Paranasal Sinus 2002 01 Slides
-
Upload
sherhaniz-melissa-abidin -
Category
Documents
-
view
11 -
download
6
description
Transcript of Paranasal Sinus 2002 01 Slides
-
1
Paranasal Sinuses:
Anatomy and Function
Glen T. Porter, MD
Francis B. Quinn, MD, FACS
The University of Texas Medical Branch
Department of Otolaryngology
Galveston, Texas
Grand Rounds Presentation
January 2002
-
2
Case Report1000B.C.
-
3
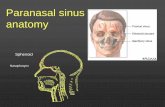
7 bones
4 paired sinuses
4 turbinates
3 meati
Drainage system
Nervous supply
Vascular supply
Related structures
Sinus Anatomy Overview
-
4
Maxilloturbinal
Ethmoturbinal
Middle turbinate Superior turbinate
Supreme turbinate
Agger nasi
Uncinate process
Ethmoid infundibulum
Sinuses
Maxillary Ethmoid
Embryology
-
5
Sinus
Development
-
6 Pediatric Sinuses
-
7
Ethmoid
Maxilla
Palatine
Lacrimal
Pterygoid plate of
Sphenoid
Nasal
Inferior Turbinate
Bony Structure
-
8
Arterial Supply
External Carotid
Maxillary A.
Sphenopalatine
Internal Carotid
Ophthalmic A.
Ant. Ethmoid
Post. Ethmoid
Supraorbital
Supratrochlear
-
9
Innervation
-
10
Neurovascular Supply
-
11
Sinus Drainage Schema
-
12
Ethmoid Sinus
Development
Present at birth
Anterior/Posterior
Variability
Structure
Volume/shape
Roof
Lateral wall
-
13
Ethmoid Roof
Anterior 2/3
Posterior 1/3
Keros I
Keros II
Keros III
-
14
Ethmoid
Cells
Supraorbital, Frontal Bulla, Concha Bullosa, Hallers, Onodi Cells
-
15
Ethmoid SinusRelated
Structures Basal Lamella of the Middle Turbinate Three planes
Agger nasi cell Childhood sinus
Ethmoid Bulla Hiatus Semiluninaris/Superior Hiatus Semilunaris
Suprabullar/retrobullar recesses (Sinus Lateralis)
Ethmoid Infundibulum/Uncinate Process
Anterior/Posterior Ethmoid Arteries
Osteomeatal complex
-
16
Basal/Ground
Lamella Basal/Ground Lamella
Of the Middle Turbinate
-
17
The Agger Nasi Cell
-
18
Ethmoid Bulla
Uncinate Process
Hiatus Semilunaris
-
19
Ethmoid Infundibulum
-
20
Suprabullar/Retrobullar Recess
-
21
Ethmoid Arteries
-
22
Osteomeatal Complex Middle meatus Maxillary Sinus Ostium
Anterior Ethmoid
Drainage
-
23
Maxillary Sinus
Development
Present at birth
Biphasic growth
Level of the floor
Structure
Volume & shape
Walls, floor, roof
-
24
Maxillary Sinus
-
25
Maxillary
Sinus
-
26
Maxillary Sinus
Related Structures
Fontanelles
Natural ostium
Hallers Cells &Sinusitis
Osteomeatal complex
Accessory Ostium
Nasolacrimal duct
-
27
Fontanelles
-
28
Natural Ostium
-Hallers cells
Accessory Ostium
-
29
Nasolacrimal Duct
-
30
Frontal Sinus
Development Frontal bone at birth
Age 5
Structure Volume and shape
Ostium
Walls Anterior vs. posterior
Related Structures Frontal recess
-
31
Frontal Sinus
Ostium
Frontal recess
Boundaries
Dumbbell shape
Sinus Lateralis
Frontal Bulla
-
32
Sphenoidal Sinus
Development
Arise within the nasal capsule (no pouch)
Age 3 begins to pneumatize
Structure
Volume/variable pneumatization
Wall thickness
Position within the sphenoid
Relation to sella turcica
Sellar and postsellar relationships
-
33
Sphenoid Sinus Pneumatization
-
34
Sphenoid Sinus
Sphenoid Sinus
-
35
Sphenoid Sinus
-
36
Sphenoid Sinus
Ostium
Size (.5-4mm)
Location (sinus floor, anterior nasal floor, anterior
sinus wall, superior turbinate, cribiform plate)
Bony dehiscence
Related Structures
Sphenoethmoidal recess
Sphenoid rostrum
Onodi cell
-
37
Sphenoid Ostium
Sphenoethmoid Recess
Sphenoid Rostrum
-
38
The Onodi Cell
-
39
Microscopic Anatomy
Mucosa
Cilliated columnar epithelial cells Anatomy
Beat frequency
Inhibitory effects of contact
Noncilliated columnar cells Distribution
Function
Basal cells
-
40
Microscopic AnatomyContd
Goblet Cells
Glycoproteinsviscosity and elasticity
Innervation (para=thick, symp=thin)
Basement membrane
Submucosal glands
Distribution
-
41
Microscopic Anatomy
-
42
Mucous Blanket
Two layers
Superficial layer
Sol layer
Function
Superficial layer traps bacteria and
particulate matter.
Enzymes, antibodies, immune cells
-
43
Mucociliary Transport
Directional Flow of Mucous
Toward the choanae
Ostium drainagea stubborn beast
Hilding, MD
Contact inhibition
Hallers cells
Surgery
-
44
Mucociliary Transport
-
45
Function of Paranasal Sinuses
Humidifying and warming inspired air
Regulation of intranasal pressure
Increasing surface area for olfaction
Lightening the skull
Resonance
Absorbing shock
Contribute to facial growth
-
46
New Frontiers
Sleep apnea and the sinuses Humidification contributes up to 6.9mm Hg serum
pO2
Mouth breathers noted to have decreased end-tital CO2increased serum CO2apneas (high baseline)
Nitric Oxide (NO) NO produced primarily in sinuses
Toxic to bacteria, fungi, viruses
Increases cilliary motility
-
47
Case Report
39 yom with h/o sinus disease c/o
headache, rhinorrhea.
PMHx of sinus surgery years ago
ROS reveals h/o two episodes of
meningitis in past few years
PE: right superior nasal mass. S/p
FESS. Clear rhinorrhea.
-
48
-
49
References
Anon, Jack B., et al, Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses, Theime, New York, c1996.
Bhatt, Nikhil J., Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: New Horizons, Singular Publishing Group, Inc., San Diego, c1997.
Bailey, Byron J., et al, Head & Neck Surgery -- Otolaryngology, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, c2001.
Lundberg, J., Weitzberg, E. Nasal Nitric Oxide in Man. Thorax 1999; 54(10):947-952.
McCaffrey, Thomas V., Rhinologic Diagnosis and Treatment, Thieme, New York, c1997.
Marks, Steven C. Nasal and Sinus Surgery, W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, c2000.
Navarro, Joao A.C., The Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses, Springer, Berlin, c2001.
Watelet, J.B., Cauwenberge P. Van, Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses. Allergy 1999; 54, Supp 57:14-25.