PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: Transcription & Translation. Protein Synthesis Videos S2ls .
Information about Cell and it's structure and protein synthesis
-
Upload
mukul-panchal -
Category
Education
-
view
436 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Information about Cell and it's structure and protein synthesis

Introduction Cell structure and
function Genetic
information, protein synthesis, and protein structure

2
Introduction

3
Methods of Science• The scientific method refers to the model for research
developed by Francis Bacon (1561–1626). This model involves the following sequence:
1. Identifying the problem
2. Collecting data within the problem area (by observations, measurements, etc.)
3. Sifting the data for correlations, meaningful connections, and regularities
4. Formulating a hypothesis (a generalization), which is an educated guess that explains the existing data and suggests further avenues of investigation
5. Testing the hypothesis rigorously by gathering new data
6. Confirming, modifying, or rejecting the hypothesis in light of the new findings

4
Living Organism
• A living organism may be defined as a complex unit of physicochemical materials that is capable of self-regulation, metabolism, and reproduction.
• Furthermore, a living organism demonstrates the ability to interact with its environment, grow, move, and adapt.

5
What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms?
1. Made of CELLS2. Require ENERGY (food)3. REPRODUCE (species)4. Maintain
HOMEOSTASIS5. ORGANIZED6. RESPOND to
environment7. GROW and DEVELOP8. EXCHANGE materials
with surroundings (water, wastes, gases)

6
Five Kingdoms and their chief characteristics• Unicellular organisms that lack a nucleus and many of the specialized cell parts, called
organelles. Such organisms are said to be prokaryotic (pro =‘‘before’’; karyotic =‘‘kernel,’’ ‘‘nucleus’’) and consist of bacteria.
• All of the other kingdoms consist of eukaryotic (eu = ‘‘true’’) organisms, which have cells that contain a nucleus and a fuller repertory of organelles.

7
Prokaryotes
• Nucleoid region (center) contains the DNA
• Surrounded by cell membrane & cell wall (peptidoglycan)
• Contain ribosomes (no membrane) in their cytoplasm to make proteins

8
Eukaryotes
• Cells that HAVE a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
• Includes protists, fungi, plants, and animals
• More complex type of cells

9
Cells and Cell Theory
• In 1665, Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork (dead plant cell walls). Hooke called them “CELLS” because they looked like the small rooms that monks lived in called “Cells”
• In 1673, Leeuwenhoek (a Dutch microscope maker), was first to view organism (living things)
Cell Theory• In 1838, a German botanist named Matthias
Schleiden concluded that all plants were made of cells
• In 1839, a German zoologist named Theodore Schwann concluded that all animals were made of cells

10
Beginning of the Cell Theory
• In 1855, a German medical doctor named Rudolph Virchow observed, under the microscope, cells dividing
• He reasoned that all cells come from other pre-existing cells by cell division

11
CELL THEORY
• All living things are made of cells
• Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life)
• Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)

12
Cell Structure and Function

13
Organelles
• Very small (Microscopic)• Perform various functions for a cell• Found in the cytoplasm• May or may not be membrane-bound
Plant Cell

14
Cell or Cell or Plasma Membrane Membrane
Outsideof cell
Insideof cell(cytoplasm)
Cellmembrane
Proteins
Proteinchannel Lipid bilayer
Carbohydratechains
• Composed of double layer of phospholipids and proteins
• Surrounds outside of ALL cells• Controls what enters or leaves the cell• Living layer

15
• Jelly-like substance enclosed by cell membrane
• Provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place
• Contains organelles to carry out specific jobs
• Found in ALL cells
Cytoplasm of a Cell
cytoplasm

16
• Controls the normal activities of the cell
• Contains the DNA in chromosomes
• Bounded by a nuclear envelope (membrane) with pores
• Usually the largest organelle• Each cell has fixed
number of chromosomes that carry genes
• Genes control cell characteristics
The Control Organelle - Nucleus

17
Nucleolus
• Inside nucleusInside nucleus• Cell may have Cell may have 1 to 31 to 3
nucleolinucleoli• DisappearsDisappears when cell when cell
dividesdivides• Makes ribosomesMakes ribosomes that that
make proteinsmake proteins

18
Cytoskeleton• Helps cell maintain
cell shape• Also help move
organelles around• Made of proteins• Microfilaments are
threadlike & made of ACTIN
• Microtubules are tube-like and made of TUBULIN
Cytoskeleton
Microtubules
Microfilaments

19
Centrioles• Found only in animal
cells• Paired structures near
nucleus• Made of bundle of
microtubules• Appear during cell
division forming mitotic spindle
• Help to pull chromosome pairs apart to opposite ends of the cell

20
Mitochondrion(plural = mitochondria)
• “Powerhouse” of the cell• Generate cellular energy
(ATP)• More active cells like muscle
cells have MORE mitochondria
• Both plants & animal cells have mitochondria
• Site of CELLULAR RESPIRATION (burning glucose)

21
MITOCHONDRIA
• Surrounded by a DOUBLE membrane
• Has its own DNA– Mitochondria come from cytoplasm
in the egg cell during fertilization – Therefore you inherit your
mitochondria from your mother!
• Folded inner membrane called CRISTAE (increases surface area for more chemical reactions)
• Interior called MATRIX

22
Endoplasmic Reticulum - ER
Two kinds of ER ---ROUGH & SMOOTH
• Network of hollow membrane tubules• Connects to nuclear envelope & cell membrane• Functions in Synthesis of cell products & Transport

23
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)• Has ribosomes on its surface • Makes membrane proteins
and proteins for EXPORT out of cell
• Proteins are made by ribosomes on ER surface
• They are then threaded into the interior of the Rough ER to be modified and transported

24
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Smooth ER lacks ribosomes on its surface
• Is attached to the ends of rough ER
• Makes cell products that are USED INSIDE the cell
• Makes membrane lipids (steroids)• Regulates calcium (muscle cells)• Destroys toxic substances (Liver)
Includes nuclear membrane connected to
ER connected to cell membrane (transport)

25
Ribosomes
• Made of PROTEINS and rRNA• “Protein factories” for cell• Join amino acids to make proteins• Process called protein synthesis• Can be attached to Rough ER OR Be free
(unattached) in the cytoplasm

26
Golgi Bodies
• Stacks of flattened sacs
• Have a shipping side (trans face) and receiving side (cis face)
• Receive proteins made by ER
• Transport vesicles with modified proteins pinch off the ends
Transport
vesicle
CIS
TRANS

27
Golgi Bodies
Look like a stack of pancakes
Modify, sort, & packagemolecules from ERfor storage OR transport out of cell

28
Golgi bodies

29
Lysosomes
• Contain digestive enzymes• Break down food,
bacteria, and worn out cell parts for cells
• Programmed for cell death (AUTOLYSIS)
• Lyse (break open) & release enzymes to break down & recycle cell parts)

30
Lysosome Digestion
• Cells take in food by phagocytosis
• Lysosomes digest the food & get rid of wastes

31
Vacuoles• Fluid filled sacks for storage• Small or absent in animal
cells• Plant cells have a large
Central Vacuole• No vacuoles in bacterial cells• In plants, they store Cell Sap• Includes storage of sugars,
proteins, minerals, lipids, wastes, salts, water, and enzymes

32
Chloroplasts• Found only in producers
(organisms containing chlorophyll)
• Use energy from sunlight to make own food (glucose)
• Energy from sun stored in the Chemical Bonds of Sugars
Surrounded by DOUBLE membraneOuter membrane smoothInner membrane modified into sacs called ThylakoidsThylakoids in stacks called Grana & interconnectedStroma – gel like material surrounding thylakoids

33
Chloroplasts
• Contains its own DNA• Contains enzymes &
pigments for Photosynthesis
• Never in animal or bacterial cells
• Photosynthesis – food making process

34
Genetic information, protein synthesis, and protein structure

35
35

36
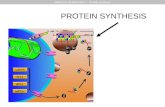
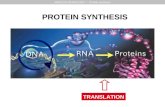
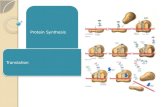
Protein Synthesis
1. DNA unwinds
2. mRNA copy is made of one of the DNA strands.
3. mRNA copy moves out of nucleus into cytoplasm.
4. tRNA molecules are activated as their complementary amino acids are attached to them.
5. mRNA copy attaches to the small subunit of the ribosomes in cytoplasm. 6 of the bases in the mRNA are exposed in the ribosome.
6. A tRNA bonds complementarily with the mRNA via its anticodon.
7. A second tRNA bonds with the next three bases of the mRNA, the amino acid joins onto the amino acid of the first tRNA via a peptide bond.
8. The ribosome moves along. The first tRNA leaves the ribosome.
9. A third tRNA brings a third amino acid
10. Eventually a stop codon is reached on the mRNA. The newly synthesised polypeptide leaves the ribosome.

37
37
Proteins
• Proteins are polymers (macromolecules) made of monomers called amino acids
• All proteins are made of 20 different amino acids linked in different orders
• Proteins are used to build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, and do much of the work in a cell

38
Protein Functions in the Body
• There are many different proteins in your body, and they perform different functions. Proteins functions include: – Contributing to enzyme activity that
promotes chemical reactions in the body
– Signaling cells what to do and when to do it
– Transporting substances around the body
– Keeping fluids and pH balanced in the body
– Serving as building blocks for hormone production
– Helping blood clot – Promoting antibody activity that
controls immune and allergy functions
– Serving as structural components that give our body parts their shapes
Storage
Structural
Transport

39
39
Primary Protein Structure
The primary structure is the specific sequence of amino acids in a protein
Called polypeptide
Amino Acid

40
40
Protein Structures
• Secondary protein structures occur when protein chains coil or fold
• When protein chains called polypeptides join together, the tertiary structure forms because R groups interact with each other
• In the watery environment of a cell, proteins become globular in their quaternary structure

41
41
Protein Structures or CONFORMATIONS
Hydrogen bond
Pleated sheet
Amino acid
(a) Primary structure
Hydrogen bond
Alpha helix
(b) Secondary structure
Polypeptide(single subunit)
(c) Tertiary structure
(d) Quaternary structure

THANK YOU
PRESENTED BY-MUKUL PANCHAL
(14/9/27)
42