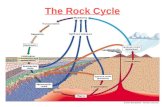
Igneous Rocks Lecture 3 Types of Rock include Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic Marble demo, rock...
-
date post
19-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
4
Transcript of Igneous Rocks Lecture 3 Types of Rock include Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic Marble demo, rock...

Igneous RocksIgneous RocksLecture 3Lecture 3
Types of Rock include Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic
Marble demo, rock specimens, Petrographic Microscope, Olivine Porphyry or GabbroTrays of mafic and felsic minerals

Characteristics of magmaCharacteristics of magma
Igneous rocks form as molten rock cools Igneous rocks form as molten rock cools and solidifiesand solidifies
Characteristics of magmas (molten rock) Characteristics of magmas (molten rock) depend on parent material and where they depend on parent material and where they crystallizecrystallize
Where determines speed of crystallizationWhere determines speed of crystallization At surface, fast cooling makes small crystalsAt surface, fast cooling makes small crystals

Geothermal
Gradient Silica-rich rocks (with Quartz, K-feldspar) melt at cooler temperatures. Melts are viscous
Silica-poor rocks (with Olivine, Pyroxene, Ca-feldspar) melt at higher temperatures Melts are very fluid Hot
Cool

Characteristics of magmaCharacteristics of magma
General Characteristics of molten rockGeneral Characteristics of molten rock Forms from partial melting of rocks inside Forms from partial melting of rocks inside
the Earththe Earth Rocks formed from lava at the surface are Rocks formed from lava at the surface are
classified as classified as extrusiveextrusive, or , or volcanic rocksvolcanic rocks Rocks formed from magma that crystallizes Rocks formed from magma that crystallizes
at depth are termed at depth are termed intrusiveintrusive, or , or plutonic plutonic rocksrocks

Igneous RocksFormed in Rift
Igneous RocksFormed AboveSinking Plate
Two Geologic Environments Where Igneous Rocks Form
Both melts are "Basaltic" i.e. Olivine, Pyroxene and Ca-Feldspars

Extrusive Igneous Rock - Lava (Hawaii)

Intrusive Igneous Rock (Granite) – This granite cooled 30 kilometers under the surface
Quartz Amphibole K Feldspar
Plagioclase Feldspar

Characteristics of magmaCharacteristics of magma
Three parts:Three parts:
– Liquid portion, called melt, that is Liquid portion, called melt, that is
mobile ionsmobile ions
– Solids, if any, are silicate minerals Solids, if any, are silicate minerals
already crystallized from the meltalready crystallized from the melt
– Volatiles, which are gases dissolved in the Volatiles, which are gases dissolved in the melt, including water vapor (Hmelt, including water vapor (H22O), carbon O), carbon
dioxide (COdioxide (CO22), and sulfur dioxide (SO), and sulfur dioxide (SO22))

Characteristics of magmaCharacteristics of magma Crystallization of magmaCrystallization of magma
Cooling of magma results in the systematic arrangement of Cooling of magma results in the systematic arrangement of ions into orderly patternsions into orderly patterns
The silicate minerals resulting from crystallization form in The silicate minerals resulting from crystallization form in a predictable ordera predictable order
Rock-forming minerals crystallize with increasing complexity as the Rock-forming minerals crystallize with increasing complexity as the magma cools. The most complex 3-D minerals crystallize last. The magma cools. The most complex 3-D minerals crystallize last. The hottest magmas can only crystallize Olivine (Independent hottest magmas can only crystallize Olivine (Independent Tetrahedra), but as the magma cools, more complex minerals can Tetrahedra), but as the magma cools, more complex minerals can form.form.

