Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints – Hold bones together – Allow for mobility Two...
-
Upload
alina-trulock -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints – Hold bones together – Allow for mobility Two...
Joints
• Articulations of bones• Functions of joints– Hold bones together– Allow for mobility
• Two ways joints are classified– Functionally– Structurally
Functional Classification of Joints
• Synarthroses– Immovable joints
• Amphiarthroses– Slightly moveable joints
• Diarthroses– Freely moveable joints
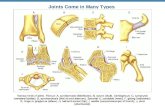
Structural Classification of Joints
• Fibrous joints– Generally immovable
• Cartilaginous joints– Immovable or slightly moveable
• Synovial joints– Freely moveable
Fibrous Joints
• Bones united by collagenic fibers• Types– Sutures
• Immobile– Syndesmoses
• Allows more movement than sutures but still immobile• Example: Distal end of tibia and fibula
– Gomphosis• Immobile
Cartilaginous Joints
• Bones connected by cartilage• Types– Synchrondrosis • Immobile
– Symphysis • Slightly movable• Example: Pubic symphysis, intervertebral joints
Synovial Joints
• Articulating bones are separated by a joint cavity
• Synovial fluid is found in the joint cavity
Figure 5.30f
Synovial joints
Scapula
Articular capsule
Articular (hyaline) cartilage
Humerus
(f) Multiaxial joint (shoulder joint)
Figure 5.30g
Synovial joints
Humerus
Articular (hyaline) cartilage
Articular capsule
Radius
Ulna(g) Uniaxial joint (elbow joint)
Figure 5.30h
Synovial joints
Ulna
Radius
Articular capsule
(h) Biaxial joint (intercarpal joints of hand)
Carpals
Features of Synovial Joints
• Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) covers the ends of bones
• Articular capsule encloses joint surfaces and lined with synovial membrane
• Joint cavity is filled with synovial fluid• Reinforcing ligaments
Structures Associated with the Synovial Joint
• Bursae—flattened fibrous sacs– Lined with synovial membranes– Filled with synovial fluid– Not actually part of the joint
• Tendon sheath– Elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon
Figure 5.31
Acromion of scapula
Ligament
Bursa
Ligament
Tendon sheath
Tendon of biceps muscle
Humerus
Fibrous layer of the articular capsule
Synovial membrane
Articular (hyaline) cartilage
Joint cavity containing synovial fluid
Figure 5.32f
NonaxialUniaxialBiaxialMultiaxial
(f)
Head of humerus
Scapula
(f) Ball-and-socket joint
Inflammatory Conditions Associated with Joints
• Bursitis—inflammation of a bursa usually caused by a blow or friction
• Tendonitis—inflammation of tendon sheaths• Arthritis—inflammatory or degenerative
diseases of joints– Over 100 different types– The most widespread crippling disease in the
United States– Initial symptoms: pain, stiffness, swelling of the
joint
Clinical Forms of Arthritis
• Osteoarthritis– Most common chronic arthritis– Probably related to normal aging processes
• Rheumatoid arthritis– An autoimmune disease—the immune system
attacks the joints– Symptoms begin with bilateral inflammation of
certain joints– Often leads to deformities
Clinical Forms of Arthritis
• Gouty arthritis– Inflammation of joints is caused by a deposition of
uric acid crystals from the blood– Can usually be controlled with diet– More common in men