ROCKS. Rock Vocabulary Sediment Sediment Rock cycle Rock cycle Weathering Weathering Stratification...
-
Upload
nickolas-owens -
Category
Documents
-
view
265 -
download
3
Transcript of ROCKS. Rock Vocabulary Sediment Sediment Rock cycle Rock cycle Weathering Weathering Stratification...
Rock VocabularyRock Vocabulary
SedimentSediment Rock cycleRock cycle WeatheringWeathering StratificationStratification Igneous rockIgneous rock Sedimentary rockSedimentary rock Metamorphic rockMetamorphic rock CementationCementation
Porphyritic texturePorphyritic texture Intrusive igneous Intrusive igneous
rockrock Extrusive igneous Extrusive igneous
rockrock ConglomerateConglomerate FossilFossil Ripple mark (look in Ripple mark (look in
chapter in chapter in sedimentary rock sedimentary rock section)section)
What is a rock?What is a rock? Maybe made of entirely one mineral or Maybe made of entirely one mineral or
several minerals. several minerals.
May contain organic matter (composed of May contain organic matter (composed of living material, usually carbon based)living material, usually carbon based)
Rocks containing varied chemical Rocks containing varied chemical compositions of the same mineral can be compositions of the same mineral can be different. different.
Forms of the same Forms of the same mineralmineral
Example: Carbon may be Example: Carbon may be found as a lump of coal or as found as a lump of coal or as a diamond. Quite different!a diamond. Quite different!
COAL DIAMOND
Types of RocksTypes of Rocks
What are theWhat are the three three classes of rocks?classes of rocks?
Types of RocksTypes of RocksWhat are theWhat are the three three classes of rocks?classes of rocks?
1. Igneous Rocks1. Igneous Rocks
2. Sedimentary Rocks2. Sedimentary Rocks
3. Metamorphic Rocks3. Metamorphic Rocks
Igneous RocksIgneous Rocks Name comes from the Latin word “ignis” Name comes from the Latin word “ignis”
meaning from fire.meaning from fire. Formed when super hot magma or lava cools. Formed when super hot magma or lava cools. There are seven different classes based on There are seven different classes based on
chemical composition of the igneous rock. chemical composition of the igneous rock.
Types of Igneous RocksTypes of Igneous RocksExExtrusive Igneous trusive Igneous
Rocks:Rocks:
Formed from lava Formed from lava that that quicklyquickly solidifies at the solidifies at the cooler surface. cooler surface.
Produces fine-Produces fine-grained rocks.grained rocks.
Ex. basalt and Ex. basalt and rhyoliterhyolite
david-amador.com
geology.com
Igneous RockIgneous Rock
The most common The most common known igneous rock known igneous rock is granite. is granite.
It is composed It is composed almost entirely of almost entirely of feldspar and quartzfeldspar and quartz
Types of Igneous RocksTypes of Igneous Rocks
IInnttrusive Igneous Rocks:rusive Igneous Rocks: Trapped magma under Trapped magma under
the crust solidifies slowly.the crust solidifies slowly. Intrusive rocks are Intrusive rocks are
composed of larger composed of larger crystals because form crystals because form slower. slower.
Larger crystals give these Larger crystals give these rocks a rougher texturerocks a rougher texture
Ex. graniteEx. granite
Mount Rushmore is Mount Rushmore is carved from granite in carved from granite in the Black Hills of the Black Hills of South Dakota. South Dakota.
Mount Rushmore is carved from granite in the Black Hills of South Dakota.
Igneous Rocks: Mafic vs. Igneous Rocks: Mafic vs. FelsicFelsic Mafic : Mafic : chemically chemically
composed of iron composed of iron and magnesium, and magnesium, and smaller and smaller amounts of quartz.amounts of quartz.
Felsic: chemically Felsic: chemically composed of composed of potassium, potassium, feldspar, and large feldspar, and large amounts of quartz.amounts of quartz.
csmres.jmu.edu
Bell Ringer: Rocks
What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks?
T or F: Intrusive igneous rocks are composed of larger crystals then extrusive igneous rocks.
Would mafic or felsic magma be magnetic? Explain your answer.
Igneous Rock Igneous Rock FormationsFormations
Extrusive Igneous Extrusive Igneous StructuesStructues::
volcanoesvolcanoes
Intrusive Igenous Intrusive Igenous Structures:Structures:
batholithsbatholiths laccolithslaccoliths sills sills dikesdikes
indiana.edu
Sedimentary RocksSedimentary Rocks All sedimentary rocks are made of materials All sedimentary rocks are made of materials
called sediments deposited by natural and called sediments deposited by natural and chemical processes.chemical processes.
Sediments become Sediments become cementedcemented or or compactedcompacted together over time forming a solid rock together over time forming a solid rock
Uluru (Ayers Rock) in Australia, the world's largest monolith, is made of sandstone.
Types of SedimentsTypes of Sediments
Tiny grains of sandTiny grains of sand Broken pieces of rock along the Broken pieces of rock along the
bottom of a streambottom of a stream Fragments of seashellsFragments of seashells Layers of mudLayers of mud Organic matter (plant and animal Organic matter (plant and animal
remains)remains)
Sediments and Sediments and Sedimentary RocksSedimentary Rocks Gravity, water, or wind carries them to a destination.Gravity, water, or wind carries them to a destination.
Sediments deposit in layers over time. (strata= layers)Sediments deposit in layers over time. (strata= layers) Loosely deposited sediments eventually form a solid rock Loosely deposited sediments eventually form a solid rock
by:by:
1.Compaction: 1.Compaction: sediments squeezed together by sediments squeezed together by gravity/pressure.gravity/pressure.
2. Cementation2. Cementation: sediments glued together by minerals : sediments glued together by minerals deposited by water. deposited by water.
Sedimentary RockSedimentary Rock
The most common The most common sedimentary rock is sedimentary rock is limestone.limestone.
Develops from living Develops from living remains (shells, remains (shells, mollusks)mollusks)
CoalCoal is another is another example of a example of a sedimentary rock sedimentary rock derived from organic derived from organic remains.remains.
Sedimentary RockSedimentary Rock
Often preserve some characteristics from Often preserve some characteristics from which they were formed. which they were formed.
Ripple marks formed in the sand will Ripple marks formed in the sand will appear in the rock formed from the sand appear in the rock formed from the sand deposits.deposits.
Ripple marks formed in thesand by wind
Sedimentary RocksSedimentary Rocks The source of most fossil The source of most fossil
remains.remains.
The age of a rock can be The age of a rock can be determined by studying determined by studying the fossils within it.the fossils within it.(Radiometric Dating)(Radiometric Dating)
Identify when prehistoric Identify when prehistoric organisms and organisms and vegetation thrived and vegetation thrived and became extinct. became extinct.
Fossilized Leaves
Sedimentary RocksSedimentary Rocks
The diverse colors The diverse colors within the sedimentary within the sedimentary layers (strata) gives layers (strata) gives scientists an idea of scientists an idea of their chemical make-their chemical make-up. up.
The red and pink The red and pink bands in the Grand bands in the Grand Canyon exhibit the iron Canyon exhibit the iron found in the sediment.found in the sediment.
Sedimentary Rocks: Sedimentary Rocks: LocationLocation
Sedimentary rocks cover Sedimentary rocks cover almost all of the ocean floor almost all of the ocean floor and about three-fourths of and about three-fourths of Earth's surface land area. Earth's surface land area.
Metamorphic RockMetamorphic Rock Metamorphism: change in the chemical Metamorphism: change in the chemical
make-up of rocksmake-up of rocks Heat, pressure, and hot fluids cause rocks to Heat, pressure, and hot fluids cause rocks to
change into other rocks. change into other rocks. Where would this most likely occur?Where would this most likely occur?
Metamorphic RockMetamorphic Rock Heat, pressure, and hot fluids cause rocks Heat, pressure, and hot fluids cause rocks
to change into other rocks. to change into other rocks. Where would this most likely occur? Where would this most likely occur?
within the Earthwithin the Earth- at subduction zonesat subduction zones
Metamorphic RockMetamorphic Rock
The geologic processes that created the North Cascades changed the original rock into metamorphic rock.
Formed from compression of Tectonic plates
Classes of Metamorphic Classes of Metamorphic RocksRocksFoliated Metamorphic Rocks:Foliated Metamorphic Rocks:
Minerals are arrangedMinerals are arranged
in planes or bands. in planes or bands. Metamorphism is slow. Metamorphism is slow.
Non-Foliate Metamorphic Rocks: Non-Foliate Metamorphic Rocks: Minerals are not arrangedMinerals are not arranged
in bands or planes. in bands or planes. Metamorphism occurs fast.Metamorphism occurs fast.
brhectorsgeoworld.blogspot.com
volcano.oregonstate.edu
Types of Metamorphic Types of Metamorphic RockRock
SlateSlate is a common is a common form that is easily form that is easily split into slabssplit into slabs
GneissGneiss (pronounced (pronounced “nice”) contains “nice”) contains light and dark bandslight and dark bands
GraniteGranite is also a is also a common typecommon type
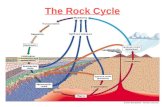
The Rock CycleThe Rock Cycle
Almost all of the rock that we have on Almost all of the rock that we have on Earth today is made of the same stuff Earth today is made of the same stuff as the rocks that dinosaurs and other as the rocks that dinosaurs and other ancient life forms walked, crawled, or ancient life forms walked, crawled, or swam over. While the stuff that rocks swam over. While the stuff that rocks are made from has stayed the same, are made from has stayed the same, the rocks themselves, have not. the rocks themselves, have not. Over Over time rocks are recycled into other time rocks are recycled into other rocks. rocks.