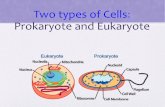
Cell Structure and Function Prokaryote bacteria cells Types of cells Eukaryote animal cells...
-
Upload
amelia-cox -
Category
Documents
-
view
236 -
download
2
Transcript of Cell Structure and Function Prokaryote bacteria cells Types of cells Eukaryote animal cells...
Prokaryotebacteria cellsProkaryote
bacteria cellsTypes of cells
Eukaryoteanimal cellsEukaryote
animal cellsEukaryoteplant cellsEukaryoteplant cells
Cell characteristics All cells:
are surrounded by a plasma membrane
have cytoplasm cytoplasm = cytosol + organelles
contain DNA
have ribosomes tiny “organelles” that make proteins using
instructions contained in genes
4
Eukaryotes Prokaryotes
DNA Associated with protein in membrane-bound nucleus
single circle.
“naked”
Size 5-100 µm 0.2-10 µm
Organization Single and multicellular, some have cell walls
single-celled, all have cell walls
Division Mitosis and Meiosis Binary Fission
Organelles membrane bound organelles like mitochondria
no organelles, different ribosomes (70S)
Examples plants, animals, protists, fungi
bacteria, archaea
14
Animal Plant
Cell Wall No, only plasma membrane
Yes, and plasma membrane
Chloroplasts no yes
Polysaccharides Glycogen Starch as storage
Cellulose for structure
Vacuole no Large fluid filled present
Shape Able to change shape. Usually
rounded.
Fixed shape.
Usually regular.
2.3.4
Cell MembraneCell Membrane
Structure: phospholipid
bilayer proteins that
function as channels, markers, and receptors.
Function: selectively
permeable boundary between the cell and external environment
NucleusNucleus
Structure: membrane bound
sphere that contains DNA and nucleolus
Function: storage center of cell’s DNA manages cell
functions
Cell WallCell Wall
Structure: Rigid wall made up of
cellulose, proteins, and carbohydrates
Function: Permeable boundary
around the outside of the plant cell membrane that provides structure and support
CytoskeletonCytoskeleton
Structure: a network of thin,
fibrous elements made up of microtubules and microfilaments
Function: acts as a support
system for organelles
maintains cell shape
RibosomesRibosomes Structure:
consist of two subunits made of protein and RNA
Function: location of protein
synthesis
Endoplasmic ReticulumEndoplasmic Reticulum Structure:
a system of membranous tubules and sacs
Function: intercellular
highway (a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another)
Rough Endoplasmic ReticulumRough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER): prominent in cells
that make large amounts of proteins to be exported from the cell
Covered with ribosomes
Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumSmooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth
Endoplasmic Reticulum (sER): involved in the
synthesis of lipids and breakdown of toxic substances
Not covered with ribosomes
Golgi ApparatusGolgi Apparatus Structure:
stacked flat sacs
Function: receives vesicle bound
proteins from the rER and distributes them to other organelles or out of the cell
receiving, processing, packaging, and shipping
AKA: Golgi body, Golgi complex or dictysome
LysosomesLysosomes
Structure: spherical organelles
that contain digestive (hydrolytic) enzymes
Function: breaks down food
particles, invading objects, or worn out cell parts
VacuolesVacuoles Structure:
a sac of fluid surrounded by a membrane
Function: used for
temporary storage of wastes, nutrients, and water
MitochondriaMitochondria
Structure: folded membrane
(cristae) within an outer membrane.
Function: converts energy
stored in food into usable energy (ATP)
Allows aerobic cellular respiration
ChloroplastsChloroplasts Structure:
stacked sacs (thylakoids) that contain chlorophyll surrounded by a double membrane
Function: photosynthesis
(conversion of light energy to chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose)
Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Important to see the similarities
transform energy generate ATP
double membranes = 2 membranes semi-autonomous organelles
move, change shape, divide internal ribosomes, DNA & enzymes
Lynn MargulisU of M, Amherst