
tRNA: (anticodon)LeucineAsparagineWhat is the mRNA strand?CUGAAUWhat amino acids does the mRNA code for?
GACUUACodon Practice!A piece of mRNA is made of 15 nucleotides (bases)How many codons does it have?How many amino acids will the protein have?
A piece of mRNA is made of 30 nucleotides (bases)How many codons does it have?How many amino acids will the protein have?
A piece of mRNA is made of 60 nucleotides (bases)How many codons does it have?How many amino acids will the protein have?
ReviewThe DNA code AAA-CTG-CAA is the gene read in the nucleusDuring transcription, the mRNA strand UUU-GAC-GUU is madeThe mRNA strand leaves the nucleus and attaches to the ribosometRNA molecules in the cytoplasm bond to the amino acids indicated by the anticodon on that tRNA During translation, the tRNA anticodons bond to the complementary mRNA codons In this example would result in the amino acids phenylalanine, aspartic acid and valine out in the cytoplasm The amino acids phenylalanine, aspartic acid and valine join together by peptide bonds to create a polypeptide (protein)