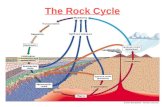
Rock types Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic. Differences in the rock textures Igneous – isometric.
Compare Igneous RockSedimentary Rock. Clastic Sedimentary Rock.
-
Upload
nelson-parsons -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
2
Transcript of Compare Igneous RockSedimentary Rock. Clastic Sedimentary Rock.
Sedimentary Rock
• How do those layers form?• Order or process:
Weathering Erosion DepositionCementation
& Compaction
Mechanical Weathering
• Disintegration/rock broken into smaller pieces
– Frost Action
– Abrasion (river, glacial, sandy environment)
– Plants and Animals #2
Chemical Weathering
• Decomposition-rock’s minerals are changed into different substances.– Acid Rain
– Oxidation
– Hydrolysis
– Caves
Which minerals are susceptible?
• Chemical Weathering– Calcite
• Mechanical Weathering– Quartz, angular minerals
Chemical WeatheringWhat affects the rate?
Faster Chemical Weathering – Warm and Moist climate
Faster Physical Weathering – Cold and Wet Climate
Erosion
• The transport of sediments/particles from a weathered rock by– Water– Wind– Glacier– Gravity
Moraine and Till
Till - Unconsolidated and unsorted rock material that is deposited by a retreating or melting glacier
Moraine – The accumulation of glacial till
Drumlins in NYS
• South ends of the Finger Lakes - northeast of Ithaca at the northern end of Cayuga (Rochester to Syracuse)
Complete Illustration
• When glacier melts, deposits slump down at the side and form long ridges - ESKER