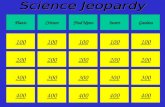
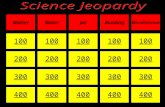
Mrs. Burlingame 100 200 400 300 400 Periodic Table Bonding Acids/bases Kinetics/ Equilibrium 300 200...
-
Upload
shauna-newman -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Mrs. Burlingame 100 200 400 300 400 Periodic Table Bonding Acids/bases Kinetics/ Equilibrium 300 200...

Mrs. Burlingame

100 100100
200 200200
400 400
300300
400400
Periodic Table Bonding Acids/bases
Kinetics/
Equilibrium
300 300 300300
200200
400400
200
100100
500 500 500500 500500
100

Row 1, Col 1
Total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
What is the mass number.?

1,2
The atom’s ability
to attract electrons to itself in bond formation.
What is electronegativity?

1,3
Reactions between acids and bases to produce salts and water
What is neutralization ?

1,4
When a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium,the reaction will try to shift in the direction
that will relieve the stress.
What is Le Chatelier’s Equilibrium?

2,1
As the atomic number increases there is an increase in ionization energy,
electronegativity as well as, a decrease in radius.
What is the chemistry of a period?

2,2
Valance electrons associated with maximum stability
and minimum potential energy content.
What is a stable octet

2,3
Red litmus paper stays redblue litmus turns red
What is a litmus paper test for acidity?

2,4
Describe what is taking place in the following example
Solid----> liquid----> Gas
What is a phase change of increasing entropy?

3,1
On the periodic tableall elements exhibit
similar or related properties.
What is a group or family?

3,2
Identify
What is a tetrahedron?

3,3
Identify the equation:
(Ma)(Va)=(Mb)(Vb)
What is the titration equation of acids and bases?

3,4
Carbonated beverages maintain their carbonation best at
What is low temperature and high pressure?

4,1
This elements exists as a diatomic molecule
under normal conditions(STP)
What is Bromine?

4,2
The bond between potassium and chlorine
What is an ionic bond?

4,3
The following are examples of:
LiOH, KOH, Ba(OH)2
What are some species classified as an Arrhenius base?

4,4
Above 0, ice changes to water according to the following equation
H2 0(s) + heat ---> H20(l). The changes in H20 involve
An absorption of heat and a change in entropy.

5,1
Spectral lines produced from the energy emitted from excited atoms.
What is the movement of electrons from
higher to lower energy levels.?

5,2
Water has a high melting point due to…
What are the dipole-dipole attractive forces known as hydrogen bonds

5,3
The H+ ion concentration of an aqueous solution that has a
PH level of 11
What is 1.0 x 10-11mol/L?

5,4
Given the reaction @ equilibrium
CO (g) + 1/2O2 (g) Co2 (g) + 67.7kcal
As the temperature increases, the rate of the forward reaction …
What is a decrease?