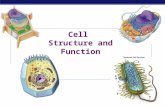
CELLS & the ORGANELLES Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Animal vs. Plant Cells.
-
Upload
giles-harrington -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
2
Transcript of CELLS & the ORGANELLES Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Animal vs. Plant Cells.

CELLS & the CELLS & the ORGANELLESORGANELLES
Prokaryote vs. EukaryoteProkaryote vs. Eukaryote
Animal vs. PlantAnimal vs. Plant
Cells

“Life is Organized”
Atoms
C,H,N,O,P,S
Molecules
Organelles
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Organism
Species
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biome
Ex: Tundra, desert, temperate forest
Biosphere
Smallest / most simple
Largest / most complex

Early MicroscopesEarly Microscopes
• Robert Hooke (1665)
Coined the term “cell” (Why?)
looking at cork, he saw little boxes
Is cork alive?
• Anton von Leeuwenhoek (1674)
saw living cells in pond water
Cells

Cell DiscoveriesCell Discoveries
• Matthias Schleiden (1838) Plants are made of cells
• Theodor Schwann (1839)Animals are made of cells
• Rudolf Virchow (1855) Saw dividing cells new living cells come from
pre-existing cellsCells

The Cell Theory
1. All living things made of cells.
2. Cell are the basic unit of structure & function for life.
3. Cells can only arise from pre-existing living cells
Cells

Types of Organisms
• Unicellular organisms living organisms that are composed of only ONE cell– Examples: bacteria, algae, protists, yeast
• Multicellular organisms any organism that is made of MORE THAN ONE cell– Evolved later
Cells

Prokaryote vs. EukaryoteProkaryote vs. Eukaryote
• Prokaryotic Cells– DNA not bound by a
membrane… no “true nucleus”
– Usually smaller, simple• Nearly all unicellular
– No membrane bound parts (organelles)
• Ex: bacteria– Read Section 6.3
• Eukaryotic Cells– DNA is bound by a
membrane bound nucleus
– Larger, complex, has internal organization
– Have internal membrane bound structures = organelles
• Ex: you, plants, algae
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WRO-DPyB9Bk

Cells

Basic Structures For ALL Cells
• Cell membrane– Surround the cell – barrier
between inside and environment
• Cytoplasm– Contains water and
organelles
• DNA– Instructions for the cell to
carry out
• Ribosomes– Makes proteins
Cells

OrganellesOrganelles• Very small size
• Have specific functions
– Create specificity of cells
• EX: muscle cells have more mitochondria than skin cells
• Found throughout cytoplasm
• Examples:
– Nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts (plants only), vacuoles, cytoskeleton, centrioles (Animal only)
Cells

Cells

Cells

The Nucleus:Control center of the cell, houses genetic material
Cells

Nucleolus• Is a small Is a small
dense region dense region in the nucleusin the nucleus
• Makes Makes ribosomesribosomes, , which make which make proteinsproteins
Cells

RIBOSOMES
• Free floating in cytoplasm
or• Attached to ER
• “reads” RNA code from DNA to assemble proteins
• “protein factory”
Cells

ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
• Internal passageway within the cell
• Can be “Rough” or Smooth – Rough has ribosomes
attached protein synthesis
– Smooth has no ribosomes membrane lipid synthesis, detoxification, cholesterol metabolism
Cells

GOLGI APPARATUS• Modifies, sorts,
packages proteins coming from ER
• Destination of products– storage in cell– export out of cell
• Customizes– Adds lipids, carbs to
proteins
Cells

LYSOSOMES• Small, enzyme-filled organelles• Digests material for use or disposal
– Only common in animals but recent evidence suggest they are in plants as well
Cells

MITOCHONDRIA
• Convert food into usable energy
• Have an outer & inner membrane
• Has its own DNA!– Inherited from your
mom
Cells

CHLOROPLASTS• Capture sunlight & convert
it to energy– Photosynthesis – make their
own food– Green plants and some algae
• Have 2 membranes
• Contain the green pigment chlorophyll
• Has its own DNA!
Cells

VACUOLES
• Stores materials
• Water, salts, protein, carbs
• Largest in plants– Gives turgor pressure
• Larger in plants
Cells

CYTOSKELETON• Structural support
& transport
MICROFILAMENTS
Actin – threadlike protein
MICROTUBULES
Tubulins – protein
basis of cilia & flagellaCells

CENTRIOLES
• Help in the process of cell division
• Only in Animals
Cells

PLANTS V. ANIMALS
• CELL WALLS made of cellulose
• LARGER VACUOLE• CHLOROPLASTS
• CENTRIOLES• Smaller or No vacuoles
Cells

Colonies
Cells
ChlamydomonasChlamydomonasVolvoxVolvox
• Volvox is a colony of individual cells.• Each cell of a Volvox resembles a Chlamydomonas (a one-celled organism). •Volvox cells coordinate the beating of their flagella so that the movement is not random through water. - shows cooperation among cells
Colonies – a group of unicellular microorganisms living togetherIf colony attaches to a solid surface = biofilm
VSVS

Colonies of Bacteria
Cells

Cell to Cell Connections• Cells in same tissue communicate with each
other through junctions– Tight junction : membranes are fused, stitched
together; no passage
– Desmosomes: protein fibers that anchor in cytoplasm of neighboring cells
• – allow passage of materials
– Gap junction : Channels formed by donut-shaped proteins btwn cells ; yes passage
– Pits & Plasmodesmata : (plants) cell walls perforated with pits, strands of cytoplasm (plasmodesmata) run through pits connecting cells
Cells

Cells

Cell to Cell Connections
Cells

Extracellular Matrix• Solution of macromolecules
(proteins & carbs) that surround cells in a tissue– Secreted by the cell itself
to the space outside• Holds cells together• Allows them to migrate &
interact• May regulate behavior in
cells– Ex: collagen
Cells

Cells
Division of Labor Division of Labor In In Multicellular Multicellular OrganismsOrganisms
Cells
Tissues – a group of cells working together
Organs – a group of tissues working together
Organ System – a group of organs working together
Organism – a group of organ systems working together
Differentiation – when cells take on a specific role