Bowen’s Reaction SeriesMolten- VERY HotNo solids
Molten- Not so hot
100% Solid
First mineral to crystallize out

Fine crystalsNeed a microscope
Course crystalsEasily seen
Low silica, HOT, fluid High silica, warm, viscousIntermediate

GraniteHand Sample
GraniteThin Section
Order ofCrystallization
Bowens reaction series says: as a granitic melt cools, Biotite Mica and Plagioclase Feldspar
crystallize out before Quartz
We can see the order of crystallization under the microscope
Microscope Demo

Zoned feldspar (plagioclase) showing change in composition with time in magma chamber (calcium-rich in core to sodium-rich at rim)
If the first formed crystals of Calcium-rich (Ca) Plagioclase touch the melt they will react with it, and will become more sodium-rich on their outer rims
Crystals can react with the melt if they touch it

However, if early crystals are removed, the melt becomes richer in Silica
A melt will crystallize its mafic components first, and the remaining melt may be granitic
Remove Fe, Mg, CaSome Si
Left withK and AlMost of Si
You can start with aMafic (silica-poor) magmaand end up with some Felsic (silica-rich)Granites. Marble Demo

Characteristics of magmaCharacteristics of magma
Igneous rocks are typically classified by Igneous rocks are typically classified by both:both:– TextureTexture– Mineral compositionMineral composition
Texture in igneous rocks is determined by the size Texture in igneous rocks is determined by the size and arrangement of mineral grainsand arrangement of mineral grains

Igneous texturesIgneous textures
Most important is crystal sizeMost important is crystal size
Factors affecting crystal sizeFactors affecting crystal size Rate of coolingRate of cooling
– Slow rate promotes the growth of fewer Slow rate promotes the growth of fewer but larger crystalsbut larger crystals
– Fast rate forms many small crystalsFast rate forms many small crystals– Very fast rate forms glassVery fast rate forms glass

Types of Igneous texturesTypes of Igneous textures
Types of igneous texturesTypes of igneous texturesAphaniticAphanitic (fine-grained) texture (fine-grained) texture
– Rapid rate of cooling of lava or magmaRapid rate of cooling of lava or magma– Microscopic crystalsMicroscopic crystals– May contain May contain vesiclesvesicles (holes from gas (holes from gas
bubbles)bubbles)PhaneriticPhaneritic (coarse-grained) texture (coarse-grained) texture
– Slow coolingSlow cooling– Crystals can be identified without a Crystals can be identified without a
microscopemicroscope

Aphanitic texture
Fine grained because it cooled quickly at the surface

Phaneritic texture
Coarse crystals cooled slowly at great depth

Igneous texturesIgneous textures
Types of igneous texturesTypes of igneous texturesPorphyriticPorphyritic texture texture
– Minerals form at different temperatures as Minerals form at different temperatures as well as differing rateswell as differing rates
– Large crystals, called Large crystals, called phenocrystsphenocrysts, are , are embedded in a matrix of smaller crystals, embedded in a matrix of smaller crystals, called the called the groundmassgroundmass
Glassy Glassy texturetexture– Very rapid cooling of molten rockVery rapid cooling of molten rock– Resulting rock is called Resulting rock is called obsidianobsidian

Porphyritic texture
GraniteTwo-stage cooling?

Glassy texture
ObsidianFast cooling

More types of Igneous More types of Igneous texturestextures
Types of igneous texturesTypes of igneous textures
PyroclasticPyroclastic texture texture–Various fragments ejected during Various fragments ejected during
a violent volcanic eruptiona violent volcanic eruption
–Textures often appear to more Textures often appear to more similar to sedimentary rockssimilar to sedimentary rocks

Pyroclastic Rock - Superheated Flows

Naming igneous rocks – pyroclastic Naming igneous rocks – pyroclastic rocksrocks
Composed of fragments ejected during a Composed of fragments ejected during a volcanic eruptionvolcanic eruption
VarietiesVarietiesTuff – ash-sized fragmentsTuff – ash-sized fragments
Volcanic breccia – particles larger than Volcanic breccia – particles larger than ashash

Ash and pumice layersAsh and pumice layers

Still more types of Igneous Still more types of Igneous texturestextures
Types of igneous texturesTypes of igneous textures
PegmatiticPegmatitic texture texture–Exceptionally coarse grained crystalsExceptionally coarse grained crystals
–Form in late stages of fractionation of Form in late stages of fractionation of magmasmagmas
–This is often what prospectors are This is often what prospectors are looking forlooking for
A Pegmatite with Feldspar and Zircon Zircon is very good for obtaining radiometric ages

Igneous CompositionsIgneous Compositions
Igneous rocks are composed primarily of Igneous rocks are composed primarily of silicatesilicate minerals that include: minerals that include:
dark (or dark (or ferromagnesianferromagnesian) colored silicates) colored silicates– OlivineOlivine
– Pyroxene Pyroxene
– AmphiboleAmphibole
– versus …versus …
“MAFIC” Magnesium and Iron
Show tray of Mafic Minerals

Igneous CompositionsIgneous Compositions
Igneous rocks also contain light colored Igneous rocks also contain light colored silicate minerals that include:silicate minerals that include:
– QuartzQuartz
– Muscovite micaMuscovite mica
– FeldsparsFeldspars
“FELSIC” Feldspar and Silica
Show tray of Felsic Minerals

Igneous Rock Classification- Bowen’s Reaction Series on its side
Felsic rocks crystallize from warm melts Mafic from hot melts
Note Minerals inNote Minerals in

Igneous compositionsIgneous compositions Naming igneous rocks – granitic (felsic) rocksNaming igneous rocks – granitic (felsic) rocks
GraniteGranite– PhaneriticPhaneritic– Over 20 percent quartz, about 25 percent or Over 20 percent quartz, about 25 percent or
more feldspar (usually much more more feldspar (usually much more feldspars).feldspars).
– Plagioclase is Sodium-richPlagioclase is Sodium-rich– Abundant and often associated with Abundant and often associated with
mountain buildingmountain building– The term granite covers a wide range of The term granite covers a wide range of
mineral compositionsmineral compositions

Igneous compositionsIgneous compositions
Naming igneous rocks – granitic (felsic) rocksNaming igneous rocks – granitic (felsic) rocks RhyoliteRhyolite
– Extrusive equivalent of graniteExtrusive equivalent of granite– May contain glass fragments and vesiclesMay contain glass fragments and vesicles– Aphanitic texture (means fine grained Aphanitic texture (means fine grained
minerals)minerals)– Less common and less voluminous than graniteLess common and less voluminous than granite– Phenocrysts can include quartz and feldsparPhenocrysts can include quartz and feldspar
fine grained because extruded, so crystallized quickly

Igneous compositionsIgneous compositions
BasalticBasaltic composition can be fine or coarse composition can be fine or coarse– Composed of dark Olivine and Pyroxene and grey Composed of dark Olivine and Pyroxene and grey
calcium-rich plagioclase feldsparcalcium-rich plagioclase feldspar– No Potassium-rich feldspar (no K-spar No Potassium-rich feldspar (no K-spar
‘Microcline’)‘Microcline’)– Designated as being Designated as being maficmafic ( (mamagnesium and gnesium and feferrum, for iron) in compositionrrum, for iron) in composition
– Much denser than granitic rocks - sinksMuch denser than granitic rocks - sinks– Comprises the ocean floor as well as many volcanic Comprises the ocean floor as well as many volcanic
islands such as Hawaii. Also rift valley lavasislands such as Hawaii. Also rift valley lavas

Igneous compositionsIgneous compositions Naming igneous rocks – basaltic (mafic) rocks: Naming igneous rocks – basaltic (mafic) rocks:
Fine-grainedFine-grained
BasaltBasalt– Volcanic originVolcanic origin
– Aphanitic textureAphanitic texture
– Composed mainly of pyroxene, some olivine and also Composed mainly of pyroxene, some olivine and also calcium-rich plagioclase feldsparcalcium-rich plagioclase feldspar
– Most common extrusive igneous rockMost common extrusive igneous rock

Scoria type Basalt: note Gas Bubble Pits

Igneous compositionsIgneous compositions Naming igneous rocks – basaltic (mafic) rocks: Naming igneous rocks – basaltic (mafic) rocks:
Coarse GrainedCoarse Grained
GabbroGabbro–Intrusive equivalent of basalt Intrusive equivalent of basalt
–Phaneritic texture consisting of pyroxene Phaneritic texture consisting of pyroxene and calcium-rich plagioclase and calcium-rich plagioclase
–Makes up a significant percentage of the Makes up a significant percentage of the oceanic crust, beneath the basalt pillow oceanic crust, beneath the basalt pillow lavas.lavas.

Igneous compositionsIgneous compositions Other compositional groupsOther compositional groups
IntermediateIntermediate (or (or andesiticandesitic) composition) composition– Contain at least 25 percent dark silicate mineralsContain at least 25 percent dark silicate minerals– Associated with explosive volcanic activityAssociated with explosive volcanic activity– Often grayOften gray

Igneous Igneous compositionscompositions
Intermediate rocksIntermediate rocks AndesiteAndesite
– Volcanic originVolcanic origin
– Aphanitic textureAphanitic texture
– Often resembles rhyoliteOften resembles rhyolite
– Intermediate silica contentIntermediate silica content
– Frequent composition in volcanoes above Frequent composition in volcanoes above subduction zones, e.g. in Andes Mountains subduction zones, e.g. in Andes Mountains

Igneous compositionsIgneous compositions Extrusive products can include:Extrusive products can include:
PumicePumice– VolcanicVolcanic
– Glassy texture, very light weight, mostly airGlassy texture, very light weight, mostly air
– Frothy appearance with numerous voids Frothy appearance with numerous voids (extrusive foam) (extrusive foam)
– Forms when lavas have a lot of water and other Forms when lavas have a lot of water and other volatilesvolatiles
Common with intermediate compositions

Igneous Igneous compositioncomposition
ss
Intermediate rocksIntermediate rocks DioriteDiorite
– Plutonic equivalent of andesitePlutonic equivalent of andesite
– Coarse grainedCoarse grained
– IntrusiveIntrusive
– Composed mainly of intermediate feldspar and Composed mainly of intermediate feldspar and amphiboleamphibole

Silica ContentSilica Content Silica content influences a magma’s Silica content influences a magma’s
behaviorbehavior Granitic magmaGranitic magma
– High silica contentHigh silica content
– Extremely viscousExtremely viscous
– Liquid exists at temperatures as low as 700Liquid exists at temperatures as low as 700ooCC
– Huge explosion if it erupts (Yellowstone, Toba)Huge explosion if it erupts (Yellowstone, Toba)
Plutonic“Granite”
Volcanic“Rhyolite”
When Yellowstone explodes, half of Wyoming will perish

Silica ContentSilica Content Silica contentSilica content influences a magma’s behavior influences a magma’s behavior
Basaltic magmaBasaltic magma– Much lower silica contentMuch lower silica content– Fluid-like behaviorFluid-like behavior
– Crystallizes at higher temperaturesCrystallizes at higher temperatures– Gurgles when it erupts (Hawaii)Gurgles when it erupts (Hawaii)

Origin of MagmaOrigin of Magma
Role of Role of PressurePressure– Reducing the pressure lowers the melting Reducing the pressure lowers the melting
temperature – the rock probably meltstemperature – the rock probably melts– RIDGE: When confining pressures drop, RIDGE: When confining pressures drop,
decompression melting occursdecompression melting occurs

Origin of MagmaOrigin of Magma
Role of volatiles - WATERRole of volatiles - WATER–Volatiles (primarily water) cause Volatiles (primarily water) cause
rocks to melt at lower rocks to melt at lower temperaturestemperatures
–This is particularly important This is particularly important where oceanic lithosphere where oceanic lithosphere descends into the mantle in a descends into the mantle in a subduction zonesubduction zone

Assimilation and magmatic differentiation
Show Samples

Basalts forming in rifts and MORs
Decompression Melting:Magma under lithosphere heats and cracks it. Mantle rock is exposed to low pressures – it partially melts

Origin of Andesite & Diorite: intermediate silica content
Good diagram for the Andes Mountains
Small blobs, not much heat in themAssimilate some crust, fractionate
Basaltic here

48
Plate Tectonics- Andesite Line
Andesites form above the deep portions of a subduction zone
Andes

Origin of Granitic Rocks
Can also get small amounts of granites from deep felsic rock passed by ascending magma
Huge blobs under thick part of continent w/ low temps but lots of magma, fractionation & assimilation => Granite Batholiths

Some intrusive igneous structures