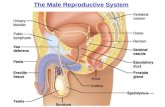
Reproductive System. The Male Reproductive System Testes Ducts Glands.
Jeopardy reproductive system
-
Upload
a-arg -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
965 -
download
1
Transcript of Jeopardy reproductive system

Human Human
Reproductive Reproductive
SystemSystem
JeopardyJeopardy

M2,1 M3,1
M2,2 M4,2
M1,4 M2,4
M4,3
M4,4
Males 1 Males 2 Males 3 Males 4
M1,3 M2,3 M3,3
M3,2
M3,4
M1,2
M4,1
M1,5 M2,5 M3,5 M4,5
M1,1

Testicles (testes) and spermatozoon/-zoa
What are the male gonads and gametes called?

Vas deferens (sing) or vasa deferentia (pl)
/væs ˈdef ə renz/
Both tubes transport sperm from the epididymis into the urethra

Cowper's glands
A pair of pea-sized organs located just inferior to the prostate. They secrete mucus to
lubricate the urethra during the intercourse

Acrosome
A vesicle at the tip of a sperm cell that helps the sperm penetrate the egg by breaking down the corona radiata that sourrounds the ovum. Male sterility can be due to the fact that its digestive enzymes don't work properly

Seminiferous tubules
What are the highly coiled tubes in the testis in which sperm are produced? Their
whole length is around 500 m

Male reproductive ducts
Seminiferous tubules > epididymis > vasa deferentia > urethra all together are called...

Urethra
Duct thet serves the dual purpose of conveying urine from the bladder and carrying the
reproductive cells with their accompanying secretions to the outside

Midpiece
Located between spermatozoon tail and head, this area contains mitochonddria to provide
the flagellum with the energy requiered

Scrotum/ˈskrəʊt əm/
The testicles make sperm best at a few degrees cooler than normal body temperature.
The testicles hang outside the body in this fold of skin to keep the sperm cool

Secretions by seminal vesicles,
prostate and Cowper's glands
Semen is made of 10% sperm and the rest consists of...

Two corpora cavernosa-dorsal side-
and a corpus spongiosum-ventral side around the urethra-
Spongy tissues containing many blood spaces that are relatively empty when the penis is flaccid but fill with blood when the organ is
erect /ɪ ˈrekt/

Flagellum
Scientific word for the sperm tail

Epididymis/ˌep ɪ ˈdɪd əm ɪs /
A coiled tubule located adjacent to the testes where sperm finish maturing and are stored. It connects the seminiferous tubules with the
vas deferens

Prostate/ˈprɒst eɪt/
Gland that lies under the urinary bladder and surrounds the first part of the urethra. It
secretes into the urethra a fluid that helps neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract

Foreskin (prepuce)
/ˈpriːp juːs/
A fold of skin that covers the penis glans*. It is removed in a circumcision, a surgery frequently performed on male babies for religious or cultural reasons. Experts disagree because it improves cleanliness and disease
prevention.
*glans (glande) /ɡlænz/

Meiosis/maɪ ˈəʊs ɪs/
The most important event in gemetogenesis because this is the stage when the number of
chromosomes is halved

Spermatogenesis
The process by which spermatozoa (sperm) is produced inside the
seminiferous tubules

Seminal vesicles/ˈsem ɪn əl …/
Two 7.5 cm long glands, behind the urinary bladder, that produces a secretion containing
large quantities of fructose and other substances that provide nourishment for the
sperm.

Ejaculation/i ˌdʒæk ju ˈleɪʃ ən/
The forceful expulsion of semen through the urethra to the outside

5 days
How long are spermatozoa alive after ejeculation and inside the female body?

F2,1 F3,1
F2,2 F4,2
F1,4 F2,4
F4,3
F4,4
Females 1 Females 2 Females 3 Females 4
F1,3 F2,3 F3,3
F3,2
F3,4
F1,2
F4,1
F1,5 F2,5 F3,5 F4,5
F1,1

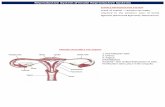
Ovaries and ova (sing. ovum)
What are the female gonads and gametes called?

1,2
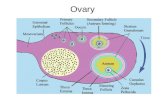
Ovarian follicle
A small fluid-filled chamber of cells. An ovum matures inside each of them. The ovaries of a
newborn female contain a large number of these chambers

1,3
Fallopian tubeor oviducts
/fə ˈləʊp iən //ˈəʊv i dʌkt/
A tube where fertilisation takes place and through which the zygote/embryo
makes its way to the uterus.

1,4
Uterus or womb/wuːm/
An organ about 7.5 cm long and 5 cm wide in which a foetus can develop. Its muscular wall is called myometrium and the lining known as
endometrium.

2,1
Endometrium/ˌend əʊ ˈmiːtr iəm/
The lining of the uterus. This inner layer changes during the menstrual cycle, first preparing to
nourish a fertilized egg, then breaking down if no fertilization occurs to be released as the menstrual
flow

2,2
Vagina/və ˈdʒaɪn/
It's muscular tube about 7.5 cm long connecting the uterine cavity with the outside.

2,3
Vulva/ˈvʌlv ə/
The external parts of the female reproductive system, which includes two pairs of lips or
labia and the clitoris, which is a small erectile organ of great sensitivity

2,4
Bartolin's glands
The vaginal opening is surrounded by these two mucus-producing glands. Like the Cowper
glands in males, these glands provide lubrication during intercourse.

3,1
Oestrogen/ˈiːs trədʒ ən/
Hormone secreted by the ovarian follicle. The effect of that hormone is rebuilding the
uterine endometrium (making its cells divide)

3,2
Graafian follicle
This is the stage of the follicle at its biggest size and containing a mature ovum about to
be released

3,3
Ovulation/ˌɒv ju ˈleɪʃ ən/
This is the process by which a ripened ovum is discharged from its ovarian follicle to the
ovary’s surface and collected by the oviduct

3,4
Corona radiata/kə ,rəʊn ə .../
This is the layer of cells surrounding the ovum and supplying it with food to be stored

4,1
Corpus luteum /,kɔːp əs ˈluːt iəm/
After the ovum has been expelled, the remaining follicle is transformed into this glandular mass. This structure secretes
progesterone. If pregnancy doesn't occur, it shrinks and is replaced by scar tissue.

4,2
Progesterone/prəʊ ˈdʒest ə rəʊn/
Hormone released by the ovary's corpus luteum. Because of this hormone, the uterine
lining thickens and also produces great number of blood vessels

4,3
Period
Approximately 14 days after ovulation, the corpus luteum shrinks and gives up producing progesterone -it pregnancy has not occurred. The highly vascularised endometrium is shed and expelled from the body via vagina. The
process lasts around 4 days

4,4
Proliferative phase
The phase in the uterine cycle in which the lining of the uterus is rebuilt thanks to the
oestrogens secreted by the maturing ovarian follicle

5,1
Luteal phase/,luːt i əl feɪz/
The phase in the uterine cycle in which the lining of the uterus reaches its maximun
thickness and vascularisation and gets ready to receive and feed the embryo

5,2
Placenta/plə ˈsent ə/
A disc on the uterine wall made of the mother's uterine blood vessels and embryo blood
vessels. This organ provides nurishment and oxygen to the embryo and takes away its
cellular waste products.

5,3
Umbilical cord/ʌm ˈbɪl ɪk əl .../
Rope-like structure which contains the foetus' blood vessels going to the placenta. The scar
that it leaves after birth is called navel or belly button

5,4
Tubal ligation AND vasectomy
/və ˈsekt əm i/
Surgical methods of contraception for females and males