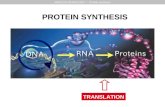
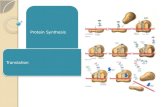
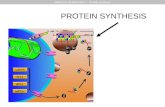
Protein synthesis
-
Upload
dluetgens -
Category
Technology
-
view
2.900 -
download
1
Transcript of Protein synthesis

DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
http://faculty.uca.edu/~johnc/mbi1440.htm
http://www.wappingersschools.org/RCK/staff/teacherhp/johnson/visualvocab/mRNA.gif

Biochemical reactions occurring in all cells are catalyzed by enzymes.
Collision model: Molecules must collide with enough kinetic at the proper orientation to break bonds

Enzymes are catalyst that lower activation energy.
In order to react must collide with enough KE to break bonds – the activation energy
With a lower activation energy, more collisions will have enough KE to react.So the reaction is faster.

Enzymes increase the rate of the reaction at the same temperature

Enzymes are proteins.
• Glycolysis is one of the simplest biochemical pathaways.
• Each of the ten steps is catalyzed by a unique enzyme
• Each of those enzymes is synthesized in each cell
• Each enzyme is coded for in the DNA of the cell

Proteins – a string of amino acids
SERINE – one of 20 amino acids

Proteins – a string of amino
acids
Peptide bonds
form between amino acids

Hydrogen bonds
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Key
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
Structure of DNASection 12-1
DNA – base pairs carry the genetic code for the sequence of the amino acids Nucleotide

Nucleotides in the DNA strand carry the code for
proteins
Image by: Riedell

Purines(2 rings)
Pyrimidines
(1 ring)
A
G
C
T
Phosphate group
Deoxyribosesugar
Nitrogen bases =“Steps of ladder”
© Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved

A
G
C
T
Phosphate group
Deoxyribosesugar
Nitrogen bases =“Steps of ladder”
© Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved
ADENINE
GUANINE
CYTOSINE
THYMINE

CHARGAFF’S RULES
A = T G = C
Image from: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/images/dna_bases.gif
_________ _________At time no one knew why…
now we know its becauseAdenine always bonds across with____________
Guanine always bonds across with ____________
THYMINE
CYTOSINE

RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
© Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved
DNA is safely stored in the nucleus. mRNA (messenger RNA) brings a copy of the code out to the cytoplasm.

RNADNA
RNApolymerase
Transcription - Making a copy of the DNA code Adenine (DNA and RNA)Cystosine (DNA and RNA)Guanine(DNA and RNA)Thymine (DNA only)Uracil (RNA only)
Enzyme called RNA polymerase separates strands of DNA, then uses one strand as a template to assemble an mRNA copy.mRNA will carry the “script” out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm

RNA- the Other Nucleic Acid
Also made of nucleotides
Sugar is ribose insteadof deoxyribose.
RNA is single stranded, instead of doubled stranded.
Contains uracil instead of thymine.
http://images2.clinicaltools.com/images/gene/dna_versus_rna_reversed.jpg

MASTER PLAN DNA stays safe in nucleus TRANSCRIPTION (DNA→ RNA)& PROCESSING (remove interons)takes place in nucleus
TRANSLATION (RNA→ proteins)takes place on ribosomes in cytoplasm
© Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved
“Blueprints” of master plan are carried to building site
http://www.home-improvement-resource.com/images/architect.jpg

Translation - Translating the base pair codes into an amino acid sequence
mRNA – the copy of the code
sequence of base pairs
tRNA – carries the amino acid to the ribosome as coded for in the mRNA – codons code for specific amino acids.

___________ on tRNA
matches up with________ on mRNA
Images modified from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved
ANTICODON
CODON
EACH tRNA carries onlyone kind of_____________amino acid

HOW CAN JUST 4 BASES GIVE DIRECTIONS TO MAKE 20 AMINO ACIDS?
Message is read in groups of 3 = _________
UCGCACGGU UCG-CAC-GGU
CODON
Codons represent different amino acids
Serine- Histidine- Glycine

The m-RNA Code
64 possible codons
Some amino acidshave more than onecodon.
START= _______
3 codons for _____
AUG
STOP


Translation - Translating the base pair codes into an amino acid sequence

Translation (continued)

Summary of protein synthesis
DNA strand in nucleus
RNA message copied from DNA Occurs in the nucleus
Occurs in the cytoplasm at the ribosome
mRNA moves out to cytoplasm

A graphic to show you translation to sequence the protein
ribosome
codon
carries a specific amino acid depending upon its code