Lipids What are the kinds of lipids? Lipids Fats Fats Waxes Waxes Steroids Steroids Phospholipids...
-
Upload
terence-roberts -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
2
Transcript of Lipids What are the kinds of lipids? Lipids Fats Fats Waxes Waxes Steroids Steroids Phospholipids...

LipidsLipids

What are the kinds of lipids?What are the kinds of lipids?
LipidsLipids
Fats Fats
WaxesWaxes SteroidsSteroids
PhospholipidsPhospholipids

LipidsLipids
What are lipids?What are lipids?
Lipids are hydrophobic molecules composed of Lipids are hydrophobic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They contain fewer carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They contain fewer polar O-H bonds and more nonpolar C-H bonds than polar O-H bonds and more nonpolar C-H bonds than do carbohydrates, thus they are insoluble in water but do carbohydrates, thus they are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar substances. soluble in nonpolar substances.
Why are lipids important?Why are lipids important?
Organisms use lipids for:Organisms use lipids for:
1. Storing energy1. Storing energy
2. Building membranes and other cell parts 2. Building membranes and other cell parts

Energy UnitsEnergy Units
One calorie = 1 cal = 4.18 JOne calorie = 1 cal = 4.18 J
One Kilocalorie = 1 Kcal = 1 Cal =4.18 KJOne Kilocalorie = 1 Kcal = 1 Cal =4.18 KJ
1g of fat = 9 Kcal1g of fat = 9 Kcal
1g of protein = 4 Kcal1g of protein = 4 Kcal
1g of carbohydrates = 4 Kcal1g of carbohydrates = 4 Kcal
* The calorie is not an SI unit* The calorie is not an SI unit

What are the most common fats found What are the most common fats found in plants and animals?in plants and animals?
Are the triacylglycerols (triglycerides), Are the triacylglycerols (triglycerides), which contain three fatty acids attached which contain three fatty acids attached to a single molecule of glycerol.to a single molecule of glycerol.

The structure of glycerol and triglycerides:The structure of glycerol and triglycerides:
HH ll
HH –– C C –– OH OH
l l
HH –– C C –– OH OH
ll
HH –– C C –– OH OH
ll
HH
glycerolglycerol
H l H – C – O – fatty acid l H – C – O – fatty acid l H – C – O – fatty acid l H
triglyceride

How do fatty acids attach to glycerol?How do fatty acids attach to glycerol?
Fatty acids attach to glycerol through a Fatty acids attach to glycerol through a condensationcondensation reaction that takes place reaction that takes place between the hydroxyl group of glycerol between the hydroxyl group of glycerol and the carboxyl group of fatty acids, the and the carboxyl group of fatty acids, the resulting bond is called an ester linkage, resulting bond is called an ester linkage, and the process is called esterification.and the process is called esterification.

Dehydration synthesisDehydration synthesis

Saturated and unsaturated fatty acidsSaturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids: have only single Saturated fatty acids: have only single bonds between the carbon atoms.bonds between the carbon atoms.
e.g.: stearic acide.g.: stearic acid
Unsaturated fatty acids: have one or more Unsaturated fatty acids: have one or more carbon – carbon double bonds.carbon – carbon double bonds.
e.g.: oleic acide.g.: oleic acid

Stearic acid Stearic acid CC1818HH3636OO22
stearic acid

Oleic acidOleic acid
oleic acid

What is a wireframe or Kekule structure?What is a wireframe or Kekule structure?
A kekule structure or a wireframe is a short A kekule structure or a wireframe is a short notation, where neither the carbon atoms nor notation, where neither the carbon atoms nor the hydrogen atoms are shown in the diagram , the hydrogen atoms are shown in the diagram , the carbon atoms are assumed to exist at every the carbon atoms are assumed to exist at every free end or bend of the wireframe.free end or bend of the wireframe.

1) Triglycerides1) Triglycerides

A saturated triglycerideA saturated triglyceride

Why are the unsaturated fatty acids liquids Why are the unsaturated fatty acids liquids at room temperature?at room temperature?
In the triglyceride molecule, the molecule bends In the triglyceride molecule, the molecule bends at the carbon – carbon double bond of the fatty at the carbon – carbon double bond of the fatty acid, these bends and kinks keep the fatty acid acid, these bends and kinks keep the fatty acid tails away from each other, reducing the tails away from each other, reducing the number of Van Der Waals attractions that can number of Van Der Waals attractions that can form along their length, and hence are liquid at form along their length, and hence are liquid at room temperature.room temperature.

What does hydrogenation of oils mean?What does hydrogenation of oils mean?
Hydrogenation of oils is adding hydrogen Hydrogenation of oils is adding hydrogen atoms to the double bonds of unsaturated atoms to the double bonds of unsaturated triglycerids to change them into semisolid triglycerids to change them into semisolid materials such as margarine and materials such as margarine and shortening.shortening.

2) Phospholipids2) Phospholipids
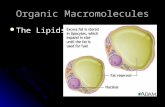
Phospholipids are composed of a glycerol Phospholipids are composed of a glycerol molecule to which is attached two fatty acids molecule to which is attached two fatty acids and a highly polar phosphate group.and a highly polar phosphate group.
The phosphate group may be thought of as a The phosphate group may be thought of as a polar head and the fatty acids as long nonpolar polar head and the fatty acids as long nonpolar tails.tails.
The polar head is hydrophilic and the nonpolar The polar head is hydrophilic and the nonpolar tails are hydrophobic.tails are hydrophobic.


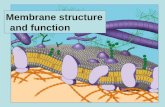
Phospholipids and the cell membranePhospholipids and the cell membrane
The cell membranes are mostly composed of The cell membranes are mostly composed of phospholipids.phospholipids.

3) Steroids3) Steroids
Steroids and the cell membraneSteroids and the cell membrane
Membranes also contain a class of lipids called Membranes also contain a class of lipids called sterols (steroids). These are compact sterols (steroids). These are compact hydrophobic molecules containing hydrophobic molecules containing four fused four fused hydrocarbon ringshydrocarbon rings and several different and several different functional groups.functional groups.
Cholesterol is an important steroid component of Cholesterol is an important steroid component of cell membranes.cell membranes.

Phospholipids/Steroids and the cell membranePhospholipids/Steroids and the cell membrane

SteroidsSteroids
EstradiolEstradiol
Testosterone Testosterone
CholestrolCholestrol
ProgesteroneProgesterone
Bile saltsBile salts
(Digestion of fats in small intestine)(Digestion of fats in small intestine)
Sex hormones Sex hormones
Vitamin DVitamin D((Healthy Bones & teeth)Healthy Bones & teeth)

4) Waxes4) Waxes
Are lipids containing long chain fatty acids linked to Are lipids containing long chain fatty acids linked to alcohols or carbon rings. alcohols or carbon rings.
They are hydrophobic molecules with firm pliable They are hydrophobic molecules with firm pliable consistency, this property makes waxes ideally suited consistency, this property makes waxes ideally suited to form to form waterproof coatingwaterproof coating on various plant parts to on various plant parts to conserve water and to prevent infection, they also conserve water and to prevent infection, they also cover some animal feathers and fur ( Penguin and Polar cover some animal feathers and fur ( Penguin and Polar Bear).Bear).
E.g.: the water resistant coat on cherries called E.g.: the water resistant coat on cherries called cutincutin